The Obesity Pandemic: What Can we do About it?
Mar 24, 2025
Table of Contents
Obesity has become one of the most pressing global health challenges, with its prevalence rising at an alarming rate. The causes of obesity are deeply rooted in modern lifestyles, where high-calorie diets, sedentary habits, and environmental influences create the perfect storm for excessive weight gain. Beyond lifestyle, genetic predisposition and metabolic factors also play a crucial role in determining a person’s susceptibility to obesity.
More than just excess weight, obesity triggers a cascade of health complications. It is a major risk factor for cardiovascular diseases, type 2 diabetes, hypertension, and even certain cancers. The burden extends beyond physical health, affecting mental well-being and overall quality of life. Diseases caused by obesity range from metabolic disorders to respiratory issues and joint degeneration, significantly reducing life expectancy.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Mobile Health Apps for Obesity Treatment: A Modern Solution to a Growing Problem
- The Rise of Energy Drinks: Power in a Can or a Health Hazard?
- Commercial
- Future Avenues for Prediabetes Treatment: The Road Ahead
- Redefining Liver Disease in the Metabolic Era: From NASH to MASH and the Rise of Obesity‐targeted...
Understanding what contributes to obesity is key to tackling this epidemic. The interplay of poor dietary habits, lack of physical activity, and socioeconomic factors has fueled its rapid growth. Processed foods high in sugar and unhealthy fats have become dietary staples, while urbanization and technological advancements have led to increasingly sedentary routines. These factors contributing to obesity demand urgent intervention through public health strategies, education, and medical innovations.
With the prevalence of obesity continuing to surge, the need for effective prevention and treatment strategies has never been greater. Addressing the etiology of obesity through lifestyle modifications, medical therapies, and policy changes is critical to curbing its long-term impact. By promoting healthier choices and advancing obesity treatments, society can work toward reversing the trajectory of this global crisis.
How is Obesity Measured?
Obesity is categorized into different classes based on the severity of excess body fat, with the most common and standardized measurement being Body Mass Index (BMI). BMI is a simple yet effective tool that calculates a person’s weight in relation to their height to assess their level of adiposity. Based on BMI values, obesity is classified into:
- Overweight (Not Obese) – BMI of 25 to 29.9
- Class 1 Obesity (Low Risk) – BMI of 30 to 34.9
- Class 2 Obesity (Moderate Risk) – BMI of 35 to 39.9
- Class 3 Obesity (High Risk or Severe Obesity) – BMI of 40 and above
While BMI is widely used, it does not account for muscle mass, fat distribution, or other metabolic factors. Therefore, additional methods to measure obesity provide more precise assessments. These include Waist Circumference, which evaluates abdominal fat; Waist-to-Hip Ratio, which determines fat distribution; Skinfold Thickness, which estimates body fat through caliper measurements; and Bioelectric Impedance Analysis (BIA), which measures body composition using electrical currents. More advanced techniques, such as Air-Displacement Plethysmography, provide highly accurate fat percentage data.
Since obesity is a complex condition, using a combination of these assessment tools helps in better understanding risk factors for obesity and tailoring effective prevention and treatment strategies.
Why is Obesity a Problem?
A new study published in March 2024 in The Lancet warns that by 2050, nearly 60% of adults and a third of children worldwide will be overweight or obese unless urgent action is taken. Researchers from the Institute for Health Metrics and Evaluation (IHME) analyzed data from 204 countries, highlighting obesity as one of the greatest health challenges of the century.
The number of overweight or obese individuals has surged from 929 million in 1990 to 2.6 billion in 2021. If trends continue, this figure could reach 3.8 billion by 2050, placing immense strain on global healthcare systems, especially as a growing proportion of obese individuals will be over 65.
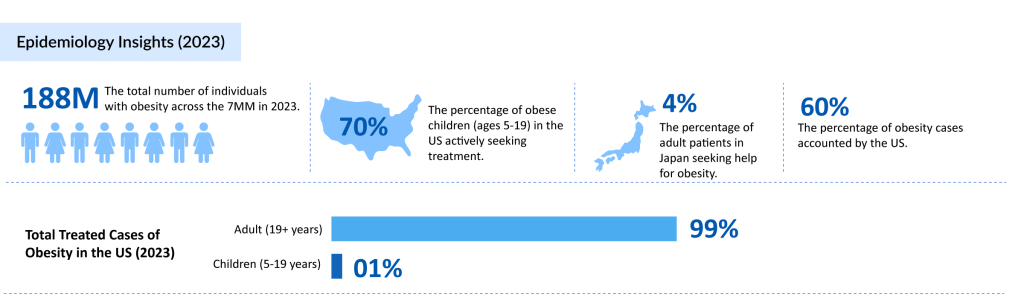
Overweight and obesity pose serious health risks, potentially leading to life-threatening conditions if left unaddressed for an extended period. Obesity is a risk factor for many health complications, such as pulmonary embolism, joint osteoarthritis (OA), cardiovascular disease, and certain types of cancer.
Besides these, it is linked to other health problems, including strokes, sleep apnea, fatty liver disease, kidney disease, pregnancy problems, etc. Obesity can hamper day-to-day physical activity, impact cognitive abilities, and lead to psychological issues such as depression, stress, and many others.
What are The Risk Factors For Obesity?
Apart from calorie and physical activity, some of the genetic and social factors also influence the prevalence of obesity. Among various factors, some of the most common risk factors include:
Genes – The genes are supposed to have a small role in obesity. The gene and unhealthy diets and lifestyles enhance the risk of obesity. The appetite pattern, calorie-burning time, and eating habits impact the risks of obesity.
Medical conditions – Certain medical conditions such as Cohen syndrome, Prader-Willi syndrome, Cushing syndrome, and other disorders are directly associated with weight increase.
Age – As per the Delveinsight, The highest prevalence of obesity in 2023 was observed in both adults (ages 19 and older) and children (ages 5-19). Age, specific hormonal changes, and an inactive lifestyle increase risk of obesity.
Socioeconomic Conditions – Education level, income, and social status are key risk factors for obesity. According to the CDC, obesity prevalence is lower among individuals with higher education. Additionally, women in middle- and low-income groups face a greater risk of obesity than those in higher-income brackets, highlighting how economic disparities influence the causes of obesity.
Sex Differences – Gender also plays a role in what obesity causes and how it develops. In the U.S., Black and Hispanic women have a significantly higher prevalence of obesity than men of the same ethnic background. These differences may stem from biological, cultural, and lifestyle factors, making sex a key risk factor of obesity.
Other Contributing Factors – Several additional factors that contribute to obesity include chronic stress, depression, poor sleep patterns, pregnancy, and smoking cessation. These physiological and behavioral changes can lead to excessive weight gain, increasing the likelihood of diseases caused by obesity such as diabetes, heart disease, and hypertension.
Obesity Treatment Market
The obesity treatment market has witnessed significant growth due to the increasing prevalence of obesity and its associated health risks. Managing obesity and its causes requires a multi-faceted approach, including lifestyle modifications, pharmacotherapy, and surgical interventions. Lifestyle interventions remain the foundation of treatment, focusing on healthy eating, regular physical activity, and improved sleep patterns. However, for many individuals, these strategies alone are insufficient, leading to the need for obesity drugs and other medical interventions.
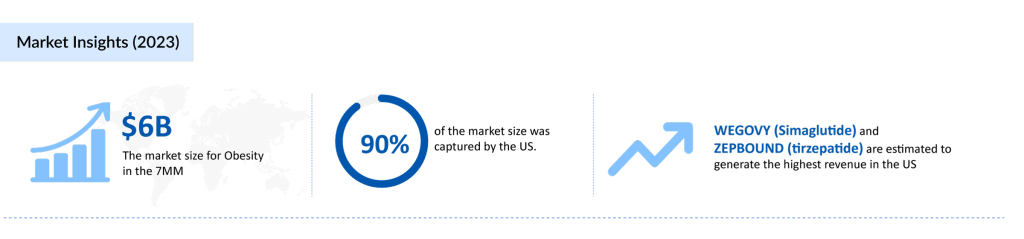
Several FDA-approved obesity therapies, including WEGOVY (semaglutide), ZEPBOUND (tirzepatide), SAXENDA (liraglutide), and CONTRAVE (naltrexone-bupropion), have demonstrated effectiveness in regulating appetite, reducing calorie absorption, and promoting weight loss. Despite their potential, these medications remain underutilized due to concerns about cost, insurance coverage, and long-term safety. Still, WEGOVY and ZEPBOUND are expected to dominate the obesity treatment market in the coming years, given their superior efficacy in clinical trials.
For individuals with severe obesity or those who fail to respond to medication, bariatric surgery remains a viable option. Procedures such as gastric bypass and gastrectomy can lead to significant weight loss but come with risks, including complications and long-term dietary restrictions. Given the risk factors of obesity and the growing economic burden, pharmaceutical companies like Novo Nordisk, AstraZeneca, and Rhythm Pharmaceuticals continue to innovate and develop new treatments. With more therapies in the pipeline, the obesity treatment market is expected to expand further, offering better solutions for individuals struggling with obesity-related diseases worldwide.
What Lies Ahead: A Call to Action Against the Obesity Epidemic
Obesity is no longer just a personal health issue—it is a global crisis demanding urgent attention. With its prevalence skyrocketing, the world faces a future where obesity-related diseases will strain healthcare systems and shorten life expectancies. The factors contributing to obesity are complex, spanning genetics, lifestyle choices, socioeconomic disparities, and environmental influences. Yet, the solutions are within reach.

Tackling this epidemic requires a collective effort. Governments must implement policies that promote healthier food choices, encourage physical activity, and enhance public health education. The pharmaceutical industry continues to drive innovation in obesity drugs and therapies, providing hope for millions struggling with weight management. Medical interventions, including pharmacotherapy and bariatric surgery, offer viable solutions for those at higher risk, while ongoing research ensures that obesity treatments will continue to evolve.
However, real change begins at the individual level. By making informed choices about diet, exercise, and lifestyle habits, people can take control of their health and reduce their risk factors for obesity. The fight against obesity is not just about shedding weight—it’s about reclaiming quality of life, preventing life-threatening diseases, and ensuring a healthier future for generations to come. The time to act is now.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- FDA Approves LUMAKRAS with VECTIBIX for KRAS G12C-Mutated Colorectal Cancer; PYC Receives FDA Rar...
- Lilly’s ZEPBOUND Clears Hurdle in Sleep Apnea Treatment
- How Bariatric Surgery Devices Are Revolutionizing Weight Loss Outcomes?
- Mobile Health Apps for Obesity Treatment: A Modern Solution to a Growing Problem
- Cytokinetics Announces Results From SEQUOIA-HCM Clinical Trial of Aficamten; FDA Approves Chiesi’...