Cybersecurity in Healthcare: Major Threats and Challenges
Dec 29, 2021
Table of Contents
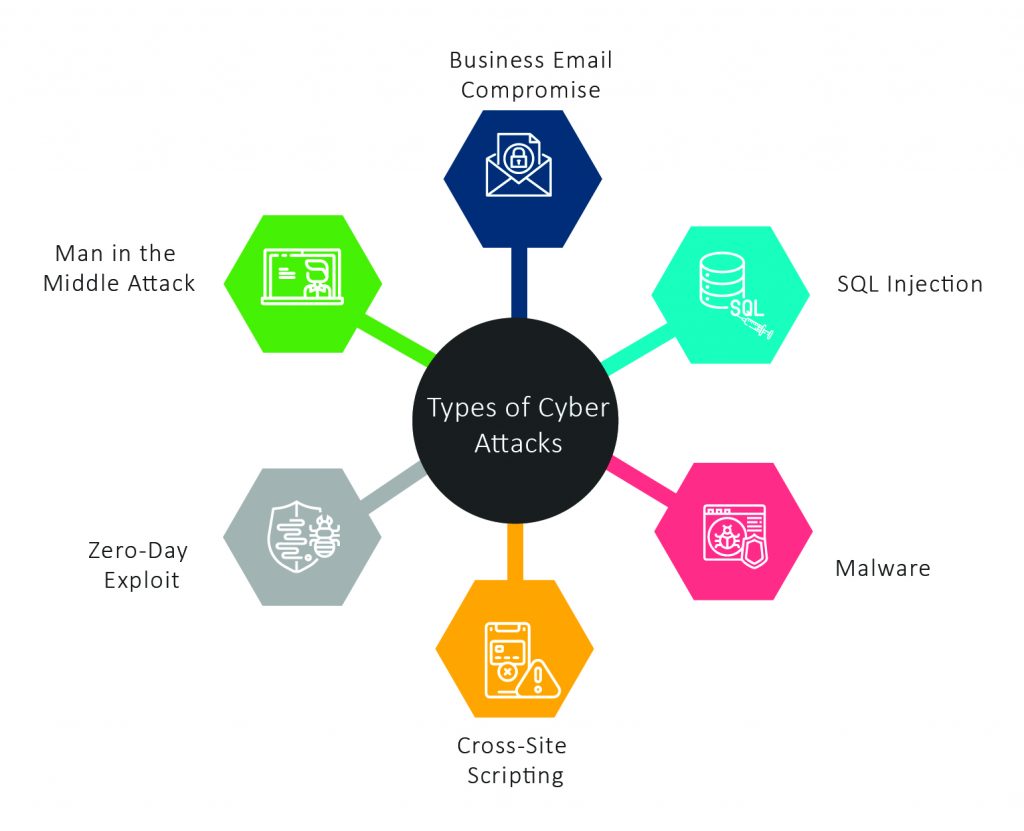
Over the last decade, cybersecurity in healthcare has been declined considerably. Unfortunately, rather than abate, these healthcare cyber attacks trends are expected to increase. Healthcare cyber attacks are of particular importance in the industry because they can directly affect the security of systems and information and the health and safety of people. The industry is beset by a slew of cybersecurity in healthcare issues. These challenges vary from malware that jeopardizes system integrity and patient privacy to distributed denial of service (DDoS) attacks that impair institutions’ capacity to deliver patient care. While similar healthcare industry cyber attacks occur in other critical infrastructure sectors, the nature of the healthcare industry’s purpose presents distinct obstacles. Cyber attacks on healthcare industry can have far-reaching consequences beyond financial loss and data leaks. For hospitals, for example, ransomware is a particularly heinous kind of malware since the loss of medical data can endanger lives. Furthermore, there are different types of cyber attacks in healthcare. The most common types of cyber attacks in healthcare are:
Both industry and government understand this new age. The susceptibility to vicious healthcare cyber attacks grows with advancements in automation, interoperability, and data analytics. Healthcare organizations have many commonalities with other businesses regarding technology and cybersecurity in healthcare. However, the healthcare industry and public health institutions confront specific cybersecurity in healthcare issues along with technological issues, requirements, and limits.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Moreover, every cloud has a silver lining. As the number and sophistication of healthcare cyber attacks are growing, the demand for cybersecurity jobs and professionals who can detect and prevent such cyber attacks on healthcare industry is also increasing. Currently, there aren’t enough cybersecurity jobs and professionals with the required skills to become the next generation of cyber-cops. But there will surge in cybersecurity jobs that will change the dynamics of healthcare industry cyber attacks in the coming years.
Cybersecurity Issues in the Healthcare Industry
The most prevalent cybersecurity in healthcare issue is misdelivery. This error is divided into two categories. One example is when an email is sent to the incorrect email address or distribution list, allowing unauthorized individuals to gain critical information. The second is the snail mail counterpart, which occurs when address labels for a large mailing go out of sync, and confidential information is sent to the wrong recipient.
Health care businesses, whether large or small, are major targets for cybercrime. The growing incidence of healthcare-related hacks indicates that smaller health providers are becoming increasingly vulnerable to hackers. Large healthcare providers frequently have the resources required to develop an effective cyber defense plan. These large hospitals and healthcare systems can frequently afford to hire a chief information security officer, staff a security operations center, and subscribe to the most up-to-date threat intelligence services.
Healthcare organizations have been the targets of some of the most prominent healthcare cyber attacks in the recent decade. Community hospitals, independent doctors, and dentists may not always have the financial resources to invest in expensive cybersecurity protections. Nonetheless, they face the same cyber hazards and provide similar opportunities for crooks. According to the American Medical Association, approximately 57% of medical practices in the United States have ten or fewer physicians, with approximately 10% being solo practitioners.
Due to these cyber attacks on healthcare industry, many small healthcare providers are unable or unable to pay high ransoms and are forced to close their doors. These professionals understand that paying a ransom demand does not ensure that the hacker would release data or equipment, and it also does not guarantee that they would not sell your patient’s data on the dark web.
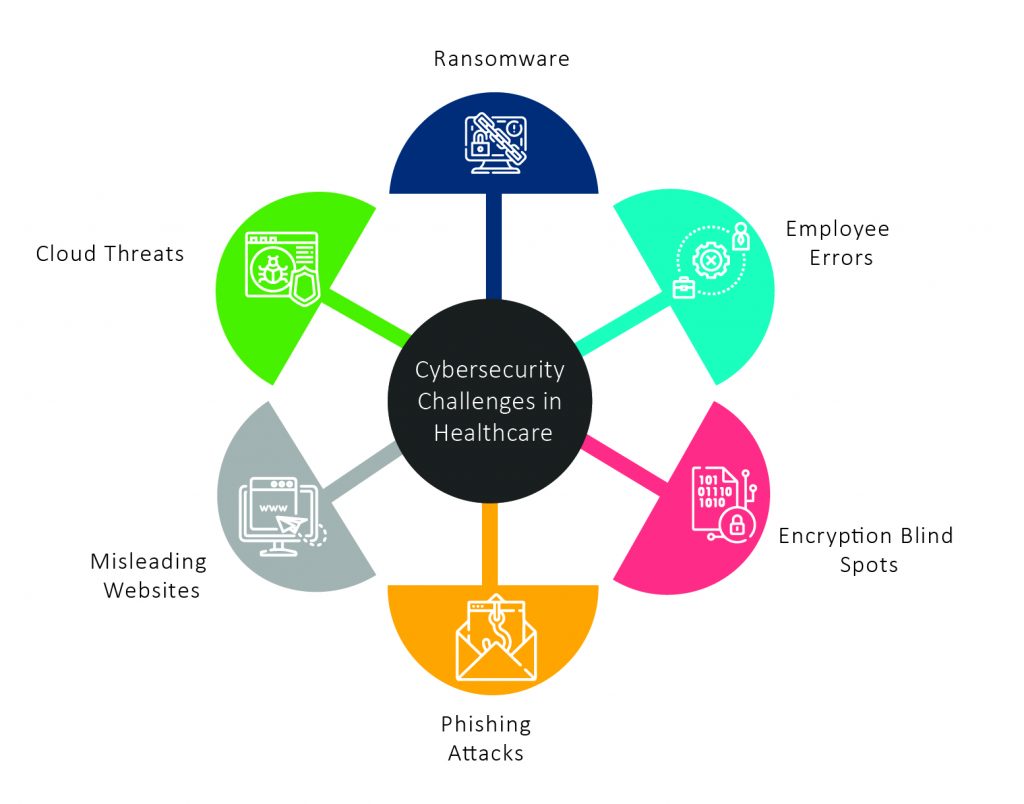
What makes cybersecurity in healthcare so challenging?
The healthcare industry faces all of the same cybersecurity threats as any other business, as well as its specific set of obstacles. In the healthcare sector, nothing is more important than the health and well-being of patients, and communication between healthcare practitioners and patients and across various healthcare activities has been honed to an art form. So, why is the healthcare industry struggling with cybersecurity in healthcare? The main cybersecurity in healthcare problems confronting the healthcare business are as follows:
- On the dark web, patient information is essential.
- Medical gadgets frequently lack proper security protections.
- Remote access to medical data is required for medical workers.
- There is little cyber risk training for healthcare staff.
- Many healthcare institutions employ out-of-date technologies.
Few healthcare professionals are unaware of the tremendous cybersecurity in healthcare dangers that the business faces and their status as the most targeted corporate sector have not gone unnoticed. The problem of cybersecurity in healthcare has come to the top of the list of issues for this industry. There are seminars, conferences, white papers, and a plethora of cybersecurity training options for healthcare workers.
Explore more about the Impact of Data Breach on Healthcare
Efficiency is implemented to boost competitive advantage in the same way that it is in any other sector. One of the primary efficiencies utilized by healthcare practitioners is the amount of time they spend with each patient. If you spend too much time with one patient, someone else’s medical requirements may go unnoticed.
Cyber Threats to watch out for in 2022
The rising digitalization of society and the more online aspect of our lives creates chances for phishers, hackers, fraudsters, and extortionists. Unfortunately, there is no evidence of this abating as we approach 2022. This is why individuals and companies must be aware of the ever-expanding channels of recent healthcare cyber attacks and what can be done to limit the dangers. So, let’s look at the most crucial and significant changes influencing our online security in the coming year.
AI-Powered Cybersecurity
Artificial intelligence (AI) in healthcare, in the same manner, that it is used in financial services to detect fraud, may combat cyber attacks on healthcare industry by finding patterns of behavior that indicate something out of the usual is happening. Importantly, AI enables this in systems that must deal with thousands of events per second, which is frequently where fraudsters try to strike. AI’s predictive capabilities are what make it so beneficial in this context, which is why more and more businesses will invest in these solutions as we approach 2022. Unfortunately, fraudsters are aware of the benefits of AI, and new healthcare cyber attacks are developing that exploit technology such as machine learning to circumvent cybersecurity in healthcare safeguards. This makes AI even more critical, as it is the only way to combat AI-powered healthcare industry cyber attacks.
Discover How will AI change the future of Healthcare
Ransomware and Phishing targeting healthcare
With the Covid-19 pandemic capturing worldwide news in 2020 and 2021, cyber attacks on healthcare industry have reached new heights. Indeed, the health sector was declared one of the top four most targeted industries in 2020, and the healthcare implications have been substantial, even forcing hospital closures. Ransomware is frequently distributed via phishing attacks, in which employees are tricked into providing information or clicking a link that downloads ransomware software (also known as malware) onto a computer. However, direct infection through USB devices by persons with physical access to machines has lately become more widespread.
According to the UK National Cyber Security Centre, the first quarter of 2021 had three times the number of healthcare cyber attacks as the entire year of 2019. According to various research, 61% of IT executives predict these healthcare cyber attacks trends to expand in 2022. Once again, we may attribute this to the pandemic and an increase in the quantity of activity conducted online and in digital surroundings.
Medical Devices Cyberattacks
The Internet of Things (IoT) has put non-traditional computer devices connected to the Internet within reach of malicious actors. While baby monitors and other smart home gadgets are susceptible, so are countless pieces of technology used in physicians’ offices and hospitals worldwide. Scientific research has demonstrated that vulnerabilities related to cybersecurity in healthcare can have significant consequences for patient health, and the supply chain must be monitored to ensure that patches are kept up to date. The newest software and firmware is maintained throughout the years that these devices are in use.
We will indeed witness an upsurge in cyber attacks on healthcare industry against IoT devices in 2022. Edge computing devices, which process data as close to the point of collection as possible, as well as centralized cloud infrastructure, are all vulnerable. Furthermore, education and awareness are two of the most effective means of mitigating these healthcare industry cyber attacks.
Critical Resources for Emergencies
The 24/7/365 nature of medical activities, many of which are critical care, is perhaps a unique component of securing healthcare facilities. Indeed, during natural disasters such as fires, floods, hurricanes, and tornadoes, as well as man-made disasters, hospital emergency rooms are critical resources for personal health issues and the general community. This one-of-a-kind job necessitates the availability of electricity, water, and other amenities even when primary supplies are unavailable. Backup systems and life-sustaining equipment must be evaluated under a variety of scenarios. When paired with man-made or natural disasters, recent healthcare cyber attacks on key systems will have even more severe consequences, costing lives and causing much more suffering in the most difficult of conditions.
Cybersecurity Solutions for the Healthcare Industry
The healthcare business is now losing momentum in its fight against healthcare industry cyber attacks. The Healthcare industry is susceptible because of outdated computing systems and a scarcity of experienced cybersecurity personnel and a rise in linked medical equipment. Technological advancements in health care equipment, systems, and procedures have outpaced advancements in backend support systems that store vital patient information. Cybersecurity in healthcare solutions should include safeguards superior to those provided by most enterprises. In terms of security, these systems and devices should be comparable to, if not superior to, those used in financial institutions. To achieve this goal, healthcare institutions must assess each new platform proposed in terms of the medical benefits provided to their patients as well as the risk of healthcare industry cyber attacks.
What’s Ahead?
Cybersecurity in healthcare impacts every part of the sector, from the confidentiality of sensitive health information to insurance costs and patient treatment. According to industry and government executives, healthcare lags in cybersecurity technology, standards, and practices. While some advocate for more government regulation to safeguard patients and their data, many healthcare leaders recognize that voluntary compliance with the tightest standards is the only way to avoid extra and often onerous compliance laws. As alarming as today’s recognized cybersecurity in healthcare concerns are, the worst of all, healthcare industry cyber attacks might still be on the horizon.
The industry faces significant challenges related to cybersecurity in healthcare that are unique to that industry. When lives, not just profits, are at stake, the finest and brightest in computer science, medical research, and business must collaborate to create new answers to the challenges threatening medical care as we know it.
FAQs
The practice of defending computers, servers, mobile devices, electronic systems, networks, and data from malicious attacks is known as cyber security. It’s also referred to as information technology security or electronic data security.
The main cybersecurity in healthcare problems are as follows:
On the dark web, patient information is essential.
Medical gadgets frequently lack proper security protections.
Remote access to medical data is required for medical workers.
There is little cyber risk training for healthcare staff.
Many healthcare institutions employ out-of-date technologies.
The different cybersecurity in healthcare threats are:
E-mail phishing attacks
Ransomware attacks
Equipment theft or data loss
Insider, accidental or intentional data loss
Attacks on connected medical devices that could jeopardize patient safety
Cybersecurity in healthcare solutions should include safeguards superior to those provided by most enterprises. In terms of security, these systems and devices should be comparable to, if not superior to, those used in financial institutions.
Downloads
Article in PDF