Which Countries Top the Chart in Global Pharmaceutical Market?
Oct 27, 2021
Table of Contents
The Pharmaceuticals segment of the Healthcare Industry has a significant market across the globe, which has grown quite extensively in the past few decades. The pharmaceutical sector has always been at the forefront of drug discovery, development, production, and marketing. The pharmaceutical industry in the twenty-first century has come a long way since its beginnings in nineteenth-century pharmacies. Over the past few decades, the inclusion of biotechnology-based diagnosis and treatment has provided a considerable boost to the healthcare segment. Over time, the pharmaceutical market has evolved to include various domains, such as biotechnology, nanotechnology, and Artificial Intelligence, among others, to encompass a holistic approach to healthcare.
The advent of new technologies, better delivery mechanisms, faster diagnosis and curative treatments have opened many doors in healthcare innovation, providing Pharma/Biotech companies with a much-deserved push towards better business opportunities. As a result, these companies have built large empires and have contributed immensely to the growth of the Pharmaceutical and Biotechnology segment of the healthcare industry across the globe. Even though the healthcare market has grown in almost every region, there are still certain countries where innovation and development has a fast pace, along with efficient healthcare disbursement to patients. On this note, let’s take a look at the top pharmaceutical markets in the world.
Downloads
Article in PDF
1. United States Pharma Market
The pharmaceutical market in the US is by far the largest in the world in terms of drug development and production, revenue generation, global image, and acceptance, generating roughly 46% of total global revenue. The United States pharmaceutical market is highly globalized with many of the world’s leading pharmaceutical companies based in the country and has offices across regions and countries. Here, companies are developing some of the world’s most innovative drugs, which go on to become blockbusters in their therapy areas. The pharmaceutical sector in the United States is responsible for inventing and manufacturing some of the most inventive and best-selling pharmaceuticals in the world.
Healthcare spending and Pharmaceutical R&D in the US
In the United States, the total amount spent on the pharmaceutical market in 2020 is expected to be around USD 539 billion. Each year the US has been investing a lot in its pharmaceutical sector. The pharmaceutical market in the United States has made great strides in recent decades as a result of a greater emphasis on research and development (R&D). In 2020, the pharmaceutical industry in the United States spent approximately USD 91 billion on R&D. A new drug can take up to 15 years to develop and can cost up to USD 2.6 billion. In terms of total revenue, the United States pharmaceutical market is one of the largest investors in R&D.
Government support for pharma and policies
Every year, the pharmaceutical industry in the United States develops a slew of new drugs that provide significant medical benefits. Many of these drugs are costly, contributing to rising healthcare costs for both the private sector and the federal government. Policymakers have considered policies that would reduce drug prices and federal drug spending. Such policies would almost certainly reduce the incentive for the pharmaceutical industry to develop new drugs. The United States government’s plan to implement cost-cutting policies, as well as the government’s tightening of rules, such as the delay in the approval of complex generics and price erosion in the U.S. generics pharmaceuticals market, are expected to have an impact on the growth prospects of the U.S. pharmaceuticals market.
Top Pharmaceutical Companies
There are numerous thriving pharmaceutical firms in the United States. The US pharmaceutical sector is booming, accounting for about half of the global market. The United States pharmaceutical sector contributes so much that it is home to five of the top 10 pharmaceutical companies in the world. These companies are all multinationals, yet they operate from the United States. These companies are Johnson & Johnson, Pfizer, Merck & Co., AbbVie, Abbott Laboratories, Roche, Gilead Sciences, Amgen, and several others.
Pricing and Drug Launch Scenario
In the last ten years, revenue generated by drug production in the United States has more than doubled. The key to this high revenue is due to an increase in repeated price. Pharmaceutical companies consider a drug’s uniqueness, competition from other companies, and effectiveness when pricing their drugs. Prescription drug prices in the US are more than 250% higher than in 32 different countries. The US Food and Drug Administration plays a crucial role in developing any drug. The US FDA is very proactive and takes a variety of approaches to encourage the development of specific drugs, particularly those that may be the first available treatment for an illness or have a significant advantage over existing drugs.
Foreign Investment and Import Scenario
International companies operating in the United States help to sustain the American pharmaceutical industry through foreign direct investment (FDI). As per Bureau of Economic Analysis (BEA) data, international pharmaceutical companies’ investment in the United States has grown more than 500% over the last 10 years and reached USD 511 billion in 2019.
In addition, the United States is the world’s largest drug importer. As a result, much of America’s collective health is dependent not only on R&D through home-based Pharma and Biotech companies, but also on the relationships with other countries for providing the final drug therapy for patient use.
2. China Pharmaceutical Market
The Chinese pharmaceutical market is one of the world’s largest, and it is well on its way to becoming a global leader in drug innovation and development. Even as the COVID-19 crisis rages on, international investment in China’s pharmaceutical sector is increasing. The Chinese pharmaceutical market is expected to increase at a compound annual rate of 12% to USD 300.9 billion by 2025. At present, China constitutes 11% of the global pharmaceutical market. Furthermore, China’s healthcare industry’s rapid growth has allowed it to transition from a pharmaceutical manufacturing base to a strategic R&D hub.
Pharmaceutical R&D in China
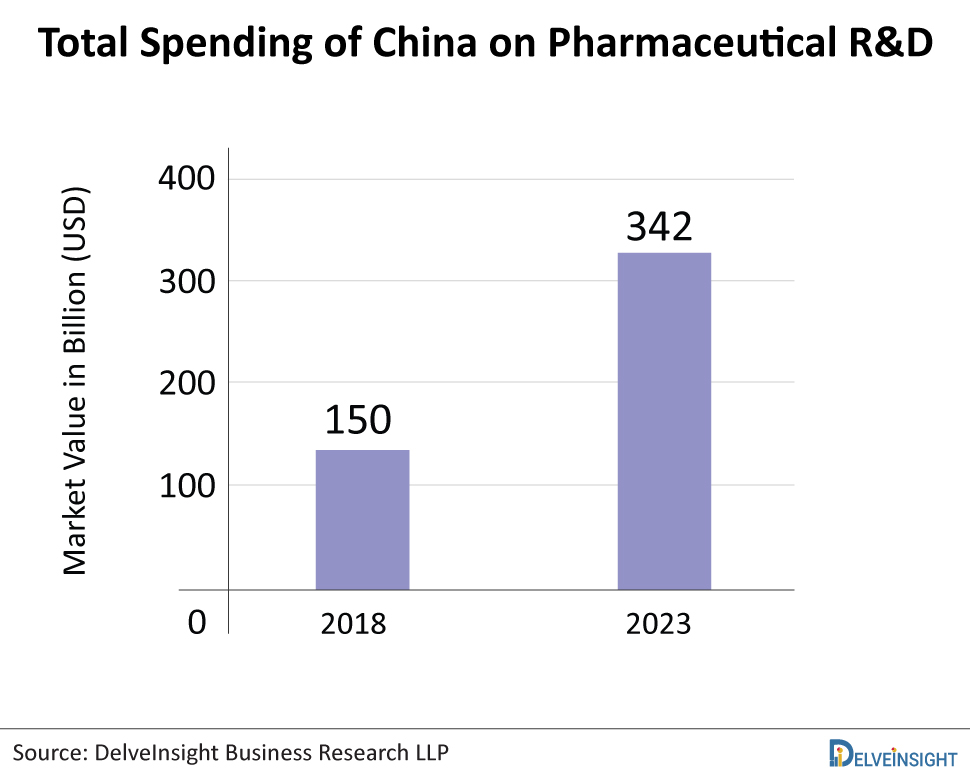
China has established itself as a strategic player in the global pharmaceutical market, both as a consumer country and as a platform for expanding R&D. Chinese pharmaceutical companies are primarily involved in the manufacture of generics, therapeutic drugs, active pharmaceutical ingredients, and traditional Chinese medicine. Generic drugs account for more than 90% of all drugs registered in China. By the end of 2019, China’s pharmaceutical R&D spending was estimated to be around USD 150 billion. It is estimated that the Chinese pharmaceutical industry’s total R&D spending will reach USD 342 billion by 2023, growing faster than the global average.
Government support for pharma and policies
The challenge for China is to promote growth in the pharmaceutical industry while ensuring affordable and easily accessible drugs for its patient population. In addressing this issue, the central government has emphasised a top-down approach. In addition to a significant investment, the government has made a number of significant reforms to the regulatory environment for pharmaceuticals. Both China’s 13th Five-Year Plan and the Healthy China 2030 plan stress the necessity of healthcare reforms including decreasing gaps in insurance coverage ranges and enhancing public services. Within the industry, reform attempts have tried to increase access to and affordability of medicine.
Top Pharmaceutical Companies

Over the last two decades, China’s pharmaceutical market has been one of the fastest-growing countries. Several leading pharmaceutical companies currently dominate the Chinese market, with rising revenues and a large market overvalue. The top pharmaceutical companies include Shanghai Pharmaceuticals, Sinopharm Group, Jiangsu Hengrui Medicine, Shanghai Fosun Pharmaceutical, Huadong Medicine, Yunnan Baiyao Group, Guangzhou Pharmaceutical, China Meheco, Harbin Pharmaceutical, and others.
Pricing and Drug Launch Scenario
The prices of drugs in China are comparatively lower than the other countries. This is due to China’s unique policies for primary healthcare institutions. In China, primary health care institutions are required to use only essential medicines, the prices of which are set by provincial centralised bidding, which means that the prices are set at the provincial level and are much lower. The National Medical Products Administration (NMPA) is China’s drug and medical device regulatory agency (formerly the China Food and Drug Administration or CFDA). It is responsible for creating laws and regulations for drugs, medical devices, and cosmetics, as well as the development of medical device standards and classification systems.
Foreign Investment and Import Scenario
The Chinese pharmaceutical market remains uncertain due to challenges with drug pricing and low levels of IP protection; China remains one of the most appealing investment destinations in the Asia Pacific region. The fact that China has many intrinsic advantages that position it favourably for continuing FDI flows into the pharmaceutical sector underpins this notion. A rapidly ageing population, a well-established pharmaceutical manufacturing business, and significant government investment in the sector’s development are among these factors.
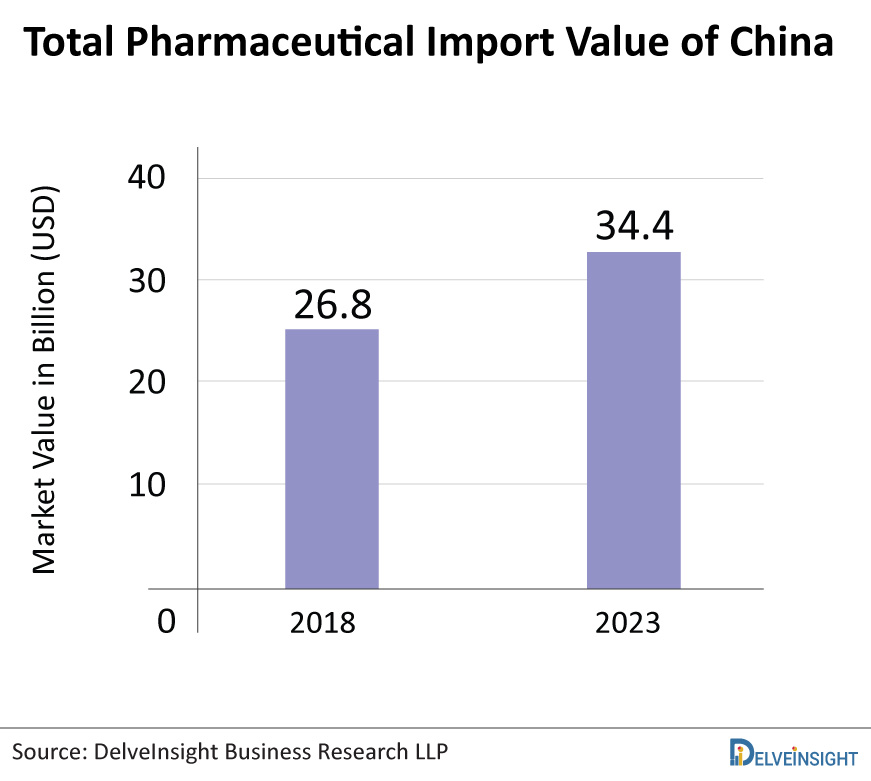
On the other hand, as Asia Pacific’s largest pharmaceuticals market, China offers a highly dynamic pharmaceutical trade environment. The value of China’s pharmaceutical import was USD 26.8 billion in 2018 and is expected to rise to USD 34.4 billion by 2023. China imports pharmaceuticals from around 50 different countries and regions. The majority of imports come from developed countries, and imported goods are high-end and expensive.
3. Japan Pharmaceutical Market
Japan is the first country to have a negative CAGR as a result of its price-cutting policies. Japan’s total growth is expected to be the slowest among developed markets, with a negative CAGR ranging from -3 to 0% in 2020-24, while global growth is expected to be positive between 3 and 6% during the same period. Despite the challenging pricing environment, the Japanese pharmaceutical market is expected to remain the third largest and most important destination for the US and foreign innovative biopharmaceutical companies due to the ongoing demand for novel therapies.
R&D in Pharmaceutical in Japan
Japan’s pharmaceutical market has faced significant challenges in recent years as a result of increased competition and a complex market. Companies have discovered that developing blockbuster drugs is becoming increasingly difficult. As a result, generic drugs are rapidly gaining market share in progressively shorter time frames. As the industry strives to consolidate quickly, rising pricing pressure has also impacted large-scale investment in R&D projects. In 2019, Japanese pharmaceutical manufacturing companies spent approximately 1.3 trillion Japanese yen on research and development (R&D). This amounted to roughly 10% of the industry’s total sales that year.
Read more about the Pharma R&D in Japan @ Japan Healthcare Outlook
Government support for pharma and policies
In recent years, Japan’s pharmaceutical market has grown at a slow pace. Pharmaceutical companies have found it challenging to introduce new innovative products due to a complex regulatory and pricing process and regular price cuts. In 2014, the Japanese government passed the Safety of Regenerative Medicine Act and revised the Pharmaceutical and Medical Device Act (PMD Act). This has increased the number of regenerative medicine product approvals in the country. Furthermore, the government has launched several initiatives to encourage foreign companies to invest in regenerative medicine.
Top Pharmaceutical Companies

In Japan, there are numerous pharmaceutical companies to collaborate with. There were over 500 pharmaceutical/biotech companies in Japan 20 years ago. This number has been reduced to 100 due to mergers and acquisitions, but the opportunities for collaboration remain vast. The leading pharmaceutical players currently dominating the Japanese pharmaceutical market are Takeda Pharmaceuticals, Daiichi Sankyo, Astellas Pharma, Otsuka, Mitsubishi Tanabe Pharma, and many more.
Pricing and Drug Launch Scenario
The drug review, approval, and all the activities are monitored by the Pharmaceuticals and Medical Devices Agency (PMDA) in Japan. It is working together with the Ministry of Health, Labour, and Welfare. Drug prices are constantly under pressure to be lowered as a result of wholesaler rivalry, and the resultant market price is reflected in the biennial price revision. Off-year price revisions in Japan will occur from April 2021, but their influence on total market value will be smaller than that of complete biannual revision. The following are the estimated price impacts:
Price revisions every two years (even years 2022 and 2024): -5.3 to -6.3%
Price changes in the ‘off-year (odd years 2021 and 2023): -4.0 to -5.0%
As Japan is the only mature pharma market with a likely negative CAGR growth, the government is now evaluating and revising drug prices every other year. This process has resulted in price cuts of up to 7%.
Foreign Investment and Import Scenario
Japan has come out as one of the most desirable markets for pharmaceutical companies to invest in because of its reward for innovation policy. Outward foreign direct investment (FDI) from Japan in the chemicals and pharmaceuticals industries was worth USD 10 billion in 2020. FDI in the chemicals and pharmaceuticals industries totalled approximately USD 42 billion in the previous year.
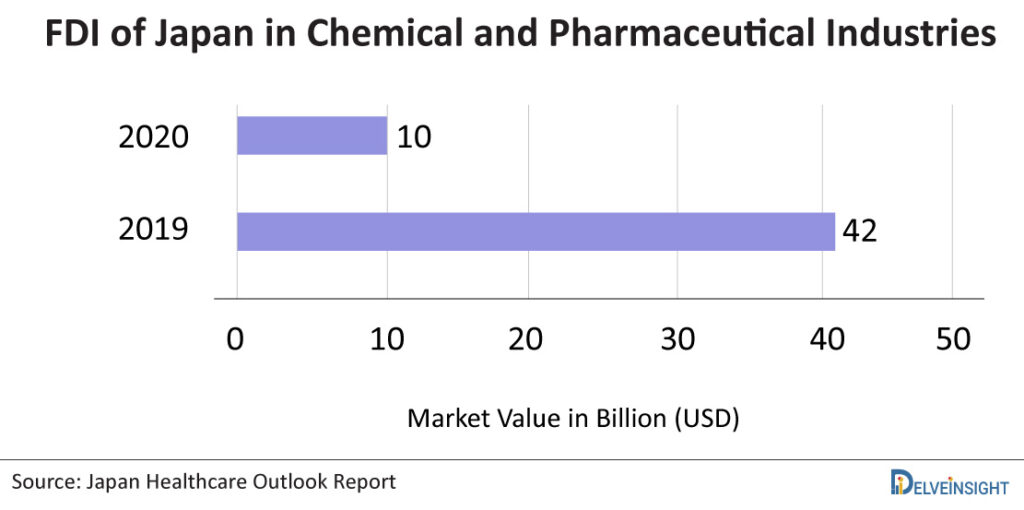
Furthermore, despite being one of the world’s largest medical producers, Japan is heavily reliant on pharmaceutical imports. As of 2019, Europe was Japan’s largest supplier of pharmaceuticals, accounting for nearly two trillion Japanese yen of total import value. Germany and the United States are the largest suppliers of pharmaceutical drugs and products in Japan, followed by several European countries such as Switzerland, France, and Belgium. The value of pharmaceutical drug imports to Japan in 2019 was nearly 2.8 trillion Japanese yen, an increase from approximately 2.5 trillion yen in 2011.
4. Germany Pharmaceutical Market
Germany is Europe’s largest pharmaceutical market and the world’s fourth-largest. Germany has a single-payer, universal healthcare system. It includes both statutory health insurance for those earning less than a set wage and private health insurance for those making more and choosing to buy their own. The global pharmaceutical market’s revenue climbed by 5.7% in 2019, reaching 46.4 billion Euros. The pharmacy section accounted for about 86% of revenue, while the clinic segment accounted for 14%.
Pharmaceutical R&D in Germany
Germany’s healthcare budget has steadily climbed since 2002. In 2018, Germany’s healthcare spending totalled 390 billion euros. This was a 15-billion-euro increase over the previous year’s healthcare spending. On the other hand, Germany also provides the best suitable environment for developing and producing research-intensive, high-grade products. In 2019, Germany spent a significant amount of money on research and development in the phases of pharmaceutical medication development. The majority of R&D spending (47.4%) is spent on clinical studies, ranging from phase one through phase three.
For more insights into healthcare spending and R&D, visit Germany Healthcare Outlook Report
Government support for pharma and policies
Germany offers ready access to a stable market of healthcare consumers and a transparent and evenly distributed expenditure system. The German healthcare system is supported by the government as well as private contributions. The public system is primarily supported by contributions in the form of payroll taxes paid by both employers and employees, with the remainder coming from government subsidies. The federal government has broad regulatory powers over health care in Germany’s legal framework, although it is not directly involved in care delivery. The Federal Joint Committee, which reports to the Federal Ministry of Health, decides which sickness funds cover services. Coverage decisions are based on data from comparative effectiveness analyses and health technology (benefit-risk) assessments to the extent possible.
Top Pharmaceutical Companies
There are numerous pharmaceutical companies that are working in the German pharmaceutical market. Some of the key players involved in the domain include Boehringer Ingelheim, Bayer, Helios Kliniken GmbH, TÜV NORD Group, Symrise AG, Sandoz International GmbH, Evotec AG, Fresenius AG, and others.
Pricing and Drug Launch Scenario
Germany’s approach to drug pricing is self-regulated by insurance, providers, and patient advocacy groups. However, it is overseen by the Federal Ministry of Health and state and federal parliamentary committees. Positive incentives (such as immediate coverage and the ability to obtain total list price for the first year after launch) and negative incentives (such as mandatory arbitration when price negotiations fail) are used in Germany to encourage manufacturers to moderate the prices of innovative drugs. As a result, the prices of drugs in Germany are lower than in other countries.
Furthermore, medicinal products in Germany must be approved by a higher federal authority (BfArM or PEI, depending on the drug). In addition to the favourable assessment by the appropriate ethical commission, this approval is required. The European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA) or European Medicines Agency (EMA) also monitors all the drug-related activities in Germany.
Import Scenario
There are several countries such as Switzerland, the United States, Ireland, Netherlands, France, Italy, Spain, and many more from where Germany is importing pharmaceutical products. Out of all the countries, Switzerland came out as the top pharmaceutical supplier for Germany in 2019, with an import value of almost 12 billion euros.
5. France Pharmaceutical Market
The French pharmaceutical sector is expanding in a highly competitive international setting and in a highly innovative and dynamic manner. France is the global leader in pharmaceutical production due to its consistent study growth, highly skilled workforce, famous industrial know-how, and capacity to respond to changing business needs. After Germany, France is the second-largest pharmaceutical market in the European region. In 2018, the French pharmaceutical market’s total revenue was close to 56 billion euros globally. France has an ageing population, which is resulting in new needs and opportunities in the pharmaceutical industry.
Pharmaceutical R&D in France
France is at the forefront of drug development innovation. Original, innovative, high-quality biomedical research and its quick application to diagnosis, therapy, healthcare, and public health are driving forces in the French pharmaceutical market. The French pharmaceutical market invests 12% of its revenue in R&D. Since 1980, the percentage of total health spending has risen in France. In 2018, healthcare spending in France accounted for 11.2% of France’s GDP. In addition, French pharmaceutical companies spent more than 1.4 billion euros on R&D outsourcing in the same year.
Get more details on France pharmaceutical industry @ France Healthcare Outlook
Top Pharmaceutical Companies

France has had several leading players operating and dominating the pharmaceutical market for many years. The key players in the French pharmaceutical market include Sanofi, Servier, Ipsen, Pierre Fabre, Supersonic Imagine, Mauna Kea Technologies, Lyonbiopôle. Rhône-Alpes, Medicen. Paris Région, Alsace BioValley. Alsace, Nutrition Health Longevity. Nord Pas de Calais, and many more.
Pricing and Drug Launch Scenario
The pharmaceutical cost-control plan in France is divided into two parts. First, the government enters into contracts with pharmaceutical companies to purchase new pharmaceuticals at a cost that represents their increased therapeutic value. Second, it employs a budget cap to keep drug spending in national health insurance (NHI) in check. In France, VAT is charged at 2.1% for prescription medicines and 5.5% for non-prescription drugs, compared to a regular rate of 18.6%.
Furthermore, the National Agency for the Safety of Medicines and Health Products (Agence Nationale de Sécurité du Médicament et des Produits de Santé, or ANSM) in France oversees all processes from drug development through launch. In addition, the European Medicines Evaluation Agency (EMEA) also monitors all the drug-related activities in France.
Import Scenario
The French pharmaceutical market is dependent on many countries, and they import various pharmaceutical products from other countries. In 2019, France imported pharmaceutical products worth 18.3 billion euros, up 5.3% from the previous year. The majority of these imports were from Germany (16.4%), the United States (15.2%), Ireland (14.5%), and Switzerland (10.4%).
Way Ahead
Several pharmaceutical companies operate in the pharmaceutical sector; some are well-established behemoths, while others are still emerging. The United States pharmaceutical market has been leading for a long time and contributing a massive revenue to the global pharmaceutical revenue. However, China’s pharmaceutical market is not so far behind the United States. The Chinese pharmaceutical landscape is looking at promising new healthcare reforms in the upcoming years as the Chinese government seeks to provide quality healthcare to its growing population. It will soon surpass the United States pharma market if the trend remains the same. The pharma companies are also continuing to grow through collaborations and mergers, resulting in a boom in buyouts and spin-offs in the pharmaceutical market. Nonetheless, pharma companies are expected to thrive across all the pharma markets owing to the rising demand for effective and standard healthcare. The innovative pharmaceutical developments are paving the way for several developing countries such as Israel, Brazil, India, and others to improve their pharma market and emerge as leading pharma countries. Israel is focussing more on its R&D while Brazil is emerging as a hotspot for pharmaceuticals. On the other hand, India is the world’s largest supplier of generic drugs. As a result, India has the potential to become one of the top ten countries in terms of medical spending in the upcoming years.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Infectious Disease and Vaccines Pipeline Reports
- Top 7 Pharma Industry Leaders in 2020 By the Numbers
- Cellectis successfully bags USD 164 million for Gene-editing and CAR-T programs
- ASH 2022 Annual Meeting – Insights Into Major Diffuse Large B-cell Lymphoma (DLBCL) Abstrac...
- The Current Scenario for Interstitial Cystitis(IC)