Future Avenues for Prediabetes Treatment: The Road Ahead
Dec 25, 2023
Table of Contents
Prediabetes is a significant health concern characterized by elevated blood sugar levels that fall between the normal range and the diagnostic threshold for type 2 diabetes. Often labeled as borderline diabetes, this metabolic condition is intricately linked to the global rise in obesity and poses an escalating worldwide health challenge. Individuals with prediabetes face an augmented likelihood of developing type 2 diabetes, as well as increased risks of heart disease and stroke.
The Rising Tide of Prediabetes: A Global Perspective
The increasing prevalence of prediabetes has emerged as a pressing global health concern, casting a shadow on populations worldwide. With millions affected, this precursor to type 2 diabetes serves as an ominous indicator of future health complications. The rising tide of prediabetes spans across demographics, transcending geographical boundaries and socio-economic statuses. Factors such as sedentary lifestyles, poor dietary habits, and genetic predispositions contribute to its surge. Addressing this issue demands a multifaceted approach, integrating education, lifestyle modifications, and accessible healthcare interventions. Understanding the global perspective of this escalating challenge becomes imperative to stem the tide, promote awareness, and foster proactive measures to curtail its progression toward full-blown diabetes.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Semaglutide: A Potential Game-Changer in Reducing Alzheimer’s Disease Risk
- 7 Promising Obesity Drugs Set to Launch by 2027
- Amgen to Acquire Horizon Therapeutics; Sanofi and Teva Announce Collaboration; Boehringer Obesity...
- Algernon’s NP-120; FDA nod to 4DMedical tool; SaNOtize’s NORSTM trial; Pole’s c...
- Ypsomed-CamDiab’s Collaboration; Vela Diagnostics’s NGS-Based Pan-Cancer Panels; Fresenius&...
As the global community grapples with the escalating prevalence of prediabetes, it becomes evident that this condition is not merely a precursor to diabetes but a significant health threat in its own right. The economic burden associated with the management of prediabetes-related complications, coupled with the strain on healthcare systems, underscores the urgency for comprehensive strategies. Cultural and societal norms also play a pivotal role in shaping lifestyle choices, making it crucial to tailor interventions to specific regions. Collaborative efforts on both local and international levels are essential, involving healthcare providers, policymakers, and communities. Emphasizing preventive measures, promoting healthy behaviors, and investing in research to understand the nuances of prediabetes across diverse populations is paramount. By fostering a global perspective that acknowledges the shared challenge of prediabetes, we can strive towards a healthier future for individuals and communities worldwide.
The Road to Reversal: Can Prediabetes Be Overcome?
While prediabetes is reversible, prevention is often more straightforward than complete treatment. Lifestyle choices play a pivotal role in the development of prediabetes, and modifying certain aspects can significantly mitigate risk factors. Prediabetes typically precedes the onset of type 2 diabetes. Exercise and weight loss emerge as the most impactful interventions for prediabetes, enhancing insulin sensitivity and reducing elevated blood sugar levels.
In addition to comprehensive lifestyle management, individuals with prediabetes may consider various pharmacological interventions as an alternative approach. These interventions aim to augment insulin effectiveness and curtail Impaired Glucose Tolerance (IGT), thereby impeding progression to T2D. Although there are no specific therapies designated for prediabetes treatment in the current treatment paradigm, approved treatments for T2D, such as metformin, thiazolidinediones, glucagon-like peptide-1 (GLP-1) analogs, dipeptidyl peptidase-4 (DPP-IV) inhibitors, and alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, are commonly utilized.
Metformin functions as an antihyperglycemic agent, enhancing glucose tolerance in individuals with prediabetes or type 2 diabetes by reducing both basal and postprandial plasma glucose levels. Its pharmacological mechanisms differ from those of other classes of oral antihyperglycemic agents. Thiazolidinediones target peroxisome proliferator activator receptor gamma (PPAR-γ), addressing two primary defects resulting from impaired glucose tolerance (IGT). By improving sensitivity to insulin in adipocytes, liver, and muscle cells, thiazolidinediones also provide support and protection to beta-cell function. Commonly utilized thiazolidinediones for prediabetes treatment encompass troglitazone, pioglitazone, rosiglitazone, and others.
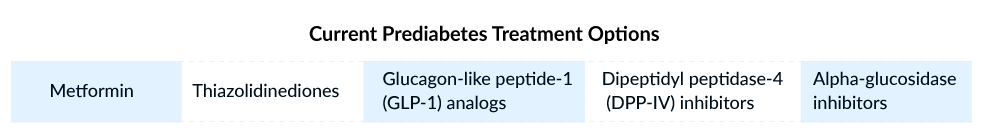
Another category of medications prescribed for prediabetes treatment includes orally administered GLP-1 analogs, which elicit a two- to three-fold increase in plasma insulin response compared to the same level of hyperglycemia induced by intravenous glucose. These analogs effectively inhibit the secretion of glucagon, delay gastric emptying, reduce appetite, control food intake, and contribute to weight loss. Commonly utilized GLP-1 receptor agonists such as liraglutide and exenatide are recommended for individuals with elevated insulin levels or those on the brink of developing diabetes.
The next category of medication for prediabetes treatment involves DPP-IV inhibitors, exemplified by vildagliptin. This class works by covalently binding to the catalytic site of DPP-4, resulting in prolonged enzyme inhibition. This action elevates intact GLP-1 levels both after meal ingestion and during fasting. Vildagliptin has demonstrated the ability to stimulate insulin secretion and inhibit glucagon secretion in a glucose-dependent manner.
Lastly, alpha-glucosidase inhibitors, sometimes termed starch blockers, function as antidiabetic medications that reduce postmeal blood glucose levels. These medications, unlike most others used in diabetes treatment, do not directly affect insulin secretion or sensitivity. Instead, they operate by slowing the breakdown of carbohydrates from starchy foods. Frequently employed alpha-glucosidase inhibitors for addressing prediabetes and T2D include acarbose, miglitol, voglibose, and similar options.
Emerging Horizons: Next-Gen Therapies for Prediabetes Treatment
The prediabetes treatment market faces a significant gap in approved therapeutic options, creating an opportunity for the development of novel prediabetes treatments that can effectively address prediabetes and potentially prevent the onset of diabetes. Prominent companies including Valbiotis, Novo Nordisk, Aphaia Pharma, and other industry leaders are actively engaged in the exploration and development of innovative therapies for prediabetes treatment.
Novo Nordisk is currently researching the subcutaneous administration of semaglutide 2.4 mg in individuals with obesity and prediabetes. The ongoing Phase III trial, STEP 10, is evaluating the drug’s potential as a once-weekly treatment. As a GLP-1 receptor agonist, semaglutide operates through multiple mechanisms, including increased glucose-dependent insulin secretion, inhibition of glucagon release, and suppression of hepatic gluconeogenesis. This comprehensive approach aims to decrease both fasting and postprandial glucose levels.
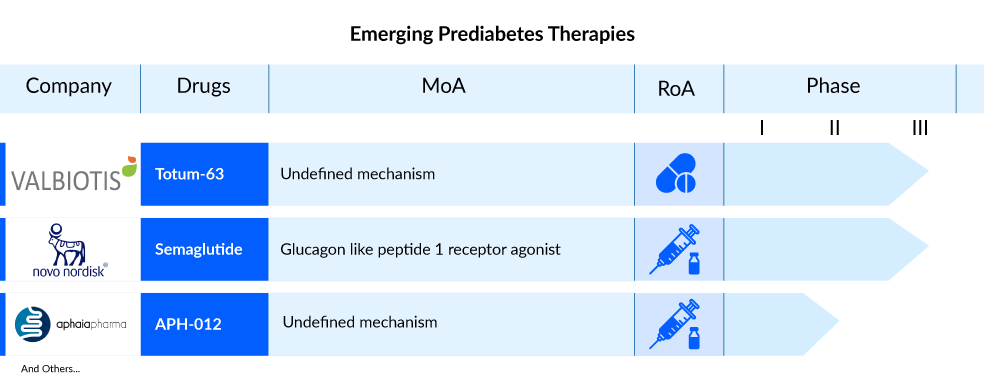
Valbiotis is advancing the development of TOTUM-63, the main active ingredient in VALEDIA, through Phase II/III clinical trials targeting individuals with prediabetes. This proprietary formulation comprises a patented combination of five plant extracts designed to address key pathophysiological mechanisms. In 2020, Valbiotis forged a global, long-term strategic partnership with Nestlé Health Science for the collaborative development and worldwide commercialization of TOTUM-63. The ongoing prediabetes Phase II/III REVERSE-IT study represents the final step in the clinical development process, paving the way for the submission of a health claim recognized by regulatory authorities in the United States, Europe, and Canada. In September 2023, Valbiotis unveiled comprehensive findings from the Phase II/III REVERSE-IT study, showcasing the impressive efficacy of TOTUM-63 against prediabetes and the early stages of type 2 diabetes. This achievement is a significant milestone, highlighting TOTUM-63 as the first non-drug active substance to exhibit such effectiveness.
Aphaia Pharma is currently assessing APH-012 in a Phase II trial to determine its efficacy in enhancing glucose tolerance among individuals with prediabetes exhibiting abnormal Oral Glucose Tolerance Test (OGTT) results. Following a six-week administration of APH-012, its impact on signaling pathways responsible for regulating various homeostatic functions, including appetite, hunger, satiety, and glucose metabolism, is being closely monitored. The compound exhibits promising potential in the prevention of type 2 diabetes.
Emerging Trends and Future Prospects in Prediabetes Treatment
The future landscape of the prediabetes treatment market holds promising advancements, marked by a paradigm shift towards personalized and proactive interventions. Emerging technologies and a deeper understanding of the underlying mechanisms of prediabetes are paving the way for more targeted therapies. Precision medicine approaches, including genetic profiling and biomarker analysis, will enable healthcare providers to tailor treatments to individual needs, optimizing efficacy and minimizing side effects.
Lifestyle interventions, such as personalized nutrition plans and exercise regimens, will play a pivotal role in managing prediabetes, with digital health tools facilitating continuous monitoring and support. Additionally, innovative pharmaceuticals targeting specific pathways involved in insulin resistance and glucose metabolism are expected to enter the prediabetes treatment market, offering new options for those at risk of progressing to type 2 diabetes. Collaborative efforts between healthcare providers, researchers, and technology developers are likely to shape a comprehensive and integrated approach to prediabetes management, ushering in an era where proactive measures take precedence in preventing the progression of metabolic disorders.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Pooled Analysis of Finerenone Presented at EASD 2024, Poised to Strengthen its Position in the Ca...
- Fujifilm acquires global rights to Cynata’s novel therapy for GvHD; Themis raises EURO 40 m...
- Semaglutide: A Potential Game-Changer in Reducing Alzheimer’s Disease Risk
- Eli Lilly’s Obesity Treatment Drug Candidates – A Show for the Competitors
- Evolution in Diabetes Management