Obesity Treatment: Which Pipeline Therapy Will Revolutionize the Therapeutics Segment?
Mar 14, 2025
Table of Contents
Obesity is the second most common cause of preventable death, associated with the risk of developing inflammatory components, directly and indirectly, related to cardiovascular disease, diabetes mellitus, respiratory problems, psychological issues, hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, cancer, and hyperlipidemia. It imposes a significant public health epidemic that has progressively worsened over the past semi-centennial. An increase in obesity has been observed in children and adults of both genders and is prevalent in both developed and developing countries.
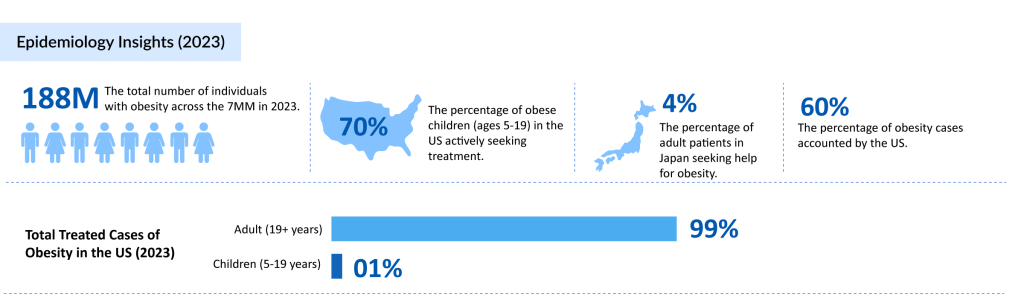
According to DelveInsight’s analysis, the total number of obesity cases across the 7MM reached ~188 million in 2023, with the United States accounting for ~144 million of these cases. Notably, around 70% of obese children aged 5-19 in the US were actively seeking treatment.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Management of Metastatic Obesity
A modern approach to obesity acknowledges the multifactorial determinants of weight gain and the health benefits of weight loss. Lifestyle change, diet, and increased physical activity are foundational to any weight loss effort. The approach should be a high-quality diet to which patients will adhere, accompanied by an exercise prescription describing the frequency, intensity, type, and time with a minimum of 150 min moderate weekly activity. Obesity medications approved in the USA or European Union are orlistat, naltrexone/bupropion, and liraglutide; in the USA, lorcaserin and phentermine/topiramate are also available. Surgical obesity management (gastric banding, sleeve gastrectomy, and Roux-en-Y gastric bypass) can produce remarkable health improvement and reduce mortality for patients with severe obesity.
Emerging Therapies for Obesity Treatment
The early-stage obesity pipeline has exploded with agents targeting multiple facets of the disease. In addition, there are new and innovative molecule types in the obesity pipeline, including monoclonal antibodies, antibody-drug conjugates, nanoparticle-drug conjugates, peptides, radiopharmaceuticals, recombinant proteins, and gene therapies, among others.
The drugs for obesity treatment are generally administered subcutaneously or orally. A few different strategies have also been utilized to administer a drug either intravenously or parenterally. Moreover, the significant rise in the obesity prevalence rate has led to a large patient population suffering from debilitating and chronic conditions that severely affect patient’s daily functioning and have severe implications for their mortality. This has led several prominent and emerging companies to engage in Research and Development initiatives to develop anti-obesity drugs.
Over 80+ key players, including the pharma giants such as Zealand Pharma, Sciwind Biosciences, Genexine, Sirnaomics, Sparrow Pharmaceuticals, Shionogi, Regor Pharmaceuticals, Innovent Biologics, Pfizer, NodThera Limited, Boehringer Ingelheim, Fractyl Health, TransThera, Clearmind Medicine, PegBio, Biolingus, and others evaluating their lead assets in different obesity clinical trials to improve the obesity treatment landscape.
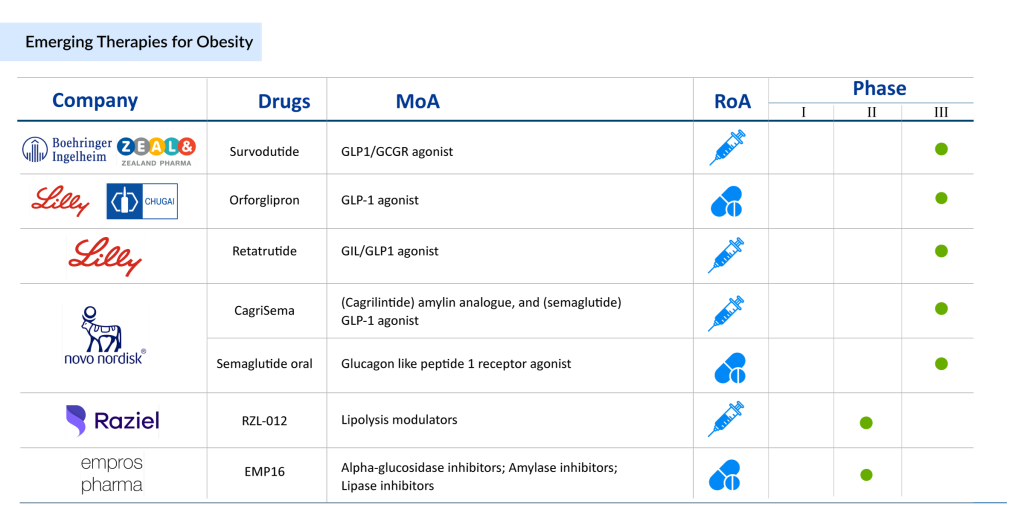
Some of the drugs for obesity treatment in the early and late stages of development include Semaglutide oral (Novo Nordisk), Tirzepatide (Eli Lilly and Company), Tesomet (Saniona), RZL-012 (Raziel Therapeutics), EMP16 (Empros Pharma), DD01 (D&D Pharmatech), ZP 8396 (Zealand Pharma), ERX-1000 (ERX Pharmaceuticals), Survodutide (Zealand Pharma), Ecnoglutide (Sciwind Biosciences), CT-868 (Carmot Therapeutics), DD01 (D&D Pharmatech), and others. Tirzepatide is a once-weekly GIP receptor and GLP-1 receptor agonist that combines the actions of both incretins into a single novel molecule. GIP is a hormone that may help GLP-1 receptor agonists work better. GIP reduces food intake while increasing energy expenditure in preclinical models, resulting in weight loss. When combined with GLP-1 receptor agonism, it may have a greater impact on metabolic dysregulation markers such as body weight, glucose, and lipids. Tirzepatide is currently in Phase III development for adults with obesity or overweight who have weight-related comorbidity, and the FDA is also reviewing it as a treatment for adults with type 2 diabetes. It’s also considered a possible treatment for non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) and heart failure with preserved ejection fraction (HFpEF).
CT-868 is a dual GLP-1 and GIP receptor modulator with a distinctive pharmacological profile, optimized for enhanced tolerability at the GLP-1 receptor. By combining the effects of GLP-1 and GIP, it promotes greater weight loss and improved glucose control. Administered once daily, CT-868 aims to maximize both efficacy and tolerability. This dual agonist was developed using Carmot Therapeutics’ chemotype evolution technology, as a peptide-small molecule hybrid compound designed to replicate the native GLP-1 hormone. In its Phase I trial, CT-868 showed strong pharmacodynamic activity across various clinical measures in overweight and obese healthy individuals, with a safe and generally well-tolerated profile. Carmot Therapeutics is now expanding the trials to include overweight and obese patients with type 2 diabetes, to assess further CT-868’s impact on glycemic control, weight loss, and tolerability. The drug is currently in Phase II development for the treatment of obesity.
In the United States, the European Union, and Japan, oral semaglutide is approved as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes under the brand name RYBELSUS. It is an analog of the naturally occurring hormone GLP-1 in the form of an oral GLP-1 RA. The company is currently developing a candidate for obesity treatment. The candidate is being evaluated in a Phase III trial to determine the drug’s safety and efficacy in subjects who are overweight or obese. In May 2023, Novo Nordisk announced positive results from its Phase III trial, OASIS 1, which successfully achieved its primary endpoint.
Recent Developments in Obesity Treatment Domain
- In February 2025, Eli Lilly launched 7.5 mg and 10 mg Zepbound (tirzepatide) vials for $499 through the Zepbound Self Pay Journey Program, alongside price reductions for 2.5 mg and 5 mg vials. These are available exclusively via LillyDirect Self Pay Pharmacy Solutions, offering direct savings outside of insurance.
- In February 2025, Amgen announced that the U.S. FDA had placed a hold on a study of the company’s early-stage obesity candidate, AMG 513, marking another potential setback in its efforts to enter the growing weight loss drug market. Amgen has provided limited information about the drug, including its mechanism of action.
- In January 2025, Novo Nordisk reported that a high dose of its obesity drug Wegovy led to greater weight loss than the approved regimen in a Phase III trial. However, the data also suggest that Eli Lilly’s rival GLP-1 drug Zepbound may still have an advantage over Wegovy.
- In January 2025, Verdiva Bio Limited launched as a clinical-stage biopharmaceutical company focused on innovative therapies for obesity and cardiometabolic disorders. The company is advancing next-generation oral and injectable treatments and raised $411M in an oversubscribed Series A round, co-led by Forbion and General Atlantic, with participation from RA Capital Management, OrbiMed, Logos Capital, Lilly Asia Ventures, and LYFE Capital.
- In January 2025, Eli Lilly filed a motion to intervene as a defendant in a case between the Outsourcing Facilities Association and FarmaKeio Custom Compounding against the FDA. The court has ordered the Outsourcing Facilities Association to respond by January 15, with Eli Lilly’s reply due by January 21.
- In Sept 2024, Immunis, Inc., a biotech firm focused on secretome therapeutics for age-related and immune disorders, received FDA approval to advance its Phase II clinical trial of IMMUNA, aimed at reversing sarcopenic obesity. This follows the completion of secretome treatments for its third patient cohort in a Phase I/IIa trial addressing age-related muscle atrophy.
- In Sept 2024, Terns Pharmaceuticals announced positive top-line results from its Phase 1 trial evaluating TERN-601 in healthy adults with obesity or overweight. The randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial assessed the safety, tolerability, pharmacokinetics (PK), and pharmacodynamics (PD) of once-daily dosing of TERN-601, showing promising results for this small-molecule treatment.
- In June 2024, researchers at Children’s Hospital of Philadelphia (CHOP) revealed mechanisms behind a molecule’s role in regulating insulin sensitivity, potentially paving the way for a new therapeutic target for obesity-related type 2 diabetes.
- In June 2024, Novo Nordisk and Eli Lilly dominated the obesity market, with Novo Nordisk generating $6.3 billion and Eli Lilly $2.3 billion in sales from their weight-loss drugs in Q1 2024.
- In June 2024, the US House Ways and Means Committee proposed a strategy for Medicare to cover GLP-1 weight-loss drugs like Wegovy and Zepbound.
- In June 2024, Zealand Pharma announced a share issuance to raise DKK 7 billion ($1 billion) to advance its obesity candidates.
- In June 2024, Form Health raised $38 million in a Series B round to accelerate its science-based obesity care initiatives and enhance its telehealth platform.
- In June 2024, Novo Nordisk announced a $4.1 billion investment to build a new factory in North Carolina to expand production of Wegovy and Ozempic.
- In June 2024, researchers found that the decline in coronary heart disease rates among people under 60 in the UK stalled, likely due to rising obesity rates.
- In June 2024, three studies presented at the ADA’s 84th Scientific Sessions showcased new data on drug therapy innovations for obesity, including insights on GLP-1 receptor agonists.
- In June 2024, Altimmune, Inc. presented data from its Phase II MOMENTUM trial of pemvidutide, a GLP-1/glucagon dual receptor agonist candidate, at the ADA’s 84th Scientific Sessions.
- In June 2024, Eli Lilly received NICE endorsement for tirzepatide in treating obesity, with some caveats for usage alongside diet and exercise changes.
- In May 2024, a study in the Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism assessed body fat percentage thresholds to define overweight and obesity, correlating with metabolic syndrome.
- In May 2024, Terns Pharmaceuticals announced senior management participation in a virtual chat at UBS Obesity Therapeutics Day.
- In May 2024, research at the European Congress on Obesity quantified the long-term health impact of childhood obesity on life expectancy.
What’s Ahead in the Obesity Treatment Market
To summarize, the clinical practice of obesity medicine has been difficult for both patients and providers. Weight management has progressed to the point where the development of some powerful tools is feasible. As a result, the emphasis can now shift from treating comorbidity with antihypertensives and lipid-lowering drugs to glycemic control drugs. Furthermore, gut hormones may be particularly promising candidates for future research because they have fewer non-specific side effects than centrally-acting drugs. It is hoped that current and future obesity drugs will provide safer and more effective tools for the long-term management of obesity. Currently, several obesity companies, such as YSOPIA Bioscience, Innovent Biologics, Glaceum, Shionogi, Aardvark Therapeutics, NuSirt Biopharma, Novartis,, and others, across the globe are developing obesity therapies. The introduction of new obesity treatments in the coming years will significantly improve the lives of people affected by obesity.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- FDA Approves LUMAKRAS with VECTIBIX for KRAS G12C-Mutated Colorectal Cancer; PYC Receives FDA Rar...
- Amgen to Acquire Horizon Therapeutics; Sanofi and Teva Announce Collaboration; Boehringer Obesity...
- Mobile Health Apps for Obesity Treatment: A Modern Solution to a Growing Problem
- Exploring the World of Anti-snoring Devices: A Comprehensive Market Assessment
- The Rise of Energy Drinks: Power in a Can or a Health Hazard?