Sickle Cell Disease Treatment: How Gene Therapy and Editing Could Transform Therapeutic Segment?
Dec 27, 2024
Table of Contents
Sickle cell disease is a hereditary blood disorder marked by abnormal hemoglobin, which leads to the deformation of red blood cells into a sickle shape. It is a major global health issue, especially common in individuals of African, Middle Eastern, Mediterranean, and South Asian descent.
Based on DelveInsight’s assessment in 2023, the total prevalent cases of SCD in the 6MM were nearly 177K. These cases are expected to increase by 2034. As per the estimates, the US accounted for approximately 54% of the total prevalent cases of SCD trait in the 6MM.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Development of Gene Therapies in Dermatology
- Is Gene Therapy the Next Cancer Treatment Revolution?
- EMA to relocate to Amsterdam; Roche’s prospects; Amgen’s Humira Biosimilar delayed; Purdue’s opio...
- AAV Vectors in Gene Therapy: How Recent Clinical Advances are Unraveling New Potentials?
- Watershed Moment for Cell Therapies and Complicated Journey of Gene Therapies in Japan
Sickle cell disease poses significant challenges for affected individuals, impacting their quality of life and life expectancy. Common complications include anemia, acute chest syndrome, stroke, organ damage (e.g., kidneys, liver), and increased susceptibility to infections.
CASGEVY and LYFGENIA — Market Leaders in Sickle Cell Disease Treatment
Gene therapy and gene editing techniques hold promise in correcting the underlying genetic mutation responsible for SCD. In December 2023, the FDA approvals of two gene therapies, Vertex/CRISPR’s CASGEVY, and Bluebird’s LYFGENIA offer the potential of a one-time transformative therapy for eligible patients with SCD.
CASGEVY is a genome-edited cellular therapy made from autologous CD34+ hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) that are modified using CRISPR/Cas9 technology. The editing occurs at the erythroid-specific enhancer region of the BCL11A gene. It is designed for a one-time treatment through a hematopoietic stem cell transplant, where the patient’s own CD34+ cells are altered to reduce BCL11A expression in erythroid lineage cells. This modification boosts the production of fetal hemoglobin (HbF), the oxygen-carrying form of hemoglobin naturally present during fetal development, which transitions to adult hemoglobin after birth. CASGEVY has shown potential in reducing or eliminating vaso-occlusive crises in patients with sickle cell disease.
In December 2023, Vertex Pharmaceuticals and CRISPR Therapeutics announced that the US FDA approved CASGEVY, a CRISPR/Cas9-edited cell therapy, for treating sickle cell disease in patients aged 12 and older with recurrent vaso-occlusive crises (VOCs).
Additionally, CASGEVY received conditional marketing authorization in Great Britain from the UK Medicines and Healthcare Products Regulatory Agency and in Bahrain from the National Health Regulatory Authority for patients 12 and older with sickle cell disease characterized by recurrent VOCs or transfusion-dependent beta-thalassemia (TDT). This approval applies to patients for whom hematopoietic stem cell transplantation is suitable but a human leukocyte antigen-matched related stem cell donor is unavailable.
LYFGENIA is a one-time, ex-vivo lentiviral vector gene therapy approved for treating patients aged 12 and older with sickle cell disease and a history of vaso-occlusive events (VOEs). It works by introducing a functional β-globin gene into the patient’s own hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs). Following successful engraftment, it allows for the durable production of adult hemoglobin with anti-sickling properties (HbAT87Q). HbAT87Q closely resembles wild-type HbA in oxygen-binding affinity, reduces red blood cell sickling, and has the potential to decrease VOEs.
Read our article “LYFGENIA or CASGEVY: Who Will Lead the Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Space?” and get a more detailed analysis
Potential Sickle Cell Disease Therapies on the Horizon
The sickle cell disease pipeline possesses some drugs in mid- and late-stage developments to be approved in the near future. The expected launch of therapies such as EDIT-301 (Editas Medicine), Inclacumab (Pfizer), Motixafortide (BiolineRx), Etavopivat (Novo Nordisk), Mitapivat (Agios Pharmaceuticals), and others shall further create a positive impact on the sickle cell disease treatment market.
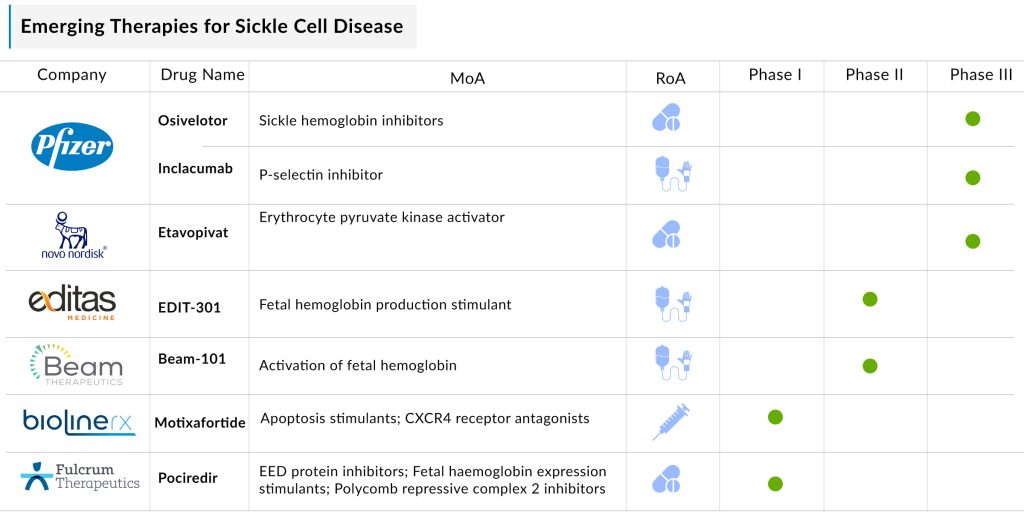
Additionally, the emergence of several mechanisms of action like, erythrocyte pyruvate kinase activator, cytidine deaminase (CDA) inhibitor, fetal hemoglobin production stimulant, DNA-dependent RNA polymerase inhibitor, and others will be expanding the treatment landscape of SCD.
Even though it is too soon to comment on the above-mentioned promising candidate to enter the market during the forecast period (2024–2034), it is safe to assume that the future of this market is bright. Eventually, the drug will create a significant difference in the landscape of sickle cell disease in the coming years. The sickle cell disease treatment space is expected to experience a positive impact in the coming years owing to the improvement in the rise in the number of healthcare spending across the world.
The European Hematology Association (EHA) 2024 Hybrid Congress: Key Highlights
Below are the potential sickle cell disease data readouts held at the 2024 EHA Hybrid Congress:
Key Developments in Sickle Cell Disease Treatment Space
- In October 2024, Kind Pharmaceutical (Hangzhou Andao Pharmaceutical Ltd. and Kind Pharmaceuticals LLC) announced that the FDA’s Office of Orphan Products Development has granted Orphan Drug Designation (ODD) to AND017 for the treatment of Sickle Cell Disease
- In September 2024, Pfizer voluntarily withdrew all lots of OXBRYTA for the treatment of SCD in all markets where it was approved. Pfizer is also discontinuing all active voxelotor clinical trials and expanding access programs worldwide.
- In March 2024, Pfizer discontinued one of its two Phase III studies evaluating the anti-P-selecting antibody inclacumab in sickle cell disease due to “poor accrual and associated recruitment challenges.”
- In February 2024, the European Commission granted conditional marketing authorization to CASGEVY for the treatment of patients who are 12 years of age and older with severe sickle cell disease.
- In December 2023, Editas Medicine announced new safety and efficacy data of EDIT-301 from the RUBY trial for severe SCD at the American Society of Hematology (ASH) annual meeting.
Sickle Cell Disease Treatment: What Lies Ahead?
Currently, the treatment of sickle cell disease involves NSAIDs, blood transfusions, chelating agents, nutritional supplements, and broad-spectrum antibiotics. Additionally, the US FDA has approved specific therapies for managing the condition, including DROXIA (hydroxyurea), ENDARI (L-glutamine oral powder), ADAKVEO (crizanlizumab-tmca), and OXBRYTA (voxelotor).
Enhancing care and outcomes for individuals with sickle cell disease requires a multidisciplinary approach. This includes access to comprehensive healthcare services, genetic counseling, early detection, and effective management of complications. Patient education and support programs play a vital role in empowering individuals to manage their condition and improve their quality of life.
Ongoing research and development efforts aim to discover new treatments and potential cures for sickle cell disease. Gene therapy and gene editing techniques show promise in addressing the underlying genetic mutation responsible for the condition. Clinical trials are actively evaluating the safety and efficacy of these innovative therapies, offering hope for a future where Sickle Cell Disease is either cured or effectively managed.
The disease poses a significant burden due to its life-threatening nature and the lack of effective treatment options. Until the last decade, hydroxyurea was the only available management option. However, despite its long presence in the market, challenges persist with low adherence to treatment and high discontinuation rates.
Delays in diagnosis, serious complications of sickle cell disease, economic burden, and lack of proper understanding of the disease will be going to hit the sickle cell disease market. As per DelveInsight analysis, in 2023, the total market size of sickle cell disease was approximately USD 650 million, which is expected to increase by 2034 during the study period (2020–2034) in the 6MM.
In conclusion, sickle cell disease is a complex genetic blood disorder characterized by abnormal hemoglobin, leading to complications and reduced life expectancy. However, advancements in treatment approaches and ongoing research efforts offer hope for improved management and potential cures. Enhancing healthcare services, raising awareness, and supporting individuals with sickle cell disease are essential steps toward addressing the challenges associated with this disease in the 6MM.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Biogen’s Aduhelm; FDA Approves Sanofi’s Enjaymo; NHS & Orchard Signs a Deal; Bri...
- EMA to relocate to Amsterdam; Roche’s prospects; Amgen’s Humira Biosimilar delayed; Purdue’s opio...
- AstraZeneca and Incyte Collaborate; Tocagen’s therapy; FDA warns companies;FDA Revokes
- Snippet
- VBL Therapeutics’ VB-111 (ofranergene obadenovec); BMS’s mavacamten (Camzyos); Merck’s KEYTRUDA; ...