Exploring the Future of Acute Kidney Injury: Market Trends and Growth Opportunities
Jan 16, 2025
Table of Contents
Acute Kidney Injury (AKI), also known as acute renal failure, is a sudden loss of kidney function that occurs over a short period of hours to weeks. This condition is primarily characterized by an increase in nitrogen waste products, as indicated by elevated blood urea nitrogen (BUN) and serum creatinine levels. Common symptoms of acute kidney injury include nausea, vomiting, weakness, dizziness, and lower back pain, although many patients remain asymptomatic. The condition can range from mild kidney dysfunction to severe failure requiring immediate medical intervention.
The causes of Acute Kidney Injury are diverse and include factors such as dehydration, infections, nephrotoxic drugs, and surgical procedures. Infections like sepsis are a significant driver of AKI cases, especially in low- and middle-income countries. Medical interventions, such as the use of contrast media during imaging or nephrotoxic medications, also contribute to the incidence of AKI. As the understanding of the disease evolves, healthcare providers are focusing on improving the management of acute kidney injury through early diagnosis, preventative measures, and effective treatment modalities.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Medivir & Karo Pharma’s deal; Astellas acquires Ganymed; Celldex Acquires Kolltan; Allergan ...
- What Does the Future Hold for Acute Kidney Injury? A Deep Dive into the Evolving Pipeline
- Cholera vaccine delivered; Rice-inspired breakthroughs; International partnerships
- Prostate Cancer Market Experiences an Influx of the Pharma Players Veering the Market Ahead
- Reblozyl under FDA review; Audentes buyout & Tecentriq’s new approval
Acute Kidney Injury Disease Burden
Globally, an estimated 13.3 million cases of AKI occur annually, representing a significant public health challenge. The condition disproportionately affects low- and middle-income countries, where infection-associated AKI is more prevalent. Hospitalized patients in high-income countries also face high rates of AKI due to surgical procedures, critical illnesses, and complex comorbidities.
According to DelveInsight’s Acute Kidney Injury Epidem-based Market Forecast Report, the annual number of hospital admissions involving AKI was approximately 98 million in 2023 in the 7MM. The burden is expected to increase over the next decade due to an aging population and rising prevalence of chronic conditions like diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular disease. For instance, in the US, nearly 9.5 million incident cases of AKI were recorded among hospitalized patients in 2023. Notably, the highest incidence of AKI was observed among individuals aged 60-79 years, followed by those aged 18-59 years.
In the EU4 and the UK, Germany reported the highest number of AKI cases in 2023. Similarly, in Japan, older adults aged 80 years and above had the highest incidence of AKI, reflecting the vulnerability of this age group to renal dysfunction. These trends underscore the urgent need for effective acute kidney failure treatments to address the growing disease burden.
Factors Driving Prevalence of Acute Kidney Injury
Several factors contribute to the increasing prevalence of AKI. Chronic Kidney Disease (CKD) is a significant risk factor, as pre-existing kidney damage makes individuals more susceptible to acute kidney dysfunction. Other key drivers include diabetes, hypertension, and cardiovascular diseases, which can impair kidney function and exacerbate the risk of AKI. For example, in the US, 50% of sepsis patients are at risk of developing AKI, while cardiac surgery patients face an AKI incidence rate of 20-30%.
Medical practices also play a role in AKI prevalence. The use of nephrotoxic drugs, including non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs), certain antibiotics, and contrast agents, can trigger acute kidney injury. Surgical procedures, particularly cardiac surgeries, further increase the risk of AKI due to potential disruptions in renal blood flow. Moreover, demographic factors such as aging, gender, and ethnicity influence AKI risk, with older adults and individuals of African American descent being more vulnerable.
Economic Burden of Acute Kidney Injury
The economic impact of acute kidney injury is substantial, encompassing both direct medical costs and indirect societal costs. Hospitalization and intensive care requirements for AKI patients contribute significantly to healthcare expenditures. In addition, the long-term costs associated with chronic kidney disease and dialysis among AKI survivors add to the financial burden. For healthcare providers, improving the management of acute kidney injury is crucial to reducing these costs and enhancing patient outcomes.
Acute Kidney Injury Current Market Scenario
The acute kidney injury therapeutics market in the 7MM reached a valuation of USD 6.2 billion in 2023 and is projected to grow significantly by 2034. The market is primarily driven by the increasing incidence of AKI, advancements in acute kidney injury treatments, and a robust pipeline of novel therapies. Currently, the market is dominated by supportive therapies, such as renal replacement therapy (RRT), and off-label medications like ACE inhibitors, ARBs, and diuretics. However, the emergence of targeted pharmacotherapies is expected to reshape the market dynamics in the coming years.
In the US, the AKI market is expanding due to the high prevalence of comorbid conditions and increasing hospital admissions. Similarly, European countries like Germany and France are witnessing growth in demand for acute kidney injury medication due to rising awareness and improved diagnostic capabilities. Japan, with its aging population, also represents a significant market for the treatment of AKI.
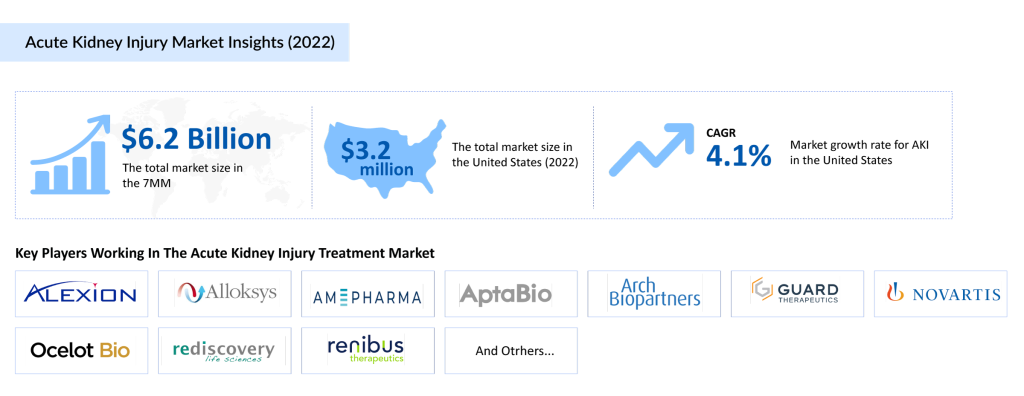
Acute Kidney Injury Market Dynamics and Key Drugs
A reliance on supportive therapies and off-label medications characterizes the current market for AKI. However, the Acute Kidney Injury pipeline is robust, with several candidates showing promise in clinical trials. Emerging therapies targeting AKI caused by sepsis, cardiac surgery, and other conditions are expected to address the unmet need for effective and targeted treatments.
Key pipeline drugs include:
- RBT-1 (Renibus Therapeutics): This investigational drug activates anti-inflammatory and antioxidant pathways, reducing postoperative complications. It is currently in Phase III trials.
- OCE-205 (Ocelot Bio): A therapeutic peptide designed to prevent fluid retention, OCE-205 is in Phase II trials for hepatorenal syndrome-associated AKI.
- Ilofotase alfa (AM-Pharma): A recombinant alkaline phosphatase targeting inflammation and ischemia-induced damage, Ilofotase alfa is in Phase III trials.
- RMC-035 (Guard Therapeutics): This biological drug candidate combats oxidative stress and aims to prevent acute and chronic kidney damage. It is in Phase II trials.
These innovative therapies hold the potential to transform the landscape of acute kidney injury treatments and improve patient outcomes.
Expected Roadblocks in the Acute Kidney Injury Treatment Market
Despite significant advancements, several barriers hinder the growth of the AKI therapeutics market. The lack of FDA-approved targeted therapies for AKI remains a critical challenge. Additionally, the reliance on supportive therapies like RRT and the off-label use of medications limit treatment options. High costs associated with novel drugs and clinical trials further impede market expansion. Limited awareness and delayed diagnosis of AKI in low- and middle-income countries also contribute to poor patient outcomes.
Opportunities and Gaps in the Acute Kidney Injury Treatment Market
The growing prevalence of AKI presents significant opportunities for pharmaceutical companies to develop targeted treatments. The emergence of novel drugs with unique mechanisms of action, such as RBT-1 and Ilofotase alfa, highlights the potential for innovation in this field. Additionally, improving early diagnosis and management of acute kidney injury through advanced diagnostic tools and biomarkers can enhance treatment outcomes and reduce mortality rates.
Gaps in the current market, such as the absence of FDA-approved medications for AKI and the limited availability of therapies in low-resource settings, represent areas for improvement. Addressing these gaps through strategic investments and collaborations can drive market growth and improve patient care.
Conclusion
Acute Kidney Injury is a complex and multifactorial condition with significant clinical and economic implications. The increasing prevalence of AKI underscores the need for effective treatment and management strategies. While the current market relies heavily on supportive therapies, the pipeline of innovative drugs for AKI offers hope for better outcomes. As the understanding of AKI evolves, healthcare providers and pharmaceutical companies must work together to address unmet needs and seize emerging opportunities in the treatment of AKI. With advancements in acute kidney injury medication and supportive therapy, the future of AKI management looks promising, paving the way for improved patient care and reduced healthcare costs.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Reblozyl under FDA review; Audentes buyout & Tecentriq’s new approval
- Alnylam’s lumasiran results; AZ’s oncology drug; Astellas Roxadustat; Evotec’s partnership with ABL
- Interstitial Cystitis: A big opportunities for emerging drugs
- Top 5 Cancers Creating Major Challenge To The Global Healthcare System
- Prostate Cancer Market Experiences an Influx of the Pharma Players Veering the Market Ahead