The Promise of Big Data in Healthcare: Transforming Treatment and Outcomes
Jan 08, 2025
Table of Contents
In recent years, the healthcare sector has undergone a major transformation, thanks to the advent of Big Data. The term “Big Data” refers to vast amounts of data—structured and unstructured—that are generated at an incredible speed. This data, when harnessed correctly, has the potential to revolutionize healthcare delivery, patient outcomes, operational efficiency, and medical research.
The Growing Role of Big Data in Healthcare
Healthcare organizations generate an enormous amount of data every day—from patient records and medical imaging to genetic data and real-time health monitoring systems. This data holds immense value in improving patient care, reducing costs, and making informed decisions at every level of healthcare provision.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
Big Data in healthcare refers not just to the size of the data, but also its variety, velocity, and complexity. The healthcare industry collects data from a variety of sources:
Electronic Health Records (EHRs): Patient histories, treatments, and outcomes are stored in digital form.
Medical Imaging: Advanced imaging technologies like MRIs and CT scans generate large amounts of visual data.
Genomic Data: With advancements in genomics, huge datasets are now available for personalized treatment and precision medicine.
Wearables and IoT Devices: Real-time health monitoring through wearables and connected devices provides continuous streams of patient data.
Clinical Trials and Research Data: Data from clinical trials and medical studies contribute to a better understanding of diseases and their treatments.
By analyzing these large datasets, healthcare providers can uncover insights that improve patient care, streamline operations, and facilitate innovation in drug development and medical research.
In addition to the traditional sources of data, the integration of social determinants of health (SDOH)—such as socioeconomic status, education level, and environment—has further expanded the role of Big Data in healthcare. This comprehensive data enables healthcare systems to address health disparities by understanding the broader context in which patients live. For instance, data on access to nutritious food, clean water, or safe housing can provide valuable insights into how these factors contribute to overall health outcomes. With this more holistic view, healthcare providers can offer more targeted interventions that not only treat illnesses but also address root causes.
Moreover, real-time data analytics is another area where Big Data is playing an increasingly important role. The continuous data streams provided by wearable devices, health apps, and hospital monitoring systems allow healthcare providers to make real-time decisions, reducing delays in treatment and improving emergency response. For instance, wearable devices that track vital signs such as heart rate, blood pressure, and glucose levels can alert doctors to potential health problems before they escalate. This capability is particularly vital in the management of chronic diseases, where ongoing monitoring and timely interventions can prevent complications and hospitalizations.
Finally, machine learning and artificial intelligence are advancing the potential of Big Data in healthcare. These technologies are becoming integral in processing and analyzing complex datasets, helping healthcare providers predict patient outcomes, detect anomalies, and identify treatment pathways that are most likely to succeed. AI-powered algorithms can detect early signs of diseases such as cancer, heart disease, and neurological disorders by analyzing patterns in imaging, genetic, and historical health data. This early detection can lead to more effective and less invasive treatments, ultimately improving survival rates and reducing healthcare costs.
Key Benefits of Big Data in Healthcare
Improved Patient Outcomes: Big Data allows healthcare providers to better understand individual patient needs. By analyzing past medical histories, genetic information, and current health metrics, physicians can tailor treatments to the specific needs of each patient, leading to more effective care. Predictive analytics also enable early diagnosis, which can significantly improve outcomes by starting treatments earlier.
Cost Reduction and Operational Efficiency: Big Data can help identify inefficiencies in hospital operations, from managing bed capacity to optimizing supply chains. By analyzing trends in patient admissions, hospitals can better manage resources, reduce wait times and lower operational costs. Additionally, predictive models can prevent readmissions and help hospitals provide preventative care.
Personalized Medicine: One of the most promising applications of Big Data in healthcare is the advent of personalized or precision medicine. By integrating genetic data with clinical records, Big Data enables the creation of individualized treatment plans that are more likely to succeed. This approach leads to fewer side effects, faster recovery, and improved patient satisfaction.
Enhanced Medical Research and Drug Development: Big Data allows researchers to sift through massive amounts of data to identify trends, relationships, and new insights into diseases. By leveraging large datasets, researchers can accelerate the drug discovery process and develop targeted therapies. Real-world evidence, derived from patient data, is also used to inform regulatory decisions and bring treatments to market more efficiently.
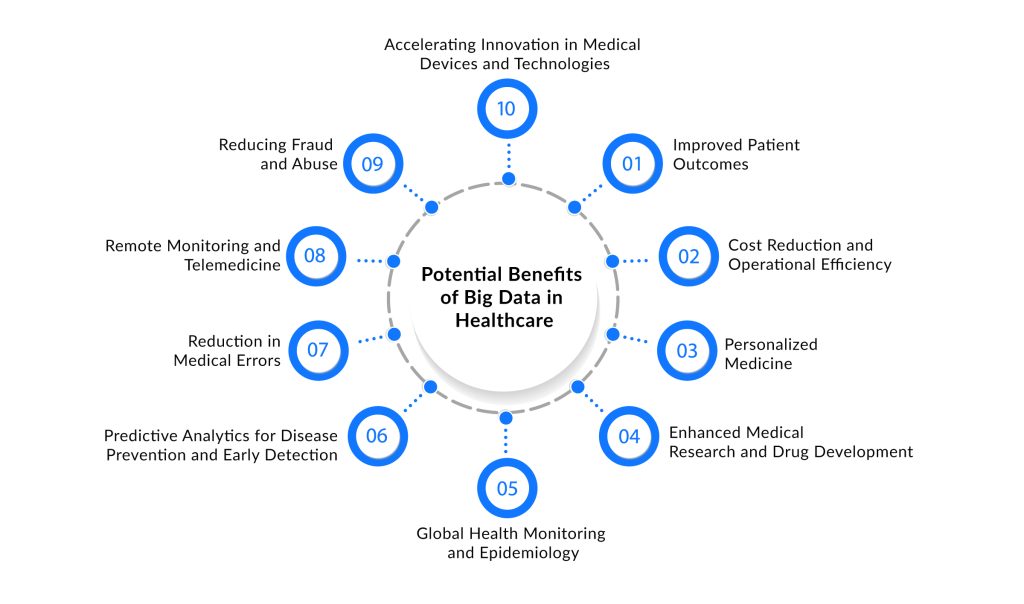
Global Health Monitoring and Epidemiology: Big Data contributes to global health monitoring by enabling the analysis of health trends on a large scale. Governments and international health organizations use Big Data to track diseases, monitor vaccination rates, and predict potential health crises. For example, the global response to the COVID-19 pandemic was informed by data analysis from multiple sources, including hospital data, mobile health apps, and global travel patterns. With Big Data, health organizations can track disease outbreaks in real time and respond more effectively, potentially saving lives and reducing the spread of infectious diseases.
Predictive Analytics for Disease Prevention and Early Detection: Big Data enables the use of predictive analytics to forecast the likelihood of diseases before they occur. By analyzing historical health data, lifestyle factors, and genetic information, healthcare providers can identify individuals at high risk for conditions like heart disease, diabetes, or cancer. Early interventions can then be implemented, which may prevent the disease from developing or mitigate its severity. For example, machine learning algorithms can predict the onset of chronic conditions by detecting subtle patterns in patient data that may not be immediately noticeable.
Reduction in Medical Errors: Big Data technologies can play a crucial role in reducing medical errors, which are a significant concern in healthcare. By providing real-time access to comprehensive patient information, healthcare professionals are less likely to make mistakes in diagnosis or treatment. Data analytics can also flag potential issues such as drug interactions, allergies, and incorrect prescriptions, helping to minimize human error. This leads to better patient safety and more effective care delivery.
Remote Monitoring and Telemedicine: With the rise of wearables and IoT devices, Big Data enables continuous patient monitoring outside the traditional healthcare settings. Patients with chronic diseases like diabetes, hypertension, or asthma can wear devices that monitor vital signs such as blood sugar levels, blood pressure, or heart rate. This real-time data is transmitted to healthcare providers, allowing for timely interventions and more accurate monitoring of disease progression. Telemedicine, which leverages Big Data, facilitates virtual consultations between patients and doctors, making healthcare more accessible and efficient, especially for patients in remote areas.
Reducing Fraud and Abuse: Big Data analytics can help detect fraudulent activities and abuse in healthcare systems. By analyzing patterns in claims data, billing information, and patient history, Big Data tools can flag unusual or suspicious activities that may indicate fraud. For example, if a provider is submitting claims for treatments or services that are inconsistent with a patient’s medical history, or if there is an unusually high volume of claims for certain procedures, it can trigger an alert for further investigation. This can save healthcare organizations billions of dollars annually and help ensure that resources are used appropriately.
Accelerating Innovation in Medical Devices and Technologies: Big Data has spurred the development of new medical technologies and devices. By analyzing vast amounts of patient data, engineers and researchers can identify areas for improvement in existing medical devices and develop innovative solutions to address unmet medical needs. For example, the data collected from continuous glucose monitors or smart inhalers helps researchers refine these devices to offer more accurate readings and improve patient compliance. Big Data accelerates the pace of innovation in medical devices, ensuring they meet the evolving needs of healthcare providers and patients.
Challenges in Implementing Big Data in Healthcare
Implementing Big Data in healthcare comes with several significant challenges, the first of which is ensuring data privacy and security. Healthcare data is inherently sensitive, containing personal and medical information that requires stringent protection under regulations such as HIPAA. With the increasing volume of data being generated, hospitals and healthcare organizations must invest heavily in advanced encryption, secure storage solutions, and robust access controls to mitigate the risk of data breaches. Any failure to protect this data not only jeopardizes patient trust but can also lead to legal and financial consequences.
Another key challenge is data quality and standardization. Healthcare data comes from a variety of sources, including electronic health records (EHRs), lab results, and wearable devices, which often use different formats and standards. This lack of uniformity makes it difficult to integrate data for comprehensive analysis. Inconsistent or incomplete data can lead to inaccurate insights and potentially harm patient outcomes. Establishing common data standards and improving the accuracy and completeness of healthcare data is crucial for the effective use of Big Data in decision-making.
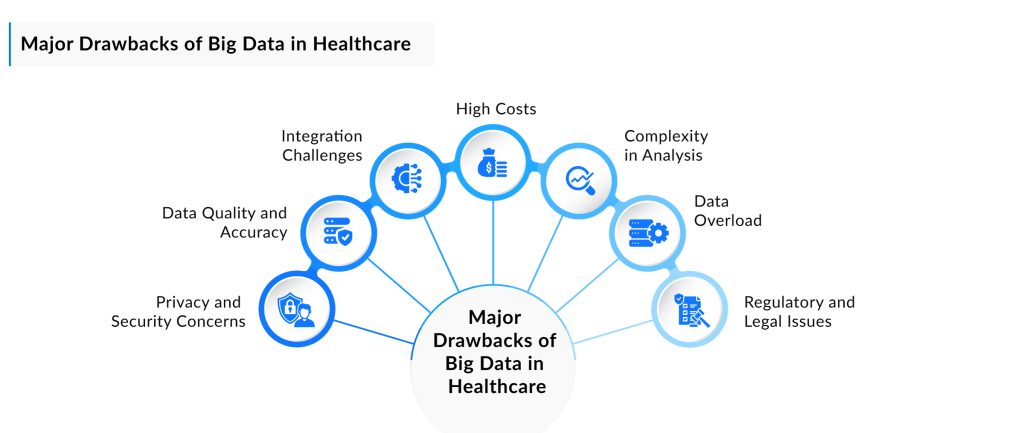
Finally, interoperability remains a significant barrier. Many healthcare organizations use disparate IT systems that are not designed to communicate with one another, creating silos of information. For Big Data initiatives to succeed, data must flow seamlessly across systems to provide a complete picture of patient health. Achieving interoperability requires collaboration between healthcare providers, technology vendors, and regulatory bodies to develop and adopt universal data standards and open interfaces, which can be time-consuming and costly.
The Future of Big Data in Healthcare
The future of Big Data in healthcare is incredibly promising, driven by advancements in artificial intelligence (AI) and machine learning. These technologies are poised to revolutionize how healthcare providers analyze and interpret vast amounts of data. AI algorithms can quickly detect patterns in patient data—such as medical histories, genetics, and lifestyle information—that would be nearly impossible for human practitioners to identify. This leads to more accurate diagnoses, better treatment plans, and proactive interventions. The integration of predictive analytics will also allow healthcare professionals to foresee health issues before they become critical, enabling preventative care that improves patient outcomes and reduces healthcare costs.
Furthermore, the continuous development of wearable devices and IoT technologies will generate real-time health data, creating opportunities for continuous health monitoring. This ongoing flow of information will allow for even more personalized and dynamic care, with healthcare providers able to monitor patients remotely and adjust treatments in real time. As data-sharing and interoperability between systems improve, healthcare providers will have a more comprehensive and unified view of patient health, fostering better collaboration and more informed decision-making. As these technologies mature, we can expect a future where Big Data seamlessly integrates into everyday healthcare, enhancing not only individual patient care but also public health management and global health research.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Aerin Medical’s RhinAer Stylus; CE Mark for Haemonetics’s VASCADE Vascular Closure Device; J&...
- Telemedicine: Can it be the future of healthcare?
- Johnson & Johnson’s Tecnis PureSee lens; Sparrow BioAcoustics’s Stethoscope Software; Better ...
- Wearable Technology in Healthcare: Major Benefits and Trends
- The Evolution and Impact of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) in Modern Healthcare