Meeting the Unmet: Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH)
Sep 04, 2024
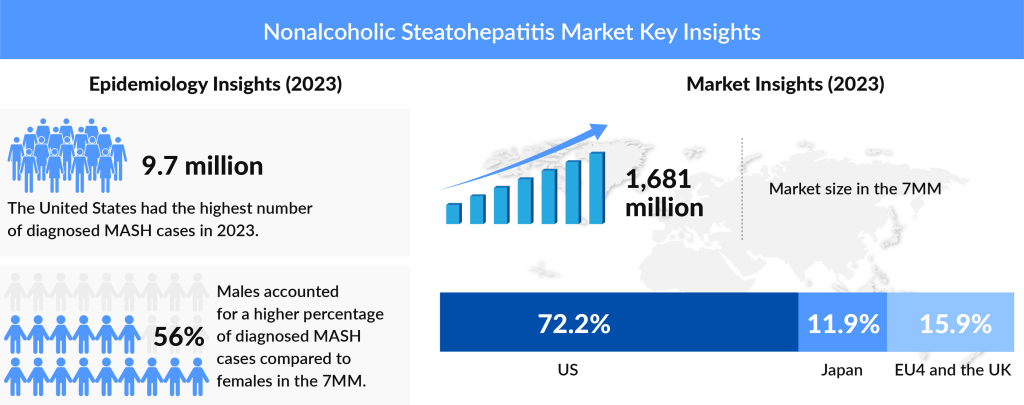
Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) is a severe form of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), characterized by liver inflammation and damage due to fat accumulation. Unlike simple fatty liver, NASH can progress to serious conditions such as fibrosis, cirrhosis, and liver failure. This chronic liver disease is increasingly recognized as a global health concern, with its rising prevalence linked to the growing incidence of obesity, type 2 diabetes, and metabolic syndrome. Affecting both children and adults, NASH often remains asymptomatic until it reaches an advanced stage, highlighting the need for early diagnosis and intervention. According to DelveInsight estimates, in the 7MM, the total prevalence of NASH in 2023 was around 43 million; out of these, the diagnosed cases were 37%.
In 2023, prominent liver disease organizations, including the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) and the European Association for the Study of the Liver (EASL), officially redefined Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) to Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Steatohepatitis (MASH), aligning the name more closely with its metabolic roots. For the most up-to-date insights, explore our comprehensive MASH Market Report.
Although the primary cause of NASH remains unidentified, it is closely linked to conditions like obesity, type 2 diabetes, and hyperlipidemia. As the prevalence of these diseases rises, so does the prevalence of NASH. Until 2024, there were no approved treatments for NASH. However, in March 2024, the FDA approved REZDIFFRA (resmetirom), marking the first drug available for this condition. Increasing awareness of NASH presents a significant opportunity for drug manufacturers, but it also comes with challenges. NASH often presents with few or no symptoms and is typically diagnosed through a liver biopsy conducted for related conditions.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- DelveInsight launches Indication Active Pharmaceutical Ingredient (API) Reports
- Antibody-Drug Conjugate and Big Pharmaceutical Companies
- Peripheral Lung Cancer Pipeline Insights, 2016
- Transforming Pompe Disease Care: Latest Innovations and Strategic Advances in Treatment
- FDA Grants Priority Review to BMS’ Luspatercept; Teva and MedinCell’s Risperidone FDA Approval; B...
Due to the high potential market, companies are extensively working on the given indication and have a robust pipeline of drugs for the treatment of NASH. Currently, there are more than 25 drugs in Phase II and Phase III stages of clinical development worldwide. There are four drugs in the Phase III stage, namely Lanifibranor (Inventiva Pharma), Saroglitazar Magnesium (Zydus Therapeutics), Semaglutide (Novo Nordisk A/S), Tirzepatide (Eli Lilly and Company), MGL-3196 (Resmetirom) (Madrigal Pharmaceuticals, Inc.), TERN-501 (Terns, Inc.), Obeticholic acid (OCA) (Intercept Pharmaceuticals), Vonafexor (EYP001) (Enyo Pharma), Pegozafermin (89bio, Inc.), Efruxifermin (EFX) (Akero Therapeutics, Inc.), among others. These drugs have shown effectiveness against following fibrosis stages.
Genfit’s Elafibranor has indicated a greater efficacy in reducing intracellular lipid accumulation and alleviating inflammation and fibrosis than Intercept’s obeticholic acid (OCA). Indeed, Elafibranor looks like a promising drug for the treatment of NASH. On the other hand, OCA has shown greater efficacy in restoring glucose homeostasis and has a breakthrough designation for the treatment of NASH.
Tobira’s Cenicriviroc, acquired by Allergan, failed to meet the primary endpoint but has depicted efficacy in mitigating fibrosis, and successfully met the secondary endpoint in its Phase IIb CENTAUR study. On the other hand, Selonsertib met both its primary and secondary endpoints in combination with Simtuzumab. Its effectiveness in monotherapy is yet to be proven.
Bristol-Myers Squibb’s BMS 986036 has demonstrated statistically significant improvements in NASH’s exploratory endpoints and safety profile.
Among all the drugs in the pipeline, Obeticholic acid seems to be leading the race in the market. It has progressed the farthest in clinical trials and successfully acquired FDA approval.
The market share of Non-Alcoholic Steatohepatitis (NASH) in the 7MM has shown an upward trend, with the highest share in the United States, followed by the EU5 and Japan. This trend is expected to continue in the near future, driven by the rising global epidemics of obesity and type II diabetes. The NASH market size reached ∼USD 1.6 billion in 2023 and is anticipated to grow throughout the study period from 2020 to 2034.
According to DelveInsight, it is estimated that the market size of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis in 7MM will increase and reach significantly in 2034. NASH is becoming a highly unmet medical need and a leading cause of liver transplantation, increasing the requirement for advanced therapies
In conclusion, Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis remains a significant and growing health concern linked to increasing rates of obesity and type 2 diabetes. The approval of REZDIFFRA represents a crucial advancement in treatment options. As the market evolves, ongoing innovation and effective strategies will be essential to address the complexities of NASH, particularly its often asymptomatic nature, and to meet the rising demand for effective therapies.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- FDA Approves PTC’s AADC Gene Therapy; DUPIXENT sBLA Acceptance for Urticaria; CHMP Recommen...
- Chemists may help solve the air-pollution health crisis
- DelveInsight Unveils Enhanced and Updated Report Store
- Antibody–Drug Conjugates: An Emerging Concept in Cancer Therapy
- FDA approves; Sun Pharma Recalls; Mezzion filed; Sanofi’s antibody to treat



