Sanofi’s Qfitlia Enters the Hemophilia Market—What Sets It Apart?
Apr 07, 2025
Over the past three years, the FDA has approved six new hemophilia treatments, including three gene therapies. Now, Sanofi’s Qfitlia (fitusiran) enters the competitive hemophilia therapeutics market, distinguishing itself as the only therapy approved for all types of hemophilia. Unlike most existing treatments, Qfitlia is indicated for routine prophylaxis to prevent or reduce bleeding episodes in adults and pediatric patients (12 years and older) for both hemophilia A and B and is effective regardless of inhibitor status—a key advantage for patients who develop factor VIII or factor IX inhibitors, which can reduce the effectiveness of standard clotting factor replacement therapies.
Qfitlia is administered subcutaneously, starting once every two months, with dose and frequency adjustments guided by a companion diagnostic test. According to Sanofi, the average annual wholesale acquisition cost for most patients will be $642,000.
Alongside Qfitlia’s approval, the FDA also authorized Siemens Healthineers’ INNOVANCE Antithrombin assay as a companion diagnostic to assess AT levels. Through the Qfitlia Testing Program with Labcorp, this FDA-cleared diagnostic will be offered free of charge to patients prescribed Qfitlia for AT level measurement.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Role of Mobile Technology in Hemophilia Management
- Fourth FDA Approval for AbbVie’s Vraylar; FDA Approves Ferring’s Adstiladrin for NMIBC; Merck and...
- Cell and Gene Therapies in Rare Disorders: From Rarity to Recovery
- A Royal Disease: Hemophilia
- Sanofi’s Qfitlia Becomes First FDA-Approved Therapy for Hemophilia A or B; FDA Approves AstraZene...
Phil Gattone, President and CEO of the National Bleeding Disorders Foundation, stated, “Many individuals with hemophilia often face a difficult choice between optimal bleed control and a convenient dosing schedule, resulting in compromises in disease management. Qfitlia offers a unique approach by providing effective protection while also reducing the dosing frequency, benefiting both patients and their families.”
Qfitlia stands out as the prophylactic hemophilia treatment requiring the fewest doses, offering comparable pricing to existing therapies. To support patients, Sanofi is launching HemAssist, a comprehensive patient support program that provides insurance and financial assistance, along with educational resources. This program will be available to those prescribed Qfitlia or other Sanofi hemophilia treatments.
The FDA has granted Qfitlia multiple regulatory designations, including Orphan Drug Designation for hemophilia A and B, Fast Track Designation for hemophilia A and B with or without inhibitors, and Breakthrough Therapy Designation for hemophilia B treatment with factor IX inhibitors.
Beyond the US, regulatory submissions are underway, with a decision expected in China in the second half of 2025, while Brazil is currently reviewing Qfitlia for hemophilia A and B in adults and adolescents with or without inhibitors.
Originally discovered by Alnylam, the first clinical data on Qfitlia was published in the New England Journal of Medicine in 2017, demonstrating its ability to reduce bleeding rates in hemophilia patients. Alnylam initiated Phase III development, and in 2014, Sanofi secured global co-development and co-commercialization rights under a license and collaboration agreement. This agreement was later amended in 2018, granting Sanofi full global development and commercialization rights, while Alnylam remains eligible for tiered royalties of 15% to 30% on global net sales.
Qfitlia is the sixth RNAi-based therapy developed by Alnylam to receive regulatory approval, marking a key milestone in its P5x25 strategy—a set of corporate objectives aimed at 2025. With an estimated one million people worldwide affected by hemophilia A and B, Qfitlia has the potential to make a significant impact.
Brian Foard, Executive Vice President and Head of Specialty Care at Sanofi, stated, “This approval underscores our dedication to driving innovation and enhancing care for those with rare blood disorders. Qfitlia has the potential to significantly impact the hemophilia landscape by providing strong bleed protection, less frequent dosing, and streamlined administration. As we expand our comprehensive portfolio of hemophilia treatments, our focus remains on delivering effective protection while minimizing treatment burden to best suit individual patient needs.”
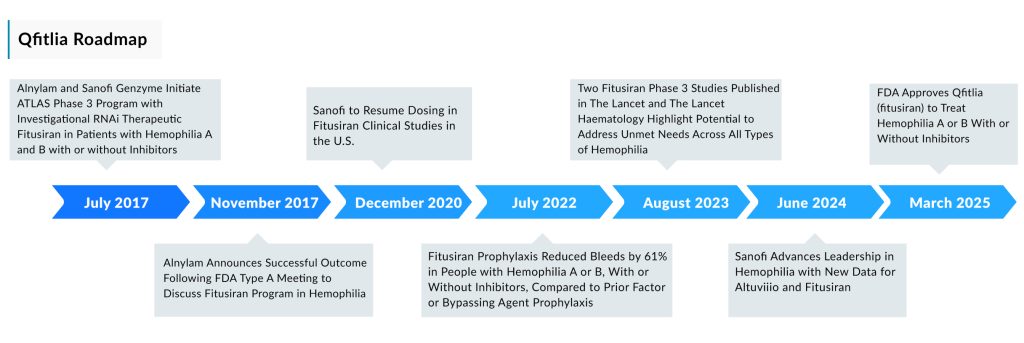
Phase III trials have demonstrated that Qfitlia is similarly effective across all four classifications of hemophilia. It has also performed well in hemophilia patients who collectively underwent 60 major surgeries. The approval was supported by two phase III trials, both of which showed that prophylactic use of Qfitlia reduced the annualized bleeding rate by 90% compared to the control group. In both studies, patients received treatment for nine months.
In the ATLAS A/B trial, which included 120 non-inhibitor patients with hemophilia A or B who had previously been treated with on-demand clotting factor concentrates, 51% of those receiving monthly prophylactic Qfitlia experienced no annual bleeds, compared to just 5% in the on-demand clotting factor group. Similarly, the ATLAS-INH trial enrolled 57 patients with severe hemophilia A or B with inhibitors. Among those treated with Qfitlia, 66% had no annualized bleeding episodes, compared to only 5% of patients in the control group who received an on-demand bypassing agent.
Qfitlia is the second RNA interference drug to receive a highly anticipated FDA approval in recent days. Just in March 2025, the agency approved Alnylam’s AMVUTTRA for the treatment of transthyretin amyloid cardiomyopathy (ATTR-CM). Although Qfitlia is entering a competitive market with a relatively small patient population, it has the potential to establish a niche due to its advantages over existing factor VIII and factor IX replacement therapies. These traditional treatments require intravenous administration once or twice a week and carry a risk of infection.
Qfitlia also offers a convenience advantage over two recently approved hemophilia drugs—Novo Nordisk’s ALHEMO and Pfizer’s HYMPAVZI. While both are suitable for hemophilia A and B patients and are administered subcutaneously, ALHEMO requires daily dosing, and HYMPAVZI is given weekly. Additionally, ALHEMO is limited to patients with inhibitors, whereas HYMPAVZI is only approved for non-inhibitors. In the hemophilia A market, Roche’s HEMLIBRA remains the leading treatment, generating $4.9 billion in sales in 2024. It is administered subcutaneously and is approved for use in both inhibitor and non-inhibitor patients.
Additionally, in the hemophilia pipeline, certain candidates will give tough competition to Qfitlia once they are approved. One such candidate is Spark Therapeutics’ SPK-8011, an investigational gene therapy for hemophilia A or factor VIII deficiency.
Another candidate in the late stage of development is Novo’s Mim8, an experimental Factor VIIIa (FVIIIa) mimetic bispecific antibody designed to provide long-lasting hemostasis for individuals with hemophilia A, both with and without inhibitors. It is intended for prophylactic use with flexible dosing options—once weekly, every two weeks, or once monthly. Delivered via subcutaneous injection, Mim8 functions by bridging Factor IXa and Factor X, effectively replacing the role of Factor VIII.
Recently, Novo Nordisk released Phase III results for its Mim8 Factor VIIIa mimetic bispecific antibody, positioning it as a potential competitor to HEMLIBRA. Findings from the FRONTIER3 trial, which focused on children aged 1 to 11, demonstrated strong efficacy and high patient satisfaction, suggesting that Mim8 could gradually challenge HEMLIBRA’s dominance. Novo Nordisk plans to submit regulatory applications for Mim8 later this year.
Belief BioMed’s BBM-H803 is another candidate in the pipeline for hemophilia treatment. BBM-H803 Injection is a gene therapy for hemophilia A. It is based on a recombinant AAV and contains a codon-optimized human factor VIII gene regulated by a liver-specific promoter. Belief BioMed holds proprietary patents for both the capsid and gene cassette.
Manufactured using the company’s in-house serum-free production and chromatographic purification process, which meets cGMP standards, BBM-H803 has shown high efficacy and safety. The therapy enables sustained FⅧ expression in patients’ plasma, offering the potential for long-term benefits from a single treatment.
On December 21, 2022, the FDA granted BBM-H803 orphan drug designation (ODD) for the treatment of hemophilia A. This marks the company’s second gene therapy candidate to receive FDA orphan drug status, following BBM-H901 for hemophilia B, which was designated on August 15, 2022, through its wholly owned subsidiary, Shanghai Belief-Delivery BioMed Co., Ltd.
The anticipated launch of these hemophilia therapies will change the dynamics of the hemophilia market in the coming years. Ultimately, it will be interesting to see how Qfitlia will maintain its position in this crowded hemophilia treatment space amid rising competition from other companies.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Bleeding Disorders: How Key Companies Are Shaping The Bleeding Disorders Therapeutics Market?
- Global Hemophilia Market
- AAV Vectors in Gene Therapy: How Recent Clinical Advances are Unraveling New Potentials?
- A Royal Disease: Hemophilia
- Novo Nordisk’s Concizumab for Hemophilia; AbbVie Ends its Alliance with Alector; ADC Therapeutics...



