Tiny Organs, Big Impact: How Organoids are Shaping the Future of Medicine
Sep 18, 2024
Table of Contents
Imagine a world where tiny, lab-grown organs could hold the key to unlocking the mysteries of disease, revolutionizing drug development, and personalizing medicine. Welcome to the fascinating world of organoids—miniature, self-organized clusters of cells that mimic the structure and function of real organs. In recent years, these biological marvels have transitioned from the pages of scientific journals to the forefront of medical research, offering unprecedented insights into human biology and disease mechanisms.
Organoids are miniature, three-dimensional structures grown in a lab that mimic the architecture and function of real human organs. These tiny but powerful biological models are revolutionizing research by providing a more accurate representation of human tissues. Scientists can now use organoids to study diseases, test drugs, and personalize treatments, all while reducing the need for animal testing. It’s a breakthrough that brings us closer to understanding the human body’s complexities in a way we never could before.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
What makes organoids so exciting is their potential in precision medicine. By growing patient-specific organoids, researchers can observe how individual cells respond to treatments, allowing for more personalized and effective therapies. From cancer research to regenerative medicine, organoids are unlocking new possibilities in how we approach health care, offering hope for more targeted, efficient solutions to some of the world’s toughest medical challenges.
Organoids vs. Traditional Cell Cultures
In the quest for understanding human biology and disease, organoids are revolutionizing the field, offering a level of complexity and mimicry that traditional cell cultures simply can’t match. Unlike conventional cell cultures that often lack the intricate 3D architecture of human tissues, organoids are miniature, self-organizing organs that replicate the structure and function of real tissues. This leap in sophistication provides researchers with a more accurate model to study diseases, test drugs, and explore developmental processes, all while bridging the gap between in vitro studies and real-world applications.
Traditional cell cultures, while foundational, are limited by their flat, two-dimensional nature and often fail to capture the dynamic interactions within a living organ. Organoids, on the other hand, present a dynamic, three-dimensional alternative that more closely mirrors the human body’s complexity. By harnessing the power of organoids, scientists are not just enhancing their ability to investigate biological questions but are also paving the way for groundbreaking advancements in personalized medicine and targeted therapies. The shift from traditional cell cultures to organoids marks a significant leap forward in our pursuit of scientific and medical innovation.
Applications and Limitations of Organoids
One of their most promising applications of organoids is in disease modeling. Scientists can use organoids derived from patient cells to understand the progression of diseases like cancer, cystic fibrosis, and neurodegenerative disorders, providing insights into personalized treatments.
In drug discovery, organoids are proving invaluable. They enable high-throughput screening of new drugs in a more physiologically relevant environment, which can significantly reduce the time and cost of bringing effective therapies to market. For instance, liver and kidney organoids can predict potential toxicity and side effects of new drugs, improving the safety profile of experimental treatments.
Another cutting-edge use of organoids is in regenerative medicine. By developing organoids from patient-specific stem cells, scientists aim to create transplantable tissues for repairing damaged organs or treating chronic conditions. This opens up the possibility of personalized transplants with reduced chances of rejection, especially in cases where donor organs are scarce.
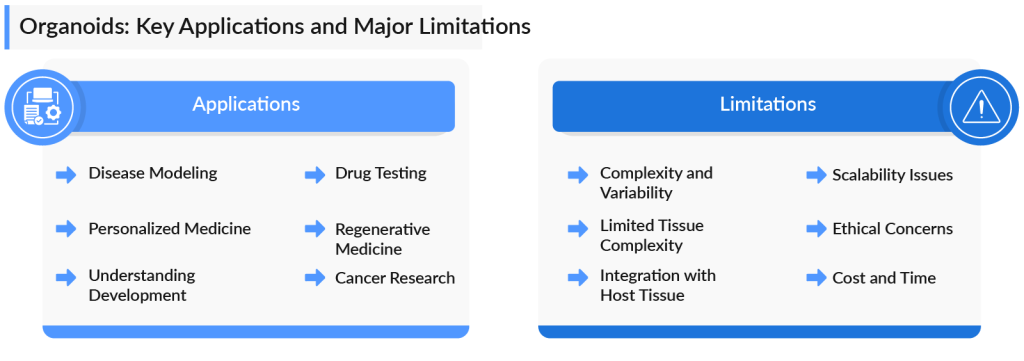
Despite their potential, organoids are not without limitations. One significant challenge is their incomplete complexity. While organoids mimic certain aspects of real organs, they often lack key features such as blood vessels, nerves, and immune cells, limiting their use in fully understanding human physiology or disease responses. This makes it difficult to study diseases that involve multiple systems or interactions within the body.
Additionally, there is the issue of variability. Since organoids are generated from stem cells, the process can result in inconsistencies between batches. This variability can affect the reproducibility of experiments, making it challenging to draw definitive conclusions. Finally, scaling up the production of organoids for industrial use, especially in drug testing or regenerative medicine, remains a technical hurdle.
In conclusion, while organoids are revolutionizing biomedical research, and bridging the gap between basic science and clinical application, their current limitations highlight the need for further technological advancements.
Key Players in the Organoids Market
The organoids space is rapidly emerging as one of the most innovative sectors in biotechnology, with major players and newcomers shaping the future of personalized medicine, drug discovery, and regenerative therapies. Companies leading the way in this space are not only pushing technological boundaries but are also poised to make significant contributions to clinical and research advancements.
Among the key players in the organoids market is Hubrecht Organoid Technology (HUB), a pioneer in developing and commercializing organoid models. Originating from the Hubrecht Institute, HUB has established itself as a leading provider of organoid technology, especially in gastrointestinal diseases. Their expertise in growing organoids from patient biopsies has helped propel the use of organoids in personalized cancer therapies, making them a major player in the global market.
Another key name is STEMCELL Technologies, which offers a range of specialized reagents and tools for growing organoids from various tissues. Their tailored solutions have simplified the organoid culture process for researchers worldwide, and they continue to expand their product lines to meet the needs of scientists working in disease modeling, toxicology, and stem cell research.
Meanwhile, Emulate Inc. is gaining momentum with its “Organ-on-a-Chip” technology, which incorporates organoid models to simulate human biological systems. Their cutting-edge platforms are being adopted by major pharmaceutical companies to revolutionize drug development and safety testing. With increasing regulatory interest in reducing animal testing, Emulate is set to make waves with its scalable and predictive organoid-based solutions.
On the horizon, several upcoming companies like Cellesce and PeproTech are capturing attention. Cellesce focuses on expanding patient-derived organoids at a commercial scale for use in drug discovery and clinical trials, addressing a major bottleneck in the scalability of organoid research. PeproTech, while traditionally known for its growth factors, has entered the organoid space with specialized solutions that enhance cell growth and differentiation, further fueling innovation in this field.

Apart from these organoids companies DefiniGE, OcellO B.V., Organovo Holdings Inc., Takara Bio Inc., Corning Incorporated, and others are also making strides. With growing demand from pharmaceutical giants and biotech firms, the organoids market is primed for explosive growth. As new entrants and established leaders continue to push the boundaries, the field promises transformative advancements in healthcare and biotechnology.
Organoids Market Dynamics and Future Prospects
The organoids market is experiencing rapid growth, driven by the increasing demand for advanced 3D cell culture models that better mimic human biology. As per DelveInsight analysis, the global organoids market is estimated to grow at a CAGR of ~14% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030.
As research intensifies in fields like oncology, neurology, and regenerative medicine, the demand for organoid models is set to skyrocket. This shift is primarily fueled by their ability to provide more accurate and personalized data compared to traditional 2D cell cultures and animal models.
The rise in precision medicine and personalized healthcare is another key factor pushing the organoid market forward. Researchers and pharmaceutical companies are increasingly leveraging organoids to study patient-specific disease mechanisms, test drug efficacy, and predict adverse effects. This shift is creating a paradigm change in drug discovery and development, reducing reliance on animal testing and significantly cutting down the time required for clinical trials. By creating organoids from patient-derived cells, scientists can customize treatment plans, revolutionizing the field of personalized medicine.
Additionally, the expansion of organoid applications in toxicology testing, regenerative medicine, and even organ transplantation is broadening the market’s horizons. In toxicology, organoids offer safer and more ethical alternatives for testing new chemical compounds, while in regenerative medicine, they hold promise for repairing damaged organs or tissues. The potential of bioengineered organoids for transplantation is still in its early stages but is showing great promise for future therapies, especially for patients with organ failure.
Technological advancements in 3D bioprinting and stem cell manipulation are also contributing to the future prospects of the organoid market. With continuous innovations, researchers are now able to create more complex and functionally accurate organoids that resemble full-sized human organs. These innovations are likely to lead to the development of next-generation organoids that can be used for large-scale drug screening, further accelerating drug discovery processes and cutting down R&D costs for pharmaceutical companies.
Looking forward, government initiatives and private investments in biomedical research are expected to foster further market growth. Countries worldwide are recognizing the potential of organoid technologies and are investing heavily in research grants and programs that support the development of this cutting-edge field. As regulatory frameworks evolve to accommodate these advances, the organoid market is expected to see exponential growth, shaping the future of healthcare and medical research.

Downloads
Article in PDF