The Next Chapter in NSCLC Treatment Space: Recent Discoveries and Innovations
Nov 29, 2024
Lung cancer was the most prevalent cancer globally, with 2.5 million new cases, representing 12.4% of all new cancer diagnoses. NSCLC is the most common type of lung cancer, accounting for over 85% of all cases. As per the latest estimates, the total incident cases of NSCLC in the 7MM were approximately 500K cases in 2022 and are expected to reach around 600K cases by 2034. In the United States, there were approximately 200K new cases of lung cancer in 2023, with 117K cases in men and 120K in women. It is important to note that lung cancer statistics typically include both small cell lung cancer (SCLC) and non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC). Approximately 10% to 15% of all lung cancers are SCLC, while around 80% to 85% are NSCLC.
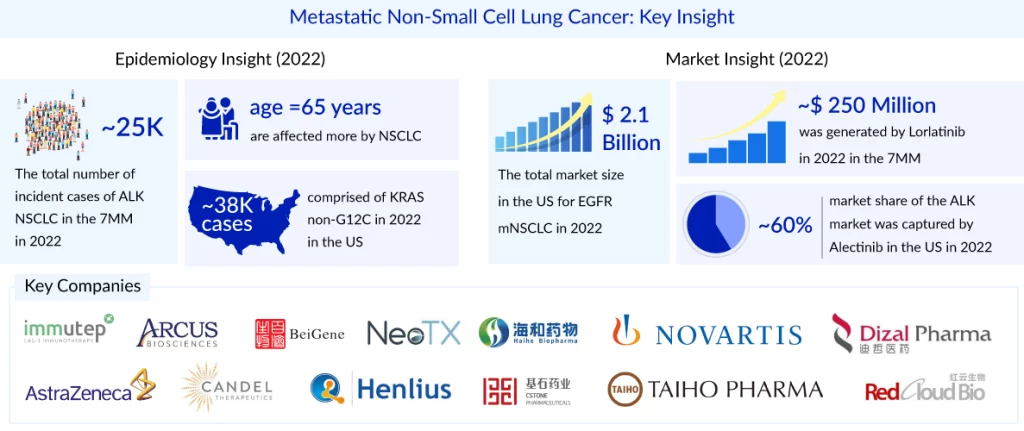
Metastatic NSCLC refers to advanced stages of cancer that have spread to other regions of the body. There is no cure for cancer once it has spread. Treatment is frequently aimed at extending a person’s life and increasing their quality of life. As per the DelveInsight assessment in the mNSCLC market report, in biomarker-specific cases, the most number of the cases are from PD-L1 followed by KRAS, and EGFR. On the other hand, NTRK accounted for the least number of cases, whereas BRAF and MET accounted for approximately 5% and 4% of cases, respectively. The two main subtypes of KRAS NSCLC are KRAS G12C and KRAS non-G12C (G12V, G12D, G13D, G12R, and others). In the United States, ~22K cases comprised of KRAS G12C, and ~38K cases comprised of KRAS non-G12C in 2023.
As NSCLC accounts for the majority of lung cancer cases, the sheer magnitude of its patient population underscores the urgent need for effective and targeted interventions. With millions of individuals grappling with NSCLC worldwide, the disease not only poses a substantial health burden but also necessitates a multifaceted approach to diagnosis, treatment, and supportive care.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- ENHERTU’s Journey in Cancer Treatment and Management
- Checkpoint Inhibitors: A Potential Approach in the Fight Against Refractory Cancer
- Sanofi’s Rare Disease Drug Xenpozyme’ Approval; FDA Approves Novartis’ Pluvicto; AstraZenec...
- Amgen a leader in Undruggable Lung Cancer; Verrica’s Skin Disease Drug Delays; Fennec’...
- Data readout of potential ADCs: Enhertu gears up for Urothelial Carcinoma Market now
Despite advances in cancer research and therapy, there are notable treatment gaps in NSCLC that present challenges to achieving optimal patient outcomes. These gaps may arise due to factors such as late-stage diagnoses, limited accessibility to advanced treatments, resistance to existing therapies, and the heterogeneity of the disease itself. Additionally, a subset of patients may experience side effects or have comorbidities that limit the applicability of certain treatments. Addressing these gaps requires a comprehensive understanding of the molecular and genetic underpinnings of NSCLC, as well as the development of innovative therapeutic approaches.
The evolving landscape of NSCLC presents significant market opportunities for pharmaceutical companies and other stakeholders. Advances in precision medicine, immunotherapy, and targeted therapies have opened new avenues for treatment, offering more personalized and effective options. The rise of biomarker-driven therapies and immunotherapeutic agents has reshaped the treatment paradigm, creating opportunities for the development of novel drugs and combination therapies. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and big data analytics in oncology research has the potential to revolutionize treatment strategies, enabling more accurate diagnostics and personalized treatment plans.
More than 50+ companies including the leading pharma and biotech giants such as BieGene, Daiichi Sankyo/AstraZeneca, Arcus Biosciences, Hoffmann-La Roche/Genentech, GlaxoSmithKline, Jiangsu HengRui Medicine, AstraZeneca, Arcus Biosciences/Gilead Sciences, Regeneron Pharmaceuticals, Shanghai Henlius Biotech, GlaxoSmithKline, Pfizer, AbbVie, AstraZeneca, AnHeart Therapeutics, Bristol-Myers Squibb, Nuvalent, Cullinan Oncology/Taiho Pharma, Daiichi Sankyo, ArriVent BioPharma, NeoTX Therapeutics, Alethia Biotherapeutics, AstraZeneca, Incyte/Macrogenics, Sanofi, Nuvalent, Xcovery, Eli Lilly and Company and others are currently developing several metastatic non-small cell lung cancer treatments. All these companies evaluate their lead assets in different stages of clinical development. The anticipated launch of these NSCLC treatment drugs will drive the market forward in the coming years.
The total market size for PD-L1 expressing NSCLC is projected to reach approximately USD 20 billion by 2034 across the 7MM, followed by EGFR and KRAS. In the US, the market for EGFR mNSCLC was valued at nearly USD 4 billion in 2023, with further growth expected due to the introduction of emerging therapies and label expansions of existing treatments.
Recently, the DelveInsight team has analyzed several abstracts related to NSCLC that were presented during the ASCO 2024 annual conference. Various outcomes and findings from clinical trials were presented by the leading pharmaceutical companies at the ASCO 2024 Annual Meeting which represents mainly the significant progress made each year in the fight against cancer. The team analyzed the launch of the results and assessed the impact on the overall NSCLC treatment domain. Apart from ASCO 2024, the team also covered other conferences and analyzed the results. A glimpse of the results from clinical trials from these conferences is mentioned below:
ASCO 2024 Lung Cancer Highlights
1. LAURA Study (Osimertinib in EGFR-mutant NSCLC)
- Osimertinib improved progression-free survival (PFS) in unresectable stage III NSCLC (39.1 months vs. 5.6 months with placebo).
- High toxicity noted: radiation pneumonitis (48%), diarrhea (36%), and rash (24%).
- Median overall survival (OS) still maturing; 81% of placebo patients received osimertinib post-progression.
2. CROWN Trial (Lorlatinib for ALK-positive NSCLC)
- Lorlatinib showed superior 5-year PFS (60% vs. 8%) compared to crizotinib.
- High efficacy in brain metastases: 96% remained intracranial disease-free without brain metastases.
- Lorlatinib demonstrated excellent CNS penetration and durable responses.
3. ADRIATIC Study (Durvalumab in Limited-Stage SCLC)
- Durvalumab improved PFS (16.6 months vs. 9.2 months) and OS (55.9 months vs. 33.4 months) compared to placebo.
- Durvalumab poised to become the standard post-chemoradiation therapy.
- Emerging data suggests potential to improve 5-year survival rates from 30%-35% to nearly 50%.
4. Tarlatamab-DLLE (BiTE for Extensive-Stage SCLC)
- Approved for use in post-platinum extensive-stage SCLC but unmet expectations at ASCO.
- Limited data on intracranial efficacy due to prior radiation confounding results.
- Subgroup analysis showed tumor shrinkage in brain metastases, but further clarity is needed.
Each study represents advancements and challenges in targeted therapies, immunotherapy, and novel approaches for lung cancer treatment.
Clinical and Registrational Updates in 2024
- On November 13, 2024, AstraZeneca and Daiichi Sankyo announced the submission of a new biologics license application (BLA) to the U.S. Food and Drug Administration (FDA) seeking accelerated approval for datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-DXd) as a treatment for non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
- In October 2024, the FDA has approved Novocure’s tumor-targeting fields (TTFields) therapy for use alongside PD-1/PD-L1 inhibitors or docetaxel in treating adults with metastatic non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have experienced progression following a platinum-based treatment.
- On October 16, 2024, the FDA approved Novocure’s Optune Lua for concurrent use with immunotherapy or docetaxel in adults with metastatic stage IV non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) that has advanced despite platinum-based treatment.
- On 26 September 2024, AstraZeneca’s TAGRISSO (osimertinib) received U.S. approval for treating adult patients with unresectable Stage III epidermal growth factor receptor-mutated (EGFRm) non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) who have not experienced disease progression during or after platinum-based chemoradiation therapy. This approval follows the LAURA Phase III trial, which showed that Tagrisso significantly extends median progression-free survival by over three years, specifically for patients with exon 19 deletions or exon 21 (L858R) mutations identified by an FDA-approved test.
- On September 9, 2024, AstraZeneca and Daiichi Sankyo announced that the TROPION-Lung01 Phase III trial for datopotamab deruxtecan (Dato-DXd) showed a clinically meaningful trend toward improved overall survival compared to docetaxel in patients with locally advanced or metastatic nonsquamous non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC).
- On September 8, 2024, Summit Therapeutics announced that ivonescimab, in the Phase III HARMONi-2 trial, showed a median progression-free survival of 11.14 months, significantly better than pembrolizumab’s 5.82 months. This makes ivonescimab the first drug to achieve a meaningful benefit over pembrolizumab in NSCLC. Summit plans to start the HARMONi-7 trial in early 2025 for PD-L1 high advanced NSCLC. The results, presented at IASLC 2024, also noted comparable serious treatment-related adverse events and highlighted upcoming Phase II data in other solid tumors at ESMO 2024.
- On August 29, 2024, Bayer announced the enrollment of the first patient in the global Phase III SOHO-02 trial. This open-label, randomized, multicenter study is investigating the efficacy and safety of BAY 2927088 as a first-line treatment for advanced non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with activating HER2 mutations.
- On August 20, 2024, Johnson & Johnson announced that the FDA approved RYBREVANT® (amivantamab-vmjw) in combination with LAZCLUZE™ (lazertinib) for the first-line treatment of adult patients with locally advanced or metastatic non-small cell lung cancer (NSCLC) with EGFR exon 19 deletions or exon 21 L858R substitution mutations, as identified by an FDA-approved test.
The anticipated growth of the NSCLC treatment market is driven by premium-priced targeted agents with superior clinical profiles and an expanded range of therapies in the first line, while the development of treatments targeting specific mutations is expected to dominate the upcoming NSCLC treatment market. The potential for premium pricing of emerging therapies, demonstrating an edge over current treatments, adds to the momentum. Fast uptake of potential emerging NSCLC drugs, characterized by improved clinical profiles and specificity towards mutations in NSCLC, along with therapies designed to overcome resistance, is expected.
However, lung cancer imposes a major disease burden on the world. Worldwide, lung cancer remains the most common cancer diagnosed and the greatest cause of cancer-related death. Because of its extraordinary disease burden and the international variability in trends for population growth, aging, and smoking behavior, the global epidemiology of lung cancer requires continual monitoring. Talking about the global scenario of lung cancer, this type of cancer ranks as the most frequent cancer in males and females worldwide, besides breast cancer and prostate cancer, respectively. The incidence of cigarette smoking is by far the most important risk factor for lung cancer. Risk increases with both the quantity and duration of smoking. Exposure to radon gas, which is released from soil and can accumulate in indoor air, is thought to be the second leading cause of lung cancer in the United States. In addition, the expected entry of generic or biosimilar for blockbuster NSCLC drugs like KEYTRUDA, OPDIVO, and TARCEVA will erode the NSCLC market sales.
Nevertheless, the research on different NSCLC immune/molecular biomarkers such as PD-L1, EGFR, KRAS, ALK, BRAF, MET, ROS-1, HER2, RET fusion, and NTRK1/2/3 Gene fusion is ongoing. Several therapies targeting these biomarkers are in different stages of clinical development. The anticipated launch of these non-small cell lung cancer treatments will give a ray of hope to all cancer patients around the world.
Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and big data analytics in oncology research has the potential to revolutionize treatment strategies, enabling more accurate diagnostics and personalized treatment plans. Furthermore, the expansion of healthcare infrastructure in emerging markets, increased awareness, and the growing emphasis on early detection contribute to the NSCLC market’s potential for growth. Collaboration between academia, industry, and regulatory bodies is essential to capitalize on these opportunities and bring forth innovative solutions that address the unmet needs of NSCLC cancer patients.
In conclusion, the NSCLC prevalence, existing treatment gaps, and emerging market opportunities underscore the importance of a holistic and collaborative approach to tackling this complex disease. As research and technology continue to advance, there is hope for a future where NSCLC is not only better understood but also effectively managed, offering improved outcomes for patients around the globe.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- X4 Pharmaceuticals’ XOLREMDI FDA Approval; ONO to Acquire Deciphera Pharmaceuticals; Johnson &...
- Roche’s TECENTRIQ HYBREZA: Setting New Standards as the First Subcutaneous Anti-PD-(L)1 Drug
- ASCO GU 2022: Renal Cell Carcinoma Highlights
- Gilead and Merck Announce Encouraging Phase II Results of Islatravir and Lenacapavir Combo; REGEN...
- A Quick Review of Antibody-Drug Conjugates (ADCs) in Lung Cancer: HER2, TROP-2, HER3, MET, and CE...