LEXICON’s INPEFA: Entry of Another Drug for Heart Failure Treatment
Jun 05, 2023
Table of Contents
Heart failure is a global pandemic that affects at least 26 million people globally and is becoming more common. Heart failure health expenditures are substantial and will rise considerably as the population ages. Despite significant advancements in medicines and prevention, mortality and morbidity remain high, and quality of life remains low. The reported prevalence, incidence, mortality, and morbidity rates vary geographically, based on the many etiologies and clinical features identified in heart failure patients.
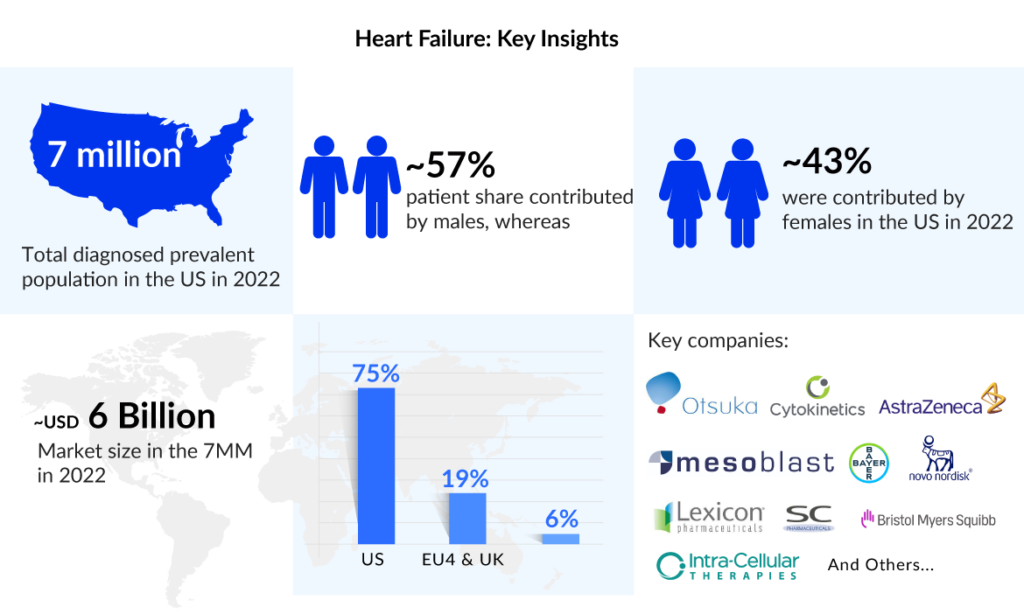
As per the DelveInsight estimates, the heart failure diagnosed prevalence was 7 million in the US in 2022. As per the estimates, around 4 million males and approximately 3 million females were suffering from heart failure in the US in 2022, which is expected to increase during the forecast period (2023–2032).
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- DelveInsight’s Cardiovascular disorders based Gene Therapy Reports
- Commercial
- Everything You Need to Know About Acute Kidney Injury
- Daiichi Sankyo’s Intravenous Iron Replacement Therapy; ANeuroTech’s Adjunctive Anti-depression Dr...
- Novartis’s Entresto; AZ, J&J and Lilly sharply cut death rates; CAR-T drugs worth; FDA warns
Current Heart Failure Treatment Space
The heart failure treatment market is highly competitive, with pharma companies competing to produce best-in-class treatments to reduce the burden of heart failure. Novartis’ Entresto (sacubitril/valsartan) is a first-in-class angiotensin-receptor/neprilysin inhibitor that has been licensed and sold for the treatment of chronic heart failure with decreased ejection fraction (HFrEF). This drug was approved in the United States in July 2015 for chronic heart failure with a decreased ejection fraction; in Europe, it was approved in November 2015 and again in October 2019 for pediatric patients with heart failure. Novartis announced in February 2021 that the US FDA had approved the following extended indication for Entresto (sacubitril/valsartan) to lower the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adult patients with CHF.

Jardiance, manufactured by Boehringer Ingelheim and Eli Lilly, is a sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor that is indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in an adult’s genital or perineal area, along with fever or malaise, to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and established cardiovascular disease, and to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death plus hospitalization for heart failure in adults. The European Commission and the FDA authorized Jardiance for the treatment of symptomatic chronic HFrEF in June and August 2021, respectively. Jardiance gained regulatory approval from Japan’s MHLW in November 2021 for treating chronic heart failure in patients receiving conventional chronic heart failure medication.
Verquvo is a soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC) stimulator developed by Bayer and Merck that is indicated to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and heart failure (HF) hospitalization following a heart failure hospitalization or the need for outpatient IV diuretics in adults with symptomatic chronic HF and an ejection fraction less than 45%. It is approved for heart failure in the United States, the European Union, and Japan. Merck began a Phase III pivotal trial of Verquvo in patients with chronic heart failure with a decreased ejection fraction of 40% or less and no recent worsening heart failure event in 2021.
Farxiga is an AstraZeneca sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor indicated in adults as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus, to reduce the risk of hospitalization for heart failure in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and either established cardiovascular disease or multiple cardiovascular risk factors, to reduce the risk of cardiovascular death and hospitalization for heart failure in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus and either established cardiovascular It is approved for the treatment of heart failure in the United States, the European Union, and Japan.
SAMTASU/OPC-61815 is a water-soluble prodrug of oral tolvaptan (tolvaptan sodium phosphate) that is appropriate for IV delivery. Tolvaptan is a novel chemical developed by Otsuka that is an orally accessible antagonist of the vasopressin V2 receptor. It inhibits water reabsorption at the renal collecting duct, resulting in increased water diuresis without electrolyte depletion. The PMDA granted regulatory approval to SAMTASU 8 mg and 16 mg IV infusion in March 2022 to treat fluid retention in heart failure patients who have not reacted adequately to other diuretics, such as loop diuretics. On May 30, 2022, the product was launched in Japan.
FUROSCIX (furosemide injection) is an investigational, patented furosemide solution with a neutral pH that is designed for SC infusion via a wearable, pre-programmed on-body infusor for outpatient self-administration. It is a new furosemide formulation packed in a prefilled Crystal Zenith cartridge. FUROSCIX is the first and only FDA-approved SC loop diuretic that can be administered at home using the FUROSCIX Infusor.
In January 2023, scPharmaceuticals announced the commercial availability of FUROSCIX on February 20, 2023, with reimbursed access to the drug for all Medicare Part D and Medicaid beneficiaries on Day 1 and that approximately 60% of all heart failure patients would have fixed tier co-pays (USD 100) at launch, with the company working hard to expand this to greater than 75% fixed tier co-pays.
LEXICON’s INPEFA: Potential Competitor to AstraZeneca’s Farxiga and Lilly’s Jardiance
Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Inc. earned a major victory before the end of May when the FDA accepted the company’s application to market sotagliflozin (brand name: Inpefa) for heart failure treatment. On the plus side, the FDA awarded the drug about as excellent a label as could possibly be expected. Inpefa’s clinical efficacy and safety outperform proven heart failure drugs such as AstraZeneca PLC’s Farxiga, Eli Lilly & Company/Boehringer Ingelheim’s Jardiance, and Johnson & Johnson’s Invokana. On the negative side, there is still a lot of expensive work to be done if Lexicon is to win enough market share to make the drug genuinely profitable.
The approval is based on the results of two randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled Phase III cardiovascular outcomes studies of INPEFA in patients with or at risk of heart failure. SOLOIST-WHF (Worsening Heart Failure) and SCORED enrolled about 12,000 patients together. In individuals who had previously been hospitalized for worsening heart failure, INPEFA dramatically reduced the risk of the composite of hospitalizations for heart failure, urgent visits for heart failure, and cardiovascular mortality by 33% compared to placebo.
INPEFA is a sodium-glucose co-transporter type 2 (SGLT2) and type 1 (SGLT1) inhibitor. The American Heart Association (AHA), the American College of Cardiology (ACC), and the Heart Failure Society of America (HFSA) recommended SGLT inhibitors as first-line treatment for heart failure in their joint 2022 AHA/ACC/HFSA Guideline for the Management of Heart Failure. An expert consensus statement issued by the American College of Cardiology (ACC) in April 2023 emphasized the value of SGLT inhibitors as part of Guideline-Directed Medical Therapy (GDMT) in patients with heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF). The ACC expert consensus statement recommends that SGLT2 inhibitors be started in all persons with HFpEF who are stable during hospitalization and have no patient population contraindications.
Lexicon anticipates that INPEFA will be accessible by the end of June 2023. The company intends to keep the wholesale acquisition cost of the pharmaceutical comparable to that of existing branded heart failure treatments.
Promising Future of Heart Failure Treatment Market
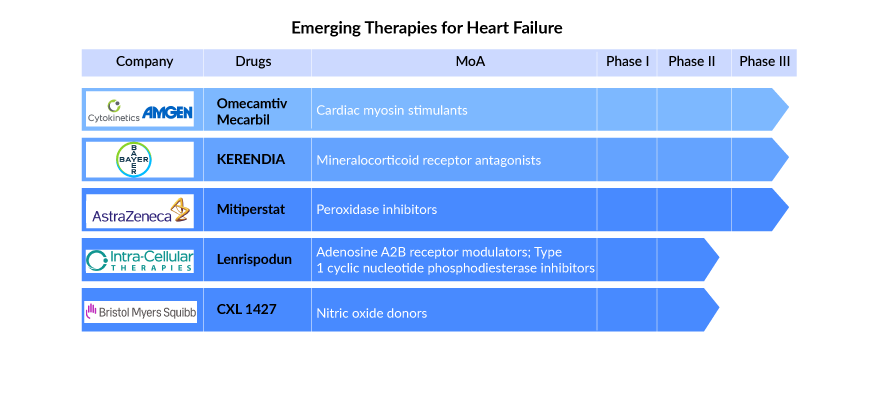
The dynamics of the heart failure treatment market are anticipated to change in the coming years owing to the improvement in the diagnosis methodologies, raising awareness of the diseases, incremental healthcare spending across the world. The drug candidates by key players, such as, Omecamtiv mecarbil (Cytokinetics), AZD4831 (AstraZeneca), Rexlemestrocel-L (Revascor) (Mesoblast), Finerenone (Kerendia) (Bayer), CXL 1427 (BMS), and others that are under late- and mid-phase of clinical development have the potential to create a significant positive shift in congestive heart failure market size.
Many clinical trials addressing the effects of drugs on HFpEF are underway, providing possible medical evidence for the future treatment of HFpEF. In addition, improved access to health services, reimbursements, and financial support may boost the congestive heart failure tratment market and improve the market accessibility of the emerging heart failure drugs in the coming years.
FAQs
Heart failure, also referred to as congestive heart failure (CHF), is a condition in which the heart muscle fails to pump blood as efficiently as it should. This causes an accumulation of blood and fluid in the lungs, resulting in shortness of breath.
At first, the heart failure signs and symptoms are subtle, and they are frequently misdiagnosed as typical signs of ageing. The most common symptoms of heart failure are caused by extra fluid or congestion, which leads to vessel blockage. The beginning of the congestion in the lungs is carried forward to other parts of the body. The cardiac output decreases as the disease progresses.
The most common causes of congestive heart failure include lowering the left ventricular myocardial utility and the dysfunction of the pericardium, myocardium, endocardium, heart valves or large vessels alone or in combination. Other pathogenic mechanisms that can lead to heart failure include excessive neurohumoral stimulation, irregular myocyte calcium cycling, augmented hemodynamic overload, ischemic dysfunction, ventricular remodelling, extreme or inadequate extracellular matrix production, enhanced apoptosis, and genetic mutations.
Heart failure diagnostic tests include a chest X-ray, transthoracic echocardiography (TTE), Computerised tomography (CT) scans, and magnetic resonance imaging (MRI), Echocardiogram, Stress test, Coronary angiogram, Myocardial biopsy, Ejection fraction, and others.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Daiichi Sankyo’s Intravenous Iron Replacement Therapy; ANeuroTech’s Adjunctive Anti-depression Dr...
- DelveInsight’s Cardiovascular disorders based Gene Therapy Reports
- Novartis’s Entresto; AZ, J&J and Lilly sharply cut death rates; CAR-T drugs worth; FDA warns
- Everything You Need to Know About Acute Kidney Injury
- MEDIT’s i700 Intraoral Scanner; Phantom Neuro and Blackrock’s Next-Generation Assistive Devices; ...