Evaluation of Rapidly Evolving Parkinson’s Disease Therapeutic Market
Jan 06, 2025
Table of Contents
What is Parkinson’s?
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects movement and coordination. It is a condition caused by the gradual loss of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain, leading to symptoms such as tremors, rigidity, bradykinesia (slowness of movement), and postural instability. As the disease progresses, non-motor symptoms like cognitive decline, mood changes, and sleep disturbances may also emerge.
The progression of Parkinson’s disease is categorized into five stages, ranging from mild symptoms that minimally impact daily life (Stage 1) to severe impairment requiring full-time care (Stage 5). Understanding these stages is crucial for managing treatment and improving quality of life.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Dengvaxia study; Opdivo racks up; FDA issues plant; Teva’s Rimsa fraud; Mission bags Fox grant
- Intensity Therapeutics Publishes Compelling Clinical Data for INT230-6 in Advanced Cancers; UCB W...
- Wireless Brain Sensors: Revolutionizing Neuroscience and Healthcare
- Evolving Landscape of Multiple System Atrophy Treatment: Recent Developments and Future Directions
- Decoding Parkinson’s Diagnosis with Gene Therapies and Prevention Insights
Life expectancy for Parkinson’s disease patients varies, often influenced by the individual’s age, overall health, and the timeliness of treatment interventions. With advancements in medical care and therapy, many patients can manage their symptoms effectively and maintain a good quality of life for years after diagnosis.
Addressing the Parkinson’s disease therapeutic market is vital to improving patient care and quality of life as the disease progresses. With rising prevalence due to aging populations, there is a growing need for innovative treatments that target both motor and non-motor symptoms. Advancing therapies, including disease-modifying options and personalized medicine, not only enhances patient outcomes but also alleviates economic and caregiving burdens, making this a crucial focus for healthcare and research.
Causes and Risk Factors
The exact cause of Parkinson’s disease remains unclear, but a combination of genetic and environmental factors is believed to play a role. Genetic mutations, such as in the LRRK2 or SNCA genes, may increase susceptibility, while environmental exposures to toxins like pesticides are linked to a higher risk. Age is a significant risk factor, as Parkinson’s is most commonly diagnosed in individuals over 60. Other contributors include a family history of the disease, male gender, and certain lifestyle factors such as prolonged exposure to heavy metals.
Symptoms and Progression
Parkinson’s disease progresses through distinct stages, starting with subtle symptoms like mild tremors and slowness of movement. As it advances, motor symptoms worsen, and patients may experience significant challenges with balance, coordination, and mobility. Non-motor symptoms, including depression, anxiety, and autonomic dysfunction, often become more prominent in later stages. The progression rate varies, with some patients experiencing slow deterioration while others face rapid decline. Early recognition and management are essential to improving long-term outcomes.
Diagnosis
Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease can be challenging, especially in its early stages, as symptoms often overlap with other neurological conditions. There is no definitive test for Parkinson’s, so clinicians rely on medical history, symptom evaluation, and physical examinations. Advanced imaging techniques, such as dopamine transporter (DAT) scans, can support the diagnosis but are not always conclusive. Accurate diagnosis requires a comprehensive approach involving neurologists and movement disorder specialists to ensure timely intervention.
Epidemiology of Parkinson’s Disease
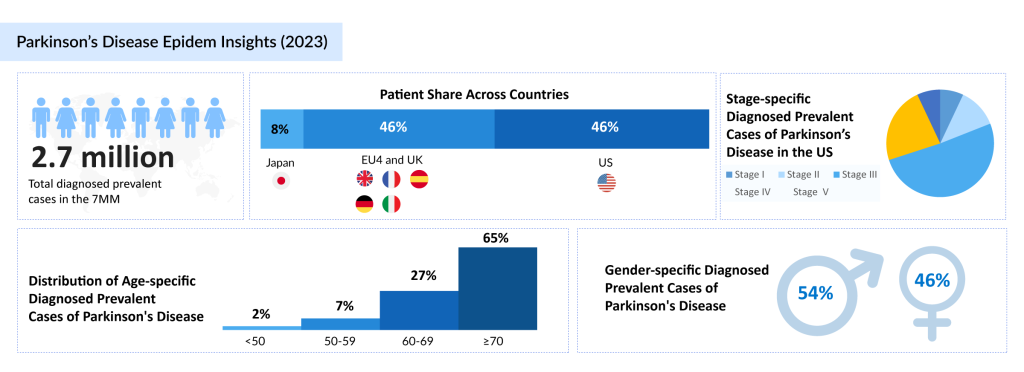
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that affects nearly 10 million people globally. It is the second most common neurodegenerative disease after Alzheimer’s. The average onset of Parkinson’s is around 60 years of age, though early-onset Parkinson’s occurs in about 10-15% of patients, typically before the age of 50.
In 2023, there were an estimated 2.7 million diagnosed prevalent cases of Parkinson’s disease across the 7MM. The United States accounted for 45% of these cases, while Japan and Germany contributed 9% and 18%, respectively. The disease shows a slight male predominance, with 54% of cases being male and 46% female in the 7MM. In Japan, Stage III Parkinson’s disease contributed the highest number of diagnosed prevalent cases in 2023.
Current Treatment Landscape
The treatment of Parkinson’s disease revolves around both pharmacological and non-pharmacological approaches aimed at managing symptoms and improving the quality of life for individuals affected by the condition. Though treatments do not address the underlying cause of neuronal loss, they significantly alleviate motor and non-motor symptoms.
Established Therapeutic Approaches
The management of Parkinson’s disease primarily involves medications that help manage the motor symptoms. The most common and effective pharmacological approach is levodopa. It is often combined with other drugs such as MAO-B inhibitors, COMT inhibitors, amantadine, and anticholinergics. These medications work by either increasing the availability of dopamine or by affecting other neurotransmitters involved in movement control. These treatments help alleviate the hallmark symptoms of Parkinson’s, including tremors, rigidity, and bradykinesia.
Surgical Interventions
For individuals whose symptoms become resistant to medication or who experience severe motor fluctuations, surgical interventions like Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) offer promising alternatives. DBS involves implanting a device that sends electrical impulses to specific areas of the brain, helping reduce motor symptoms such as tremors and rigidity. Additionally, levodopa-carbidopa enteral suspension, delivered via a pump, can be used for individuals experiencing “off” periods, where their symptoms return or worsen as their medication wears off.
Lifestyle and Supportive Therapies
Non-pharmacological treatments play an important role in enhancing the overall well-being of Parkinson’s patients. Regular exercise is crucial as it helps with mobility, balance, and motor function. Physical therapy focuses on improving movement, posture, and flexibility. Speech therapy is vital for patients dealing with voice, swallowing, and communication difficulties. Occupational therapy helps individuals adapt to daily tasks and maintain their independence for as long as possible.
Recent Developments in Parkinson’s Treatments
Several FDA-approved therapies are available that aim to improve both motor and non-motor symptoms of Parkinson’s disease. XADAGO, DUOPA/DUODOPA, INBRIJA, and ONGENTYS are among the key treatments used to enhance patients’ quality of life.
In 2024, there were significant advancements in Parkinson’s treatment. In August, the US FDA approved CREXONT extended-release capsules for the treatment of Parkinson’s disease. This innovative treatment combines immediate-release (IR) granules and extended-release (ER) pellets to provide sustained release of carbidopa and levodopa, helping to control motor symptoms. In February 2024, it was also licensed to Zambon Biotech for distribution in Europe.
In October, AbbVie received FDA approval for VYALEV (foscarbidopa/foslevodopa), a treatment for motor fluctuations in advanced Parkinson’s patients. This marked the introduction of the first continuous 24-hour subcutaneous infusion of a levodopa-based therapy. Meanwhile, PRODUODOPA, another infusion therapy developed by AbbVie for advanced Parkinson’s, was launched in the EU in January 2024. However, the FDA issued a Complete Response Letter (CRL) for PRODUODOPA in June 2024, indicating regulatory challenges in the US.
Additionally, XADAGO (safinamide), marketed by Newron Pharmaceuticals and others, is an MAO-B inhibitor used with levodopa to treat “off” episodes in Parkinson’s patients. It is available in the US and Europe as XADAGO and in Japan as EQUFINA.
Additionally, Sunbird Bio introduced new diagnostic technology in November 2024, showing promising results in detecting aggregated alpha-synuclein proteins, a biomarker linked to Parkinson’s, with 86% accuracy. This offers potential for early diagnosis, which is critical for managing the disease effectively.
While current treatments provide symptomatic relief, there remains a need for therapies that slow or stop the progression of Parkinson’s disease, making continued research into innovative therapies crucial for the future.
For a detailed overview of the marketed drugs in Parkinson’s disease treatment, click here.
Pipeline Therapies for Parkinson’s Disease
The pipeline for Parkinson’s disease (PD) treatment is rapidly advancing, with a focus on new drug candidates, gene therapies, and innovative surgical techniques. Various emerging therapies are in different stages of clinical development, from preclinical to Phase III, aiming to address both motor and non-motor symptoms and potentially modify the disease course.

Emerging Drug Candidates
Several promising drug candidates are currently under investigation. Buntanetap (Annovis Bio) targets neurodegeneration by inhibiting neurotoxic proteins like amyloid beta, tau, and alpha-synuclein. This drug is in Phase III trials for Parkinson’s disease. Tavapadon (Cerevel Therapeutics), a selective D1/D5 receptor partial agonist, aims to balance motor control while reducing side effects like dyskinesia. It is in Phase III trials and has shown encouraging results. Prasinezumab (Roche), a monoclonal antibody targeting alpha-synuclein, is in Phase II trials and has demonstrated the potential to reduce neurodegeneration. Risvodetinib (Inhibikase Therapeutics), an oral small molecule targeting Abl kinase, is designed to halt and potentially reverse Parkinson’s disease progression by restoring neuroprotective mechanisms. This drug is currently in Phase II trials.
Explore in-depth insights on each promising drug in the Parkinson’s Disease treatment pipeline, along with the latest updates on their clinical trials and advancements. Discover the most innovative therapies shaping the future of Parkinson’s care.
Gene and Stem Cell Therapies
Gene and stem cell therapies represent the cutting edge of Parkinson’s disease treatment. GT-02287 (Gain Therapeutics), a small molecule targeting GCase for GBA1-PD, is currently in Phase I trials. Another promising candidate, NNI-362 (Neuronascent), focuses on neuron regeneration, showing potential for restoring lost neurons in chronic neurodegenerative disorders, including Parkinson’s disease.
Discover the exciting potential of Cell and Gene Therapy in Parkinson’s disease treatment in our newly curated, in-depth blog! Don’t miss out on the future of Parkinson’s care.
Innovations in Surgical Techniques
While drug therapies continue to dominate the Parkinson’s treatment landscape, surgical interventions like Deep Brain Stimulation (DBS) remain a key option for patients with advanced disease, particularly when medications are no longer effective. In addition, new devices like the SPN-830 apomorphine infusion pump are being developed to deliver continuous treatment for motor fluctuations in PD patients. This device has shown potential for improving quality of life by reducing “off” episodes. The continuous innovation in the Parkinson’s disease therapeutic pipeline promises more effective treatments, better management of symptoms, and potential disease-modifying therapies for patients.
Are you curious about the groundbreaking progress of risvodetinib in Parkinson’s disease treatment? Dive into our latest blog to explore the exciting Phase II trial results, patient enrollment updates, and promising data that could revolutionize Parkinson’s care. Don’t miss out – read more now!
Advancements in Parkinson’s Disease Diagnostics
Parkinson’s disease diagnosis is complex and largely clinical, relying on the patient’s medical history, symptoms, and neurological evaluations. The absence of a definitive diagnostic test complicates early detection, with many patients misdiagnosed or diagnosed in later stages of the disease. However, recent advancements in diagnostic tools and biomarkers are improving early detection and providing more accurate assessments of Parkinson’s disease.
Biomarker Discovery
One of the most significant areas of research in Parkinson’s disease diagnostics is biomarker discovery. While no singular biomarker for Parkinson’s has been validated, several potential biomarkers are being investigated. One promising discovery comes from Sunbird Bio, which released data in November 2024 demonstrating that their diagnostic technology successfully classified blood samples from Parkinson’s patients with 86% accuracy by detecting aggregated alpha-synuclein proteins. These findings indicate that blood-based biomarkers could play a key role in diagnosing Parkinson’s disease and tracking disease progression.
Role of Artificial Intelligence and Imaging Techniques
Advancements in imaging technologies and artificial intelligence (AI) are also making significant contributions to Parkinson’s diagnostics. Imaging techniques like DaTscan, a dopamine transporter scan, are already being used to assess dopamine levels and help confirm the diagnosis by identifying reduced dopamine transporter activity in the brain. Other neuroimaging techniques, such as MRI, PET scans, and SPECT, are being utilized to differentiate idiopathic Parkinson’s disease from other parkinsonian disorders. Additionally, AI applications in analyzing neuroimaging data are improving the accuracy and speed of diagnosis. AI algorithms can assist in detecting subtle changes in the brain that may indicate early-stage Parkinson’s disease, enhancing early diagnosis.
Early Detection Initiatives
Detecting Parkinson’s disease early is crucial for slowing disease progression and improving outcomes. Efforts to improve early detection are centered around understanding the genetic and environmental risk factors of the disease, which can inform targeted diagnostic screenings. These advancements are critical as they could help detect Parkinson’s disease before significant neuronal damage occurs, allowing for earlier intervention and treatment.
The continuous development of biomarker-based diagnostics, AI-enhanced imaging techniques, and early detection initiatives are revolutionizing Parkinson’s disease diagnosis. These advancements can potentially improve diagnosis accuracy, reduce misdiagnoses, and provide timely interventions, ultimately enhancing patient outcomes and quality of life.
Learn more about the latest in Parkinson’s disease diagnostics and stay updated with new advancements—visit our blog for detailed insights and comprehensive updates!
Preventive Strategies for Parkinson’s Disease
Parkinson’s disease (PD) is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder that primarily affects movement. While there is currently no cure for Parkinson’s, adopting preventive strategies can help reduce the risk or delay the onset of the disease. These strategies focus on lifestyle modifications, proper nutrition, exercise, and advancements in neuroprotection research.
Lifestyle Modifications
While genetics play a key role in Parkinson’s disease, lifestyle factors also contribute significantly to its onset and progression. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle can reduce the risk of developing Parkinson’s. For instance, individuals are encouraged to quit smoking, limit alcohol consumption, and manage stress. Engaging in mentally stimulating activities, such as reading, learning new skills, or practicing mindfulness, can help keep the brain active and reduce the risk of neurodegenerative diseases. Social engagement is also crucial, as it has been shown to improve mental health and cognitive function, which can potentially delay the onset of Parkinson’s symptoms.
Role of Nutrition and Exercise
A balanced diet and regular physical activity are fundamental to overall health and have been shown to play a role in the prevention and management of Parkinson’s disease. A Mediterranean-style diet, rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and healthy fats, may provide neuroprotective benefits. Additionally, ensuring adequate intake of omega-3 fatty acids, antioxidants, and vitamin D has been linked to a reduced risk of developing PD.
Exercise is equally important, as it helps maintain motor function, balance, and flexibility. Aerobic exercises like walking, swimming, or cycling, as well as strength training and activities like yoga and tai chi, have been shown to improve the quality of life for Parkinson’s patients and may even delay disease progression. Exercise improves dopamine production, which is essential for motor control, and can help counteract the physical symptoms of Parkinson’s disease.
Advances in Neuroprotection Research
Neuroprotection research aims to discover treatments that can protect or even repair the neurons that are damaged or lost in Parkinson’s disease. While this area of research is still in its early stages, promising results are emerging. Current studies focus on understanding the underlying mechanisms of neurodegeneration in PD and identifying therapies that can slow or halt this process.
One of the promising areas of neuroprotection research is the exploration of drugs that target oxidative stress, inflammation, and mitochondrial dysfunction – factors believed to play a role in the death of dopamine-producing neurons. Additionally, gene therapy and stem cell treatments hold potential for future Parkinson’s treatments, as they could help regenerate damaged neurons or replace lost dopamine-producing cells.
Market Analysis of Parkinson’s Disease Therapeutics
Current Market Overview
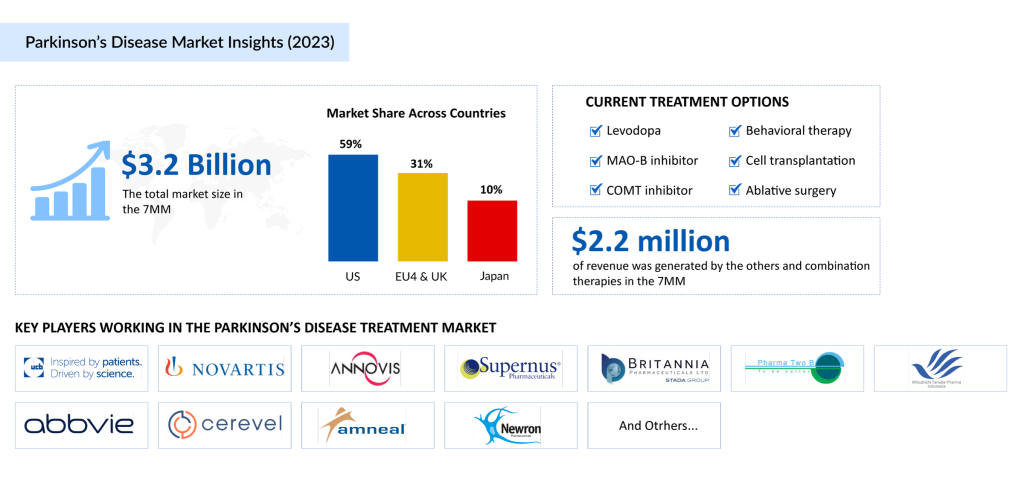
The Parkinson’s disease therapeutics market is set to experience steady growth from 2024 to 2034, driven by advancements in diagnostics, increased awareness, and the rising prevalence of the condition. The Parkinson’s disease market in the 7MM was valued at approximately USD 3.2 billion in 2023 and is expected to grow significantly during the forecast period.
Parkinson’s disease is a progressive neurodegenerative disorder with unclear causes, characterized by motor and non-motor symptoms. Its growing global burden is primarily due to an aging population and environmental factors. Diagnosing Parkinson’s disease remains challenging, with imaging technologies like PET scans assisting in distinguishing it from other movement disorders.
Key Players and Competitive Landscape
A few key players, including Amgen, AbbVie, and Supernus Pharmaceuticals dominate the Parkinson’s disease treatment landscape. Despite significant advancements in pharmacological treatments such as carbidopa/levodopa, there remains a gap for more innovative and disease-modifying therapies. New formulations, like CREXONT and RYTARY, are adding value, but the search for better treatments continues.
The market is also witnessing the emergence of late-stage drugs targeting a-synuclein pathology, which is considered a key driver of neurodegeneration in Parkinson’s disease. Companies like Supernus Pharmaceuticals, AbbVie, and Pharma Two B are leading the charge with their promising therapies, such as SPN-830, tavapadon, and P2B001.
Market Trends and Opportunities
As the Parkinson’s disease market continues to grow, opportunities for pharmaceutical companies are vast. There’s an increasing demand for disease-modifying therapies and treatments aimed at alleviating motor symptoms like tremors, rigidity, and gait issues. The success of drugs that can target the root causes of neurodegeneration, such as a-synuclein, presents substantial growth potential. In addition to pharmaceutical treatments, regenerative therapies like stem cell and gene therapies are showing promise for disease modification.
Economic Impact and Funding Dynamics
The economic impact of Parkinson’s disease is significant, with a growing burden on healthcare systems globally. As treatment options evolve, the cost of care and funding dynamics will play a critical role in shaping the market. Continued investment in research and development is essential for bringing innovative therapies to market, and regulatory support will be crucial for expediting approvals of new treatments.
But that’s just the tip of the iceberg—there’s so much more happening beneath the surface! From cutting-edge therapies to market shifts, explore all the latest trends, opportunities, and insights driving the future of Parkinson’s disease treatment. Don’t miss out on what’s shaping this rapidly growing sector.
To truly understand the evolving dynamics of the Parkinson’s disease market, click here.
Future Directions in Parkinson’s Disease Management
The future of Parkinson’s disease management is poised for transformative change, driven by an increased focus on understanding and targeting the root causes of neurodegeneration. As current therapies primarily address symptom relief, there is a significant opportunity for pharmaceutical companies to develop novel treatments that slow or potentially halt the progression of the disease. By targeting mechanisms such as alpha-synuclein aggregation, mitochondrial dysfunction, and neuroinflammation, we are edging closer to the possibility of disease-modifying therapies. Innovations in drug delivery systems, including brain-penetrant small molecules and gene therapies, are opening new doors for more effective treatments, providing greater precision in targeting affected brain areas. The integration of biomarkers for early detection and patient stratification will pave the way for personalized treatments that offer tailored solutions for each patient’s unique needs.
Despite the progress, there are still significant challenges ahead on the road to a cure. The complexity of Parkinson’s disease, coupled with its multifaceted nature, means that a single solution is unlikely. However, with continued collaboration across the pharmaceutical industry, research institutions, and policymakers, a comprehensive approach to finding a cure is within reach. A concerted effort is needed to accelerate clinical trials, improve treatment accessibility, and bring attention to the importance of early intervention. While the journey towards a cure will be long and filled with obstacles, the commitment to groundbreaking research and patient-centered care gives hope that one day, Parkinson’s disease may no longer be an insurmountable challenge but a treatable and manageable condition.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- NICE endorsement for Pfizer’s Vizimpro; Eisai, Dundee targets Cancer; Capital raise for AgaMatrix
- Japan has got new ways to treat corneas
- What Lies Ahead For Parkinson’s Disease Psychosis Treatment Market?
- Parkinson’s Disease Therapeutic Market Trends and Future Prospects
- Byondis’s HER2-targeting ADC trastuzumab duocarmazine; AbbVie Migraine Drug Atogepant; Grünenthal...