Mobile Health Apps for Obesity Treatment: A Modern Solution to a Growing Problem
Mar 12, 2025
Table of Contents
Obesity is the second leading cause of preventable death, associated with a range of inflammatory conditions that contribute to cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory problems, mental health issues, hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, cancer, and high cholesterol. This represents a significant public health challenge that has been intensifying over the past fifty years. Obesity rates have been rising among both children and adults in both developed and developing countries.
According to DelveInsight, ~188 million individuals with obesity across the 7MM were affected in 2023, with numbers expected to rise significantly by 2034. In the United States, the prevalence of obesity continues to climb, especially among adults. The highest number of individuals with obesity was seen in both adults (19+) and children (5-19) in 2023, with these figures projected to grow at a steady rate for both groups in the coming years.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Cardio Flow’s FreedomFlow Orbital Atherectomy Peripheral Platform; Medtronic’s Aurora EV- ICD Sys...
- How Bariatric Surgery Devices Are Revolutionizing Weight Loss Outcomes?
- The Race to Redefine Obesity Treatment
- Obesity: A Worldwide Pandemic with Advancing Management Options
- Rise In Bispecific Antibodies Utilization As Antibody Therapeutics
In 2023, approximately 70% of obese children (ages 5-19) in the US were actively seeking treatment. Additionally, based on DelveInsight’s assessment, about 4% of adult patients in Japan were seeking help for obesity in 2023. DelveInsight estimates that the total number of prevalent obesity cases among adults in the United States accounted for approximately 60% of the cases across the 7MM in 2023.
In recent years, mobile health apps have emerged as a powerful tool to support obesity treatment, offering a range of features designed to assist users in managing their weight more effectively.
The Rise of Mobile Health Apps
The rise of mobile health apps has revolutionized the way individuals manage and monitor their health. These apps, ranging from fitness trackers and diet monitors to medication reminders and telemedicine platforms, offer users unprecedented access to personalized health information and tools. By leveraging the capabilities of smartphones and wearable technology, mobile health apps enable users to track various health metrics in real-time, such as physical activity, heart rate, and sleep patterns. This data-driven approach empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health and well-being, often leading to improved lifestyle choices and more proactive management of chronic conditions.
Moreover, the integration of mobile health apps with other digital health technologies, such as electronic health records and virtual care platforms, is enhancing the overall healthcare ecosystem. These apps facilitate seamless communication between patients and healthcare providers, allowing for more efficient consultations and continuous monitoring of health conditions. As technology advances, mobile health apps are expected to become even more sophisticated, incorporating artificial intelligence and machine learning to offer more precise health recommendations and predictions. The ongoing development and adoption of these apps highlight their growing importance in modern healthcare, offering a promising path toward more personalized and accessible health management.
Key Features of Obesity Treatment Apps
Obesity treatment apps have become increasingly popular as tools to support individuals in managing their weight and achieving healthier lifestyles. Here are some key features commonly found in these apps:
Calorie Tracking: Calorie tracking is a pivotal feature in obesity treatment apps, offering users a real-time view of their daily caloric intake and expenditure. By logging meals and snacks, individuals can better understand their eating habits and make informed dietary choices. Many apps provide visualizations and trends that highlight how caloric consumption aligns with personal goals, such as weight loss or maintenance. Additionally, these apps often include barcode scanners and food databases to simplify logging. Integrating calorie tracking with activity monitoring helps users balance their diet with physical exercise, enhancing overall weight management efforts.
Exercise Tracking: Exercise tracking is a cornerstone of obesity treatment apps, offering several key features. By monitoring physical activity, these apps help users set and achieve fitness goals, providing real-time feedback and motivation. They often integrate with wearable devices to track metrics such as steps, distance, and calories burned. Additionally, many apps offer personalized workout plans and adjust recommendations based on progress and user feedback. This data-driven approach not only promotes accountability but also helps users understand the impact of exercise on their weight loss journey.
Personalized Plans: Some apps offer customized diet and exercise plans based on individual user data. These plans typically adapt to individual user needs, preferences, and goals by considering factors such as age, weight, activity levels, and dietary habits. By customizing exercise routines, meal plans, and progress tracking, these apps enhance user engagement and effectiveness. They also adjust recommendations based on real-time data and feedback, ensuring a dynamic and responsive approach to treatment. This personalization helps users stay motivated and achieve sustainable weight loss results.
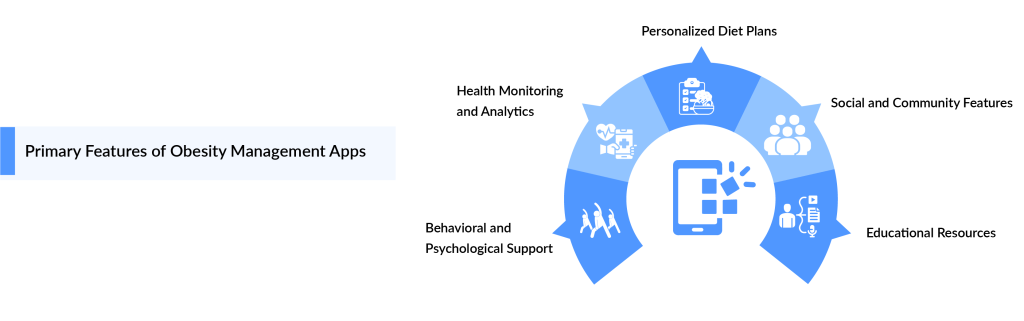
Behavioral Support: Many obesity treatment apps incorporate behavioral health strategies, such as goal setting, progress tracking, and motivational reminders. By focusing on behavioral modification, these features aim to address the psychological and habitual aspects of obesity, facilitating sustainable weight management and long-term health improvements.
Integration with Wearable Devices: Integration with wearable devices is a key feature of modern obesity treatment apps, enhancing their effectiveness and user engagement. By syncing with devices like fitness trackers and smartwatches, apps can monitor real-time metrics such as physical activity, heart rate, and sleep patterns. This data allows for personalized feedback and tailored recommendations, improving adherence to weight management plans. Additionally, the integration facilitates the tracking of progress over time, helping users stay motivated and make informed adjustments to their lifestyles. Overall, it creates a more interactive and dynamic approach to managing obesity.
Educational Resources: Obesity treatment apps increasingly leverage educational resources as a core feature to support users in achieving their weight loss goals. These resources often include articles, videos, and interactive content that educate users about nutrition, exercise, and healthy lifestyle habits. By providing evidence-based information, these apps empower users to make informed decisions about their health. Additionally, the educational materials can help users understand the underlying causes of obesity and the importance of a holistic approach to weight management. The accessibility and convenience of these resources make them a valuable tool in the fight against obesity, offering continuous support and motivation.
Limitations and Challenges of Mobile Health Apps for Obesity
Mobile health apps for obesity offer promising tools for managing and preventing excess weight, but they come with several limitations and challenges. One significant limitation is the variability in user engagement and adherence. Many apps rely on self-monitoring and self-reporting, which can lead to inconsistent data and reduced effectiveness if users do not consistently log their activities or follow the prescribed plans. Additionally, these apps often lack personalized feedback and support, which can be crucial for maintaining motivation and achieving long-term behavioral changes.
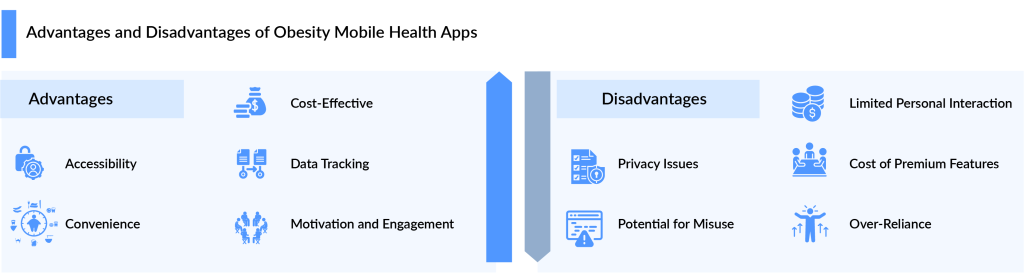
Another challenge is the concern over data privacy and security. Health apps collect sensitive personal information, and the handling of this data can be problematic if proper security measures are not in place. Users may be hesitant to share their information due to fears of data breaches or misuse. Furthermore, the effectiveness of these apps can be hindered by the lack of integration with other healthcare systems and the variability in the quality of app design and evidence-based content. Ensuring that apps are backed by scientific research and validated by healthcare professionals is essential for their reliability and success.
Key Companies in the mHealth App Market for Obesity Treatment
The mHealth app market for obesity treatment is witnessing significant growth, driven by key companies that are leveraging technology to provide effective solutions for weight management. One of the leading companies in this space is Noom, Inc. Known for its psychological approach to weight loss, Noom combines cognitive behavioral therapy with personalized coaching to help users develop healthier eating habits and sustain long-term weight loss. Their app’s user-friendly interface, comprehensive tracking tools, and supportive community features have made it a popular choice among individuals seeking to combat obesity.
Another major player in the mHealth app market for obesity treatment is MyFitnessPal, which was acquired by Under Armour. MyFitnessPal offers an extensive database of food items, allowing users to easily track their calorie intake and nutritional information. The app also integrates with various fitness trackers and wearables, providing a holistic approach to weight management by monitoring both diet and physical activity. Its strong emphasis on data-driven insights and community support has helped MyFitnessPal maintain a robust user base, contributing significantly to its success in the mHealth space.
Fitbit, now a part of Google, is also a prominent company in the mHealth app market for obesity treatment. While primarily known for its wearable fitness trackers, Fitbit’s companion app provides a comprehensive platform for weight management. The app allows users to set personalized goals, track their physical activity, monitor their heart rate, and log their food intake. With features like guided workouts, sleep tracking, and social challenges, Fitbit offers a well-rounded approach to obesity treatment, appealing to a broad audience seeking to improve their overall health and well-being through a combination of technology and community engagement.

Emerging startups like Lumen and BetterMe are also making significant strides by incorporating advanced technologies such as metabolic analysis and AI-driven insights to deliver more tailored and effective obesity treatment solutions. As these players continue to innovate and expand their offerings, the mHealth app market is poised to play a crucial role in combating obesity on a global scale.
The Future of Mobile Health Apps in Obesity Treatment
The future of mobile health apps in obesity treatment and management looks promising, driven by advancements in technology and a growing focus on personalized healthcare. These apps are evolving from basic calorie trackers to sophisticated platforms that offer comprehensive support for managing obesity. With the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning, these apps can provide personalized recommendations, predict potential health risks, and adapt to users’ changing needs. This customization not only enhances user engagement but also improves the effectiveness of weight management strategies by tailoring them to individual metabolic rates, dietary preferences, and activity levels.
Moreover, the integration of wearable devices and real-time data monitoring is revolutionizing how obesity is treated. Mobile health apps can now sync with fitness trackers, smart scales, and other health-monitoring gadgets to offer a holistic view of a user’s progress. This connectivity allows for more accurate tracking of physical activity, sleep patterns, and biometric data, enabling users and healthcare providers to make informed decisions. The continuous feedback provided by these apps helps users stay motivated and adhere to their treatment plans, which is crucial for long-term success in managing obesity.
Additionally, the future of mobile health apps in obesity treatment will likely see increased incorporation of social support and gamification elements. Social features, such as community forums and group challenges, can foster a sense of accountability and motivation among users by creating a supportive environment. Gamification, including rewards and progress tracking, can make the journey towards healthier habits more engaging and enjoyable. As these apps continue to evolve, their ability to integrate various support mechanisms will enhance their role in obesity management, making them an indispensable tool for both individuals and healthcare professionals.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- FDA Grants Priority Review to Merck’s Application for KEYTRUDA Plus Padcev; Roche and Carmot Ther...
- How Bariatric Surgery Devices Are Revolutionizing Weight Loss Outcomes?
- Digestive Health Products: Exploring the Market Dynamics and Key Factors Driving the Demand
- An Insight Into the Weight Loss and Obesity Market
- Cytokinetics Announces Results From SEQUOIA-HCM Clinical Trial of Aficamten; FDA Approves Chiesi’...