A Deep Dive into the 17th Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease (CTAD) Conference
Nov 19, 2024
The 17th Clinical Trials on Alzheimer’s Disease (CTAD) Conference, held in Madrid from October 29 to November 1, 2024, set the stage for groundbreaking updates in Alzheimer’s research, as pharmaceutical leaders presented their latest findings on novel therapies and cutting-edge clinical trials. With an ever-growing urgency to tackle this devastating disease, the event attracted top industry players who shared pivotal insights into the future of Alzheimer’s, a disease with a prevalence of approximately 6.9 million in the US alone with 97% of the patients aged 65 and above, as per Delveinsight’s estimates in Alzheimer’s Disease Epidem Report. The conference illuminated significant advancements in Alzheimer’s research, particularly in the realm of amyloid-targeting therapies and precision medicine.
Eli Lilly dominated the stage with compelling updates on KISUNLA (donanemab), its monoclonal antibody that has already received the US FDA approval for treating early symptomatic Alzheimer’s in July 2024 followed by approval in Japan and Great Britain in September 2024 and October 2024 respectively. The TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 6 Phase IIIb study revealed the potential for alternative dosing regimens to reduce amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA-E), showcasing a 41% reduction in ARIA-E incidence with a modified titration approach. These results, along with the genetic insights showing a 67% reduction in ARIA-E risk in APOE4 carriers, underscore the growing significance of personalized treatments in improving safety and efficacy. Additionally, the TRAILBLAZER-ALZ 6 study’s reaffirmation of amyloid plaque clearance as a key mechanism to slow cognitive decline solidified KISUNLA’s role in the evolving landscape of Alzheimer’s therapies.
Alongside KISUNLA, Lilly also presented data on emerging assets such as Ceperognastat (LY3372689), an O-GlcNAcase inhibitor, and remternetug (LY3372993), which focus on tau pathology and microglial-mediated amyloid clearance, respectively. Although Ceperognastat failed to meet its primary endpoint in the PROSPECT-ALZ study, its biomarker data highlighted the ongoing relevance of tau-targeting approaches. Meanwhile, remternetug enters Phase III trials with a decentralized study design aimed at expanding participant accessibility and enhancing recruitment. The trial’s focus on plasma P-tau levels as a biomarker for early-stage Alzheimer’s reflects the growing shift toward blood-based diagnostics in clinical trials, offering a glimpse into the future of more efficient and inclusive Alzheimer’s research. The conference underscored a collective drive toward multi-targeted therapies and personalized medicine, with both amyloid and tau remain central to future breakthroughs in Alzheimer’s treatment.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Semaglutide: A Potential Game-Changer in Reducing Alzheimer’s Disease Risk
- FDA Grants Priority Review for Zolbetuximab BLA; FDA Traditional Approval for LEQEMBI for Alzheim...
- Antihypertensive drugs decrease Dementia rate
- Coherus Biosciences’ Toripalimab; Keymed’s CMG901; Biogen Alzheimer’s Drug Aduhelm; Vicore’s Digi...
- Gene and Cell Therapies in CNS Disorders: Miracle Cure? Opportunities Galore!
Next, Eisai, a longstanding leader in the Alzheimer’s space showcased pivotal advancements in the Alzheimer’s treatment landscape, with key presentations focusing on LEQEMBI (lecanemab) and the company’s broader pipeline. LEQEMBI, an anti-amyloid beta (Aβ) protofibril antibody approved in July 2023, is designed to target the toxic protofibrils of amyloid beta that accumulate early in Alzheimer’s disease and drive neurodegeneration. The latest findings from the Phase III Clarity AD study further solidified LEQEMBI’s position as a potential disease-modifying therapy. After three years of continuous treatment, the drug demonstrated significant long-term benefits, 59% of patients with low tau accumulation showed improvement or no decline in cognitive function, as measured by CDR-SB. Furthermore, LEQEMBI was associated with a 30% reduction in the risk of progression to more advanced stages of Alzheimer’s, underscoring its potential as an early intervention treatment. Importantly, the long-term safety profile remained favorable, with minimal amyloid-related imaging abnormalities (ARIA) after the first six months, differentiating LEQEMBI from other amyloid-targeting agents that have faced greater safety concerns in extended use.
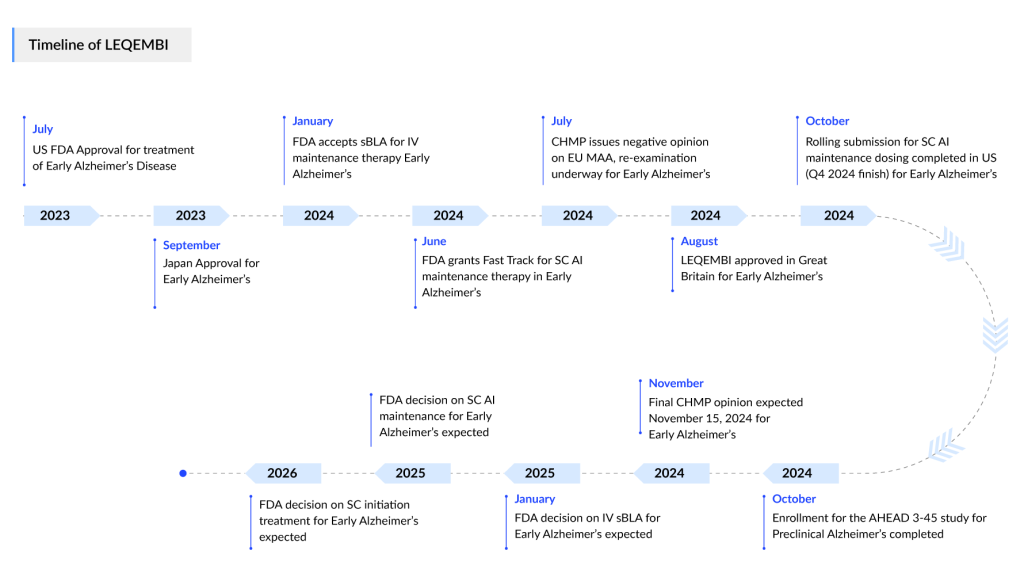
In addition to the LEQEMBI updates, Eisai also presented exciting data on E2814, an investigational anti-MTBR tau antibody developed in collaboration with University College London. E2814 targets the microtubule-binding region (MTBR) of tau, a protein implicated in the formation and spread of neurofibrillary tangles in Alzheimer’s. Data from the Phase I/II studies presented at CTAD showed substantial reductions in tau biomarkers like p-tau217 and MTBR-tau243 in cerebrospinal fluid, as well as stabilization or reduction in tau accumulation on tau PET scans. This evidence supports E2814’s ability to halt tau propagation, a major driver of neurodegeneration in Alzheimer’s. Notably, E2814 has been selected as the first investigational drug for the Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer’s Network’s (DIAN-TU) Tau NexGen study, a Phase II/III trial designed to explore tau-targeting therapies in Dominantly Inherited Alzheimer’s Disease (DIAD). Additionally, Eisai launched Study 202, a Phase II trial investigating E2814 in sporadic early Alzheimer’s, in combination with LEQEMBI. These findings underscore Eisai’s strategy to target both amyloid and tau, aiming for a comprehensive approach to disease modification. With ongoing trials and global submissions, Eisai is positioning itself at the forefront of Alzheimer’s research, offering a multi-pronged approach that addresses the disease’s hallmark pathologies.
| Alzheimer’s Severity Segmentation | % Contribution in Approximation |
| MCI | 54% |
| Mild Dementia | 19% |
| Moderate Dementia | 16% |
| Severe Dementia | 11% |
| Delveinsight’s Estimates | |
Other significant presentations at CTAD 2024 included Lexeo Therapeutics’ transformative interim results from their Phase I/II study of LX1001, a groundbreaking gene therapy targeting the APOE4 allele in individuals at 15 times higher risk for Alzheimer’s progression. LX1001 demonstrated dose-dependent increases in APOE2 protein expression, sustained for up to 12 months, effectively counteracting the toxic effects of the APOE4 allele. This was coupled with reliable reductions in tau biomarkers, including CSF T-tau and P-tau181, and tau PET scans, suggesting a potential breakthrough in reversing tau-driven neurodegeneration. Furthermore, amyloid pathology remained stable in most patients, signifying that LX1001 has the potential to halt disease progression by addressing Alzheimer’s pathology at its very core. As FDA engagement intensifies, Lexeo is positioning LX1001 for pivotal trials, paving the way for a new era of precision medicine in Alzheimer’s treatment.
In addition to Lexeo Therapeutics, Athira Pharma also presented intriguing insights from its Phase II/III LIFT-AD trial of fosgonimeton in Alzheimer’s disease. Despite failing to meet statistical significance for the primary endpoints, cognition, and function showed directional improvements, particularly among participants with moderate Alzheimer’s and those carrying the APOE4 allele. The biomarker data revealed favorable trends in amyloid, tau, and neurodegeneration markers, highlighting fosgonimeton’s potential to modulate hepatocyte growth factor (HGF) and offer neuroprotective benefits in Alzheimer’s disease. This reinforces the growing interest in therapies that work by enhancing neuroprotection and slowing disease progression from the inside out.
Moreover, Annovis Bio presented promising Phase II/III buntanetap data, showing significant improvements in primary endpoints, including cognitive function (as measured by ADAS-Cog) and functional outcomes (via ADCS-ADL), in early Alzheimer’s patients. Buntanetap also demonstrated a reduction in tau and amyloid biomarkers, further positioning it as a disease-modifying therapy that targets both neurodegeneration and amyloid pathology—key hallmarks of Alzheimer’s disease. The company’s findings underscore the importance of multi-targeted approaches that can intervene at multiple stages of Alzheimer’s pathology, which is essential in slowing the relentless progression of this debilitating disease.
The below-mentioned table provides a glimpse of upcoming competitors in Alzheimer’s space:
| Emerging Competitive Landscape of Alzheimer’s Disease | ||||||
| Drug Name | Company | Indication | Phase | Molecule Type | RoA | MoA |
| Masitinib | AB Science | Mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease | III | Small molecule | Oral | Inhibition of the c-Kit, Lyn, Fyn and CSF1R kinases |
| ACP-204a | ACADIA Pharmaceuticals Inc. | Adults with Alzheimer’s disease psychosis | III | Small molecule | Oral | 5-HT2A serotonin receptor agonist |
| Valiltramiprosate/ALZ-801 | Alzheon | Early Alzheimer’s disease and APOE4/4 genotype | III | Small molecule | Oral | Amyloid beta-protein inhibitors; GABA A receptor agonists |
| Mirodenafil (AR1001) | AriBio | Early Alzheimer’s disease | III | Small molecule | Oral | Type 5 cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterase inhibitors |
| Bupropion/dextromethorphan (AXS-05) | Axsome Therapeutics | Alzheimer’s Disease Agitation | III | Small molecule | Oral | NMDA receptor antagonist |
| Bezisterim (NE3107) | BioVie | Mild-to-moderate probable AD | III | Small Molecule | Oral | Anti-inflammatory |
| Simufilam (PTI-125) | Cassava Sciences | Mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease | III | Small Molecule | Oral | Microfilament protein modulators |
| Tricaprilin (CER0001) | Cerecin | Mild-to-moderately severe probable Alzheimer disease | III | Medium-chain triglyceride (MCT) | Oral | Ketosis inducer |
| Lecanemab** | Eisai | Early Alzheimer’s disease | III | mAb | IV/SC | Amyloid beta-protein inhibitors |
| Donanemab** | Eli Lilly and Company | Preclinical Alzheimer’s disease | III | mAb | IV | Pyroglutamyl(3)-amyloid beta-protein (3-42) inhibitors |
| Remternetug** | Eli Lilly and Company | Early symptomatic Alzheimer’s disease | III | mAb | IV/SC | Pyroglutamyl(3)-amyloid beta-protein (3-42) inhibitors |
| KarXT (Trospium chloride/xanomeline ) | Karuna Therapeutics (Bristol Myers Squibb) | Psychosis associated with Alzheimer’s disease | III | Small molecule | Oral | Muscarinic M1/M4 receptor agonists |
| Semaglutide | Novo Nordisk | Early Alzheimer´s disease | III | Peptides | Oral | GLP-1 analogue |
| Masupirdine (SUVN-502) | Suven Life Sciences | Agitation in participants with dementia of the Alzheimer’s type | III | Small molecule | Oral | 5-HT6 antagonist |
| E2814** | Eisai; University College London | Dominantly inherited Alzheimer’s disease | III | mAb | IV | Tau protein inhibitors |
| Sabirnetug (ACU193)b ** | Acumen Pharmaceuticals | Early Alzheimer’s disease | II/III | mAb | IV | Amyloid beta-protein inhibitors |
| AGB101 | AgeneBio | Mild cognitive Impairment due to Alzheimer’s disease | II/III | Small molecule | Oral | SV2A protein modulators |
| ANAVEX2-73c (Blarcamesine) | Anavex Life Sciences | Early Alzheimer’s disease | II/III | Small molecule | Oral | Muscarinic receptor modulators; Sigma-1 receptor agonists |
| Buntanetap (ANVS401 or posiphen) | Annovis Bio | Mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease | II/III | Small molecule | Oral | Acetylcholinesterase inhibitors; Alpha-synuclein inhibitors; Amyloid beta-protein precursor inhibitors; HD protein inhibitors; Tau protein inhibitors |
| Fosgonimeton (ATH-1017) d | Athira Pharma | Mild-to-moderate Alzheimer’s disease | II/III | Small molecule | SC | Hepatocyte growth factor stimulants; Proto-oncogene protein c-met stimulants |
| Piromelatine | Neurim Pharmaceuticals | Mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease | II/III | Small molecule | Oral | Melatonin MT1, 2, and 3 and serotonin 5-HT-1A and -1D receptors agonist |
| TRx0237 | TauRx Therapeutics | Alzheimer’s disease | III | Small molecule | Oral | Synuclein inhibitors; Tau protein inhibitors; TDP-43 protein inhibitors |
| ABBV-552 | AbbVie | Alzheimer disease | II | Small molecule | Oral | SV2A protein agonists |
| ABBV-916** | AbbVie | Alzheimer disease | II | mAb | IV | Amyloid beta-protein inhibitors |
| AL002** | AbbVie/ Allector Pharma | Alzheimer disease | II | mAb | IV | TREM2 protein-stimulants |
| Trontinemab (RG6102)/ RO 7126209** | Roche | Alzheimer disease | II | mAb | IV | Amyloid beta-protein inhibitors |
| bepranemab (RG6416)/ UCB0107** | Roche/ UCB Pharma / Genentech | Prodromal-to-mild Alzheimer’s disease | II | mAb | IV infusion | Anti-tau antibody |
| Mevidalen | Eli Lilly and Company | Alzheimer disease | II | Small molecule | Oral | Dopamine D1 receptor modulators |
| LY3372689 ( O-GlcNAcase inhibitor) | Eli Lilly and Company | Alzheimer disease | II | Small molecule | Oral | Hexosaminidase C inhibitors |
| AL001e | Alzamend Neuro | Alzheimer disease | II | lithium-delivery system | Oral | Sortilin inhibitors |
| Human Mesenchymal Stem Cells | Stemedica Cell Technologies | Alzheimer disease | IIa | Adult stem cll | IV | Reduction of amyloid-beta plaques and hyperphosphorylated tau |
| NEFLAMAPIMOD (VX-745) | Cervomed | Early onset Alzheimer disease | II | Small molecule | Oral | Inhibition of p38α |
| CT1812 | Cognition Therapeutics | Mild-to-moderate Alzheimer disease | II | Small molecule | Oral | Prevent the binding of toxic oligomers |
| Varoglutamstat (PQ912)f | Vivoryon Therapeutics | Alzheimer disease | II | Small molecule | Oral | Glutaminyl cyclase (QC) enzyme inhibitor |
| ACI-24.060g * | AC Immune SA | Alzheimer disease | II | Vaccine | IV | Immunostimulants |
| Seltorexant | Janssen | Probable Alzheimer’s with clinically significant agitation/aggression | II | Small Molecule | Oral | Selective antagonist of the human orexin-2 receptor |
| Posdinemab** | Janssen | Alzheimer’s disease (AUTONOMY) | II | mAb | IV | Immunomodulators |
| Pepinemabh ** | Vaccinex | Alzheimer disease | II | mAb | IV | SEMA4D Inhibitor |
| T3D-959 | T3D Therapeutics | Alzheimer disease | II | Small Molecule | Oral | PPAR (Peroxisome Proliferator-Activated Receptor) delta agonist |
| GRF6019 | Alkahest/ Grifols | Mild-to-moderate Alzheimer disease | II | plasma-derived product | IV | Neurogenesis stimulants |
| TB006i ** | TrueBinding | Alzheimer disease | II | mAB | IV | Galectin-3 (Gal-3) |
| GSK4527226 (AL-101)** | GlaxoSmithKline/Alector | Alzheimer disease | II | mAB | IV | Anti-sortilin monoclonal antibody |
| Hydroxypropyl Beta Cyclodextrin | Cyclo Therapeutics | Early Alzheimer’s disease | IIb | Beta-Cyclodextrins | IV infusion | Cholesterol modulators |
| RG6289 | Roche | Alzheimer disease | II | Small molecule | Oral | γ-secretase modulator (GSM) |
| Nanolithium (NP03) | Medesis Pharma | Alzheimer disease | II | microdose lithium formulation | transmucosal | Inhibition of BACE1 |
| AADvac1* | Axon Neuroscience | Alzheimer disease | II | Peptide vaccine | SC | Promotion of Tau Clearance |
| BPN14770 | Tetra Discovery Partners | Cognition Alzheimer disease | II | Small molecule | Oral | PDE4D Inhibitor |
| BMS-986446** | Bristol-Myers Squibb | Alzheimer disease | II | mAb | IV/SC | Anti-MTBR Tau |
| IONIS MAPTRx/ BIIB080 | Ionis Pharmaceutical/ Biogen | Alzheimer disease | II | Antisense oligonucleotides | Intrathecal | Tau protein expression inhibitors |
| Allogeneic MSC | Longeveron | Mild Alzheimer disease | II | Mesenchymal stem cell therapies | Infusion | Cell Replacement |
| AD-35 | Zhejiang Hisun Pharmaceutical | Alzheimer disease | II | Small molecule | Oral | Amyloid beta-protein inhibitors; Astrocyte inhibitors |
| PRI-002 | PRInnovation GmbH/ Priavoid | MCI-to-Mild dementia due to Alzheimer’s disease | II | Peptide | Oral | Amyloid Beta-protein inhibitor |
| Xanamem | Actinogen Medical | Mild or moderate dementia due to AD | IIb | Small molecule | Oral | 11β-HSD1 inhibitors |
| ABvac40* | Araclon Biotech | Alzheimer disease | II | Peptide vaccines | SC | Amyloid beta-protein inhibitors; Immunostimulants |
| BAC | Charsire Biotechnology | Alzheimer disease | II | Small molecule | Topical | – |
| Tertomotide (GV1001)* | GemVax & Kael | Alzheimer disease | II | Peptide Vaccine | SC | Immunostimulants |
| Dalzanemdor (SAGE-718) | Sage Therapeutics | Alzheimer’s disease mild cognitive impairment and mild dementia | II | Small molecule | Oral | NMDA receptor modulators |
| ITI-1284 | Intra-Cellular Therapies | Psychosis associated with Alzheimer’s disease | II | Small molecule | Oral | Serotonin uptake inhibitors |
| APH-1105 | Aphios | Alzheimer disease | II | Amyloid precursor protein secretase modulators | Intranasal | Amyloid precursor protein secretase modulators |
| IGC-AD1 | IGC Pharma | Alzheimer disease | II | Small molecule | Oral | Neuroinflammation AB Plaque Neurofibrilaaru Tangles |
| ACI-35.030* | AC Immune | Alzheimer disease | II | Vaccine | IV | Immunostimulants |
| LX1001 | Lexeo Therapeutics | Alzheimer disease | I/II | Gene therapy | Gene Transfer | Expression of APOE2 gene |
| ALZN002 | Alzamend Neuro | Alzheimer disease | I/II | Biologics | IV | Dendritic Cell Activation |
| aAccording to CT it is in Phase III but in the pipeline it is in Phase IIbCurrently in recruting phase II/III trial, results Phase Ib availablecBlarcamesine is an investigational drug that is not available for sale and has not been determined to be safe and effective by any regulatory authority.dNegative clinical trial resultseAnticipate initiating a Phase II clinical studies in Alzheimer’s patients in 2025flatest trial is terminated Phase IIagPartnered with TakedahIt is available only on pipeline. Do not have any details related to clinical trialiTB006 received FDA renewal approval for expanded access program*Vaccine candidates**Monoclonal antibody Updated as of September 2024 | ||||||
Several companies, including UCB, Hoffmann-La Roche, Janssen Research & Development, Anavex Life Sciences, Acumen Pharmaceuticals, Vaccinex, Cognition Therapeutics, and others also contributed to the conference with oral presentations, symposiums, and posters on their developing Alzheimer’s treatments. These presentations demonstrated the broad scope of ongoing research and innovation in the Alzheimer’s space, signaling an exciting future with diverse strategies aimed at tackling the disease from every possible angle.
Overall, the 17th CTAD conference highlighted a pivotal moment in Alzheimer’s research, where the convergence of novel therapies, advanced biomarker technologies, and personalized medicine has laid the foundation for the next generation of treatments. From amyloid-targeting monoclonal antibodies like KISUNLA and LEQEMBI to gene therapies like LX1001, and tau-targeting agents like E2814, the therapeutic landscape is evolving rapidly. The data shared at CTAD demonstrate a clear shift towards multi-targeted approaches that address the root causes of Alzheimer’s, offering more precise, personalized solutions for patients. The progress seen at CTAD 2024, coupled with promising early-phase results and pivotal clinical trial advancements, marks a crucial milestone on the path to disease-modifying therapies. This collective drive towards innovation, collaboration, and cutting-edge technology provides a hopeful outlook for the future, as the battle against Alzheimer’s enters a new and more targeted phase.
For more epidemiology, competitive landscape and market related insights on Alzheimer’s Disease, refer to our reports:
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Valo Health receives $110M Series B Cognito’s therapy slows Alzheimer’s disease Venty...
- GSK’s Covifenz; Idorsia’s Quviviq; GSK’s ZEJULA; EMA Expands its Nod for BMS, Eli Lilly, an...
- Genentech’s gantenerumab Fails in Phase III Trial; CHMP Recommends’ Dupixent; FDA Clears Imfinzi ...
- NOTIZIA
- Biogen seeks the FDA approval to revive its Alzheimer’s drug Aducanumab



