PPAR and NOX Agonist: Savior of Underserved Primary Biliary Cholangitis Patients
Feb 13, 2023
Table of Contents
Primary biliary cholangitis (PBC), earlier known as primary biliary cirrhosis, is an autoimmune disorder that leads to the gradual destruction of intrahepatic bile ducts resulting in periportal inflammation cholestasis. Prolonged hepatic cholestasis subsequently leads to cirrhosis and portal hypertension.
As per longitudinal studies of trends in primary biliary cholangitis among patients under routine clinical care in the United States, it has been found that from 2006 to 2014, the prevalence of PBC increased from 21.7 to 39.2 per 100,000 persons.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Merck and Moderna Initiate Study to Evaluate V940; FDA Approves Vertex and CRISPR Therapeutics’ C...
- GSK Receives FDA Fast Track Designation for Bepirovirsen; Gilead to Acquire CymaBay Therapeutics;...
- FDA’s No to Intercept’s NASH Drug; Roche’s Phesgo gets approval; Gilead’s Remdesivir pricing
- Gilead’s Livdelzi FDA Approval for Primary Biliary Cholangitis; Incyte and Syndax’s Niktimv...
- Moderna’s Phase III Trials for Dual Influenza and COVID-19 Vaccine; Almirall’s Klisyri FDA Approv...
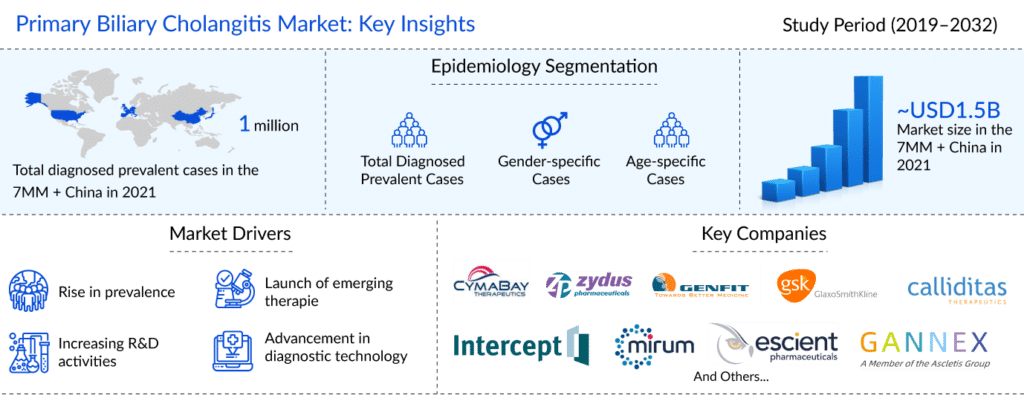
As per the latest “Primary Biliary Cholangitis Epidemiology Report” published by DelveInsight, it was found that primary biliary cholangitis affected around 136K people in the US, 105K in the EU4 and the UK, and 44K in Japan and 719K in China in 2021.
UDCA and OCALIVA – The Only Available Therapies for Primary Biliary Cholangitis Treatment Despite Controversies
There are only two primary biliary cholangitis medications approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for primary biliary cholangitis treatment: ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) and obeticholic acid (OCALIVA). Despite the emergence of promising primary biliary cholangitis drugs in the second-line setting (PBC patients intolerant to UDCA or UDCA-naive), UDCA continues to be the preferred first-line treatment. The continued trust is based on UDCA’s excellent long-term efficacy and safety profile and low primary biliary cholangitis treatment cost. UDCA exerts anti-cholestatic properties by improving hepatobiliary secretory function and reducing bile toxicity. Obeticholic acid (OCA), OCALIVA was the second drug to receive approval for patients with incomplete response to UDCA or were intolerant, and for UDCA-naïve patients. OA synthetic bile acid derivative, OCA, has a high affinity for FXR (a nuclear receptor closely regulating bile acid synthesis and secretion), and can mediate anti-inflammatory andante-fibrotic effects. The therapy received conditional approval from the US FDA and EMA in 2016.
Fatigue is the most commonly reported symptom in primary biliary cholangitis patients, with 40–80% of patients encountering it during their illness. In addition to debilitating physical effects on patients’ ability to perform daily activities, fatigue significantly impacts mental health, social life, family life, sexual life, and job performance. Several pathophysiological mechanisms for explaining the development of fatigue have been generated; however, the understanding of fatigue in patients with liver disease is still incomplete. A better understanding of the pathways and the neurotransmitter systems involved may provide directed specific therapies for liver disease‐associated fatigue. Managing fatigue in chronic liver disease can involve combining methods to beneficially alter behavioral components and pharmacological interventions, of which several treatments can potentially improve fatigue in chronic liver disease.
With no current licensed therapy available to treat fatigue, a huge unmet need must be addressed, as the current mainstay of management is largely supportive. The supportive approach includes various nonpharmacological measures to help patients with coping and supportive strategies. These include energy pacing and daytime planning (fatigue is typically worse later in the day, meaning it is helpful for patients to plan important activities for the morning).
Musings on the Primary Biliary Cholangitis Treatment
The primary biliary cholangitis market was valued at around USD 1,500 million in 2021 for the seven major markets and China, as per DelveInsight’s estimates. The primary biliary cholangitis treatment market is expected to reach ~USD 6,300 million by 2032 at a CAGR of approximately 12%.
Some of the promising PBC drugs to enter the primary biliary cholangitis treatment market include seladelpar, which is being developed by CymaBay Therapeutics, elafibranor (Genfit), setanaxib (Genkyotex SA), saroglitazar Mg (Zydus), and linerixibat (GlaxoSmithKline). All assets are in the late stage of development for the management and primary biliary cholangitis treatment in the 7MM + China.
Several late-stage assets with distinct MoA are being developed for treating primary biliary cholangitis patients. They are expected to enter the US, EU4 (Germany, Italy, France, Spain), the United Kingdom, Japan, and China primary biliary cholangitis treatment markets in the upcoming years.
Recent Developmental Activities in the Primary Biliary Cholangitis Treatment Space
- In January 2023, Karolinska Development AB announced that the United States had granted Orphan Drug Designation to its portfolio company Umecrine Cognition. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) approval for golexanolone, the company’s most advanced drug candidate in Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC). The designation will be critical in golexanolone’s planned clinical development.
- In January 2023, CymaBay Therapeutics announced a collaboration with Kaken Pharmaceutical Co., Ltd. to develop and market seladelpar for primary biliary cholangitis in japan.
- In November 2022, CymaBay Therapeutics, Inc. announced encouraging seladelpar data in patients with primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) that were presented at The Liver Meeting of the American Association for the Study of Liver Diseases (AASLD) in Washington, DC (November 4th – 8th). A clinical poster presentation titled “Seladelpar Improved the Lipid Profile of Patients with Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC): Results from Phase II and III Clinical Studies” reported positive results and showed that treatment with seladelpar resulted in significant improvements in total cholesterol (TC), LDL-C, HDL-C, and triglycerides (TG). A second poster presenting clinical data titled “Seladelpar, a PPAR-delta Agonist, Improves Inflammatory Lipid Mediators in the Serum Metabolome in Patients with Primary Biliary Cholangitis (PBC)” revealed that seladelpar treatment in patients with PBC resulted in broad changes in serum metabolomics.
- In August 2022, Gannex Pharma Co., Ltd., owned by Ascletis Pharma Inc., announced that it had finished its first dosing in the US drug-drug interaction (DDI) study of Farnesoid X Receptor agonist ASC42 for the primary biliary cholangitis treatment. The DDI study and ongoing phase II clinical trial in PBC patients in China will provide more evidence to support upcoming phase III trials in the US, China, and the European Union.
- GENFIT is currently evaluating its proprietary drug candidate, elafibranor, a dual agonist of PPARα and PPARδ in PBC. Enrollment is ongoing for the Phase III clinical trial ELATIVE (NCT04526665), which aims to confirm elafibranor 80mg efficacy based upon changes in biochemical parameters and its potential to improve pruritus and safety in patients with PBC. Elafibranor was granted Breakthrough Therapy designation by the FDA in April 2019 for the treatment of PBC in adults with inadequate response to UDCA, as well as Orphan Drug Designation by the FDA and the EMA (European Medicines Agency) in July 2019. In November 2022, Genfir announced that Phase III data for elafibranor in primary biliary cholangitis (PBC) is expected in 2Q23.
- CNP-104 is being developed utilizing Cour’s nanoparticle platform (CNP), a novel, proprietary system which combines disease-specific pathogenic antigens with state-of-the-art pharmaceutical nanoparticles that mimic the normal removal of dead or dying cells from the body. Cour’s platform has shown proof of technology in clinical and preclinical settings. COUR is currently conducting a clinical study with top-line data expected to read out in 2023. In January 2022, the US Food and Drug Administration (FDA) granted Fast Track designation to CNP-104 for the treatment of primary biliary cholangitis (PBC).
Primary Biliary Cholangitis Treatment Market All Set to Grow Significantly
The development of disease-specific therapies for primary biliary cholangitis treatment will auger well for the market landscape, which, in turn, will facilitate significant changes during the forecast period (2019–2032). The primary biliary cholangitis treatment market is expected to grow considerably with improved diagnosis and safe and efficacious primary biliary cholangitis treatment options. Nevertheless, pricing and reimbursement challenges, along with associated long-term side effects of approved therapies, are two major factors that influence the primary biliary cholangitis treatment market success of the upcoming therapies.

FAQs
Primary biliary cirrhosis (PBC) is an autoimmune-related chronic and slowly progressive cholestatic liver disease characterized by intrahepatic bile duct injury that can lead to liver failure. At the time of primary biliary cirrhosis diagnosis, most patients are in their fifth to seventh decades of life, and 90% are female.
PBC does not always cause symptoms, but some people may experience bone and joint aches, fatigue (extreme tiredness), itchy skin, dry eyes and mouth, and pain or discomfort in their upper right stomach. Most patients are asymptomatic at the time of diagnosis; however, some patients present with fatigue and pruritus.
A combination of clinical features, an abnormal liver biochemical pattern in a cholestatic picture that persists for more than six months, and the presence of detectable antimitochondrial antibodies (AMA) in serum are used to make the primary biliary cirrhosis diagnosis.
There are only two primary biliary cholangitis medications approved by the Food and Drug Administration (FDA) for primary biliary cholangitis treatment: ursodeoxycholic acid (UDCA) and obeticholic acid (OCALIVA). Despite the emergence of promising primary biliary cholangitis drugs in the second-line setting (PBC patients intolerant to UDCA or UDCA-naive), UDCA continues to be the preferred first-line treatment.
Many molecules are in the pipeline to treat PBC patients across many countries to cater to their needs. Some major late-stage products likely to hit the market during our study period 2019–2032 include seladelpar (CymaBay Therapeutics), elafibranor (Genfit), and setanaxib (Calliditas Therapeutics AB).
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Merck and Moderna Initiate Study to Evaluate V940; FDA Approves Vertex and CRISPR Therapeutics’ C...
- GSK Receives FDA Fast Track Designation for Bepirovirsen; Gilead to Acquire CymaBay Therapeutics;...
- Moderna’s Phase III Trials for Dual Influenza and COVID-19 Vaccine; Almirall’s Klisyri FDA Approv...
- FDA’s No to Intercept’s NASH Drug; Roche’s Phesgo gets approval; Gilead’s Remdesivir pricing
- Gilead’s Livdelzi FDA Approval for Primary Biliary Cholangitis; Incyte and Syndax’s Niktimv...



