The Evolution and Impact of Surgical Cameras in Modern Medicine
May 22, 2024
Table of Contents
In the fast-paced and precision-driven world of modern medicine, surgical cameras have emerged as a transformative technology. Among the myriad of technological advancements, surgical cameras stand out as a transformative innovation. These devices have revolutionized the way surgeons perform operations, offering unparalleled visualization and control. These advanced devices enable surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures with unparalleled accuracy, leading to better patient outcomes, shorter recovery times, and reduced healthcare costs.
The Evolution of Surgical Cameras
The journey of surgical cameras began with the invention of the endoscope in the early 20th century. Initially, these instruments were rudimentary, with limited visualization capabilities. However, technological advancements over the decades have dramatically improved their functionality. The introduction of fiber optics in the 1950s allowed for better illumination and flexibility. By the 1980s, the advent of video endoscopy revolutionized the field, providing real-time, high-definition images of the surgical site.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Telemedicine Service: Delving into Opportunities and Key Growth Factors Driving Market
- 22 Healthcare Trends & Innovations to Watch in 2022 and Beyond
- Mobile Clinics: Bridging the Healthcare Gap
- Telehealth: Opportunities and Hurdles in Virtual Healthcare Market
- Medical Odyssey: Solving the Dynamic Puzzle of Global Tourism Market
This breakthrough paved the way for minimally invasive surgery, reducing patient recovery times and minimizing surgical risks. Over the decades, advancements in camera technology, such as the miniaturization of components and the improvement of image resolution, have continued to enhance the capabilities of these devices. Today, surgical cameras are equipped with 4K resolution, 3D imaging, and even robotic assistance, making them indispensable tools in the operating room.
Types of Surgical Cameras
Surgical cameras are essential tools in modern medical procedures. These cameras come in various types, each tailored to specific surgical needs and technological advancements. Some of the important types of surgical cameras are
Endoscopic Cameras
Endoscopic cameras are widely used in minimally invasive surgeries. These cameras are attached to endoscopes—flexible or rigid tubes inserted into the body through small incisions or natural orifices. They provide real-time video feeds, allowing surgeons to view internal organs and structures without large incisions.
The global endoscopy camera market is estimated to grow at a CAGR of 5.63% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030. The increase in demand for endoscopy cameras is primarily attributed to the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases that require the use of endoscopy cameras for diagnosis and visualization of some disorders, such as some gastrointestinal diseases like irritable bowel syndrome (IBD), gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), peptic ulcer disease, and Crohn’s disease, increase in the number of the geriatric population who are more prone to chronic ailments, increasing awareness and demand of minimally invasive surgeries, and rise in technological advancements in endoscopy cameras like image magnification, high-definition optical systems, and digital imaging are anticipated to bolster the market.
Laparoscopic Cameras
Laparoscopic cameras, also known as minimally invasive cameras, are pivotal instruments in modern surgical procedures. These compact marvels offer surgeons a direct view inside the body without the need for large incisions, revolutionizing surgical techniques across various medical fields. Equipped with high-resolution imaging capabilities and flexible maneuverability, these cameras transmit real-time images to monitors, providing surgeons with enhanced precision and clarity during intricate procedures. Their small size and advanced optics allow for exploration and manipulation within the body’s cavities with minimal disruption, leading to reduced scarring, faster recovery times, and improved patient outcomes. From abdominal surgeries to delicate interventions, laparoscopic cameras continue to redefine the boundaries of surgical innovation, ushering in a new era of precision medicine.
Arthroscopic Cameras
Arthroscopic cameras, a marvel of modern medical technology, revolutionize the way orthopedic procedures are conducted. These miniature cameras, equipped with high-resolution lenses and fiber-optic illumination, enable surgeons to visualize the interior of joints with remarkable clarity and precision. By inserting these cameras through small incisions, surgeons can explore and diagnose joint conditions such as torn ligaments, damaged cartilage, or inflammation without the need for invasive open surgery. This minimally invasive approach not only reduces the risk of complications and accelerates recovery but also provides patients with a less painful and cosmetically appealing alternative to traditional surgery. With their ability to magnify and capture detailed images of the joint’s interior, arthroscopic cameras empower orthopedic surgeons to perform intricate procedures with enhanced accuracy, ultimately improving patient outcomes and quality of life.
Robotic Surgery Cameras
Robotic surgery cameras represent the cutting edge of medical technology, offering unparalleled precision and visualization in surgical procedures. These sophisticated cameras are equipped with high-definition imaging capabilities, providing surgeons with clear and magnified views of the surgical site. By integrating seamlessly with robotic surgical systems, these cameras enable surgeons to perform minimally invasive procedures with enhanced accuracy and control. Moreover, their ability to navigate tight spaces within the body allows for precise maneuvers, reducing the risk of complications and promoting faster recovery times for patients. With continuous advancements in robotics and imaging technology, robotic surgery cameras continue to redefine the possibilities of modern medicine, paving the way for safer and more effective surgical interventions.
The other types of surgical cameras used in the healthcare industry include Microsurgery Cameras, Wireless and Capsule Endoscopy Cameras, Fluorescence Imaging Cameras, Dermatology Cameras, Ophthalmology, Dental Cameras, and others. The diversity of surgical cameras allows for greater precision, minimally invasive techniques, and improved outcomes across a wide range of medical disciplines. As technology advances, the capabilities of these cameras continue to expand, offering even more sophisticated imaging solutions to meet the evolving needs of modern surgery.
Benefits of Surgical Cameras
Surgical cameras have revolutionized modern medicine by enhancing the precision and safety of surgical procedures. One of the primary benefits is the significant improvement in visualization. These cameras provide high-definition, magnified views of the surgical field, allowing surgeons to see intricate details that would be difficult to discern with the naked eye. This enhanced visibility is crucial in minimally invasive surgeries, where small incisions limit the surgeon’s direct view. By enabling better visualization, surgical cameras help reduce the risk of errors, ensuring that even the most delicate procedures can be performed with greater accuracy and confidence.
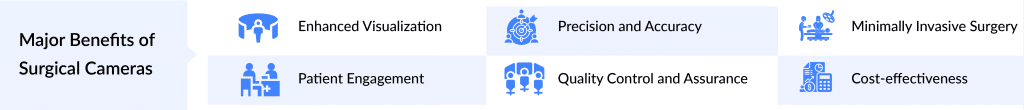
Another notable benefit is the ability to document and review surgeries. Surgical cameras can record procedures in real time, which is invaluable for educational and training purposes. Surgeons can review the footage to analyze their techniques, identify areas for improvement, and share insights with colleagues and trainees. Additionally, these recordings can be used to inform patients about the specifics of their surgeries, enhancing transparency and trust. Furthermore, the ability to review surgical footage helps in post-operative assessments and can be instrumental in addressing any complications that arise, ensuring that patient care continues to improve over time.
Evolving Surgical Cameras Market Dynamics
The surgical camera market is experiencing significant growth driven by advancements in medical technology and increasing demand for minimally invasive surgeries. With the rise in chronic diseases and the aging global population, there is a growing need for less invasive surgical procedures, reduce recovery time, and minimize complications. Surgical cameras, integral to these procedures, provide high-definition visuals that enhance the precision and accuracy of surgeries. Innovations such as 3D imaging, high-definition cameras, and integration with robotic surgical systems are propelling market growth, as these technologies offer surgeons better visibility and control during operations.
As per DelveInsight assessment, the surgical cameras market was valued at USD 3.29 billion in 2023 and is likely to register a CAGR of 7.13% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030 to reach USD 5.31 billion by 2030.
Moreover, the market dynamics are influenced by the expanding healthcare infrastructure, especially in developing regions, where there is a rising adoption of advanced medical equipment. Government initiatives and increased healthcare spending are further bolstering the market. However, the high cost of surgical cameras and stringent regulatory requirements pose challenges. Competition among key players is intense, leading to continuous product innovation and strategic collaborations to capture larger market shares. Companies are also focusing on developing portable and user-friendly surgical cameras to cater to outpatient surgical centers and smaller clinics, thereby expanding their customer base.
Major Players in the Surgical Cameras Market
The surgical camera market is highly competitive, with several key players driving innovation and growth. Leading the market are companies like Stryker Corporation, Olympus Corporation, Richard Wolf GmbH, Canfield Scientific, Inc., Carestream Dental LLC, Topcon Corporation, Fujifilm Holdings Corporation, Sony Corporation, Canon Inc., Zimmer Biomet, GE Healthcare, Johnson & Johnson, Karl Storz GmbH & Co. KG, Medtronic plc, Siemens Healthineers AG, Samsung Electronics Co., Ltd., Hamamatsu Photonics K.K., Mindray Medical International Limited, Intuitive Surgical, Inc., Leica Microsystems, and others.
Olympus, renowned for its high-quality optics and imaging solutions, has a strong presence in the endoscopic camera segment, offering advanced systems that enhance surgical precision. Stryker, a prominent player in medical technology, offers a comprehensive range of surgical cameras integrated with its surgical equipment, providing seamless and high-resolution imaging solutions that are critical for minimally invasive procedures. Karl Storz, a pioneer in endoscopy, continues to lead with its sophisticated imaging technologies that support various surgical disciplines, emphasizing image clarity and ergonomic design.

Other significant contributors include Medtronic, CONMED Corporation, and Smith & Nephew. Medtronic’s surgical cameras are part of its broader portfolio of surgical instruments, known for their reliability and integration with its advanced robotic surgery platforms. CONMED Corporation offers versatile camera systems that cater to both general and specialized surgeries, focusing on user-friendly interfaces and high-definition imaging. Smith & Nephew, with a strong foothold in orthopedics and sports medicine, provides innovative camera systems that facilitate precise visualization during complex procedures. These major players, through continuous R&D and strategic partnerships, are shaping the future of surgical imaging, enhancing surgical outcomes, and expanding the capabilities of minimally invasive surgery.
Challenges and Future Directions in Surgical Camera Market
The global surgical camera market faces several significant challenges as it evolves. One major challenge is the high cost associated with advanced surgical camera systems, which can be prohibitive for many healthcare institutions, particularly in developing regions. Additionally, the integration of these advanced systems with existing medical infrastructure can be complex and requires significant investment in training and adaptation. Another challenge is the rapid pace of technological advancement, which can render existing equipment obsolete quickly, necessitating continuous upgrades and thereby increasing operational costs. Moreover, the market is highly competitive, with numerous players striving to innovate, which can create uncertainty and volatility.
Looking ahead, the future directions for the surgical camera market are promising, with a focus on enhancing image quality, reducing costs, and improving ease of use. Innovations such as 3D imaging, robotic integration, and artificial intelligence are expected to revolutionize the field, making surgeries more precise and less invasive. The development of wireless and miniaturized camera systems can provide surgeons with greater flexibility and improved access to hard-to-reach areas. Additionally, as telemedicine and remote surgeries gain traction, there will be an increased demand for high-definition, real-time imaging capabilities. Expanding the market to include more cost-effective solutions and focusing on the needs of emerging markets will also be crucial for sustained growth and broader accessibility.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Telemedicine Service: Delving into Opportunities and Key Growth Factors Driving Market
- Top healthcare innovations changing the healthcare dynamics
- Healthcare Mobility Solutions: Revolutionizing Patient Care and Operational Efficiency
- The Promise of Big Data in Healthcare: Transforming Treatment and Outcomes
- 8 Game-Changing Applications of Healthcare Mobility Solutions