Medication Management Systems: The Key to Optimizing Pharmaceutical Care
Feb 12, 2025
Table of Contents
Medication management is a critical aspect of healthcare that ensures patients receive the right medication, in the correct dosage, at the appropriate time, and for the intended purpose. With increasing complexity in treatment regimens and rising incidences of medication errors, an effective medication management system is essential for improving patient outcomes and promoting safety in healthcare settings.
What is a Medication Management System?
A medication management system (MMS) refers to a comprehensive set of processes, tools, and technologies designed to optimize the entire lifecycle of medication use, from the initial prescription and dispensing to administration and monitoring. Its purpose is to ensure that patients receive the correct medications in the proper dosages, at the right times, and in the most efficient way possible. By streamlining medication-related workflows, MMS improves clinical outcomes, enhances patient safety, and reduces the potential for medication errors, which can lead to adverse drug events (ADEs) or suboptimal treatment.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- 7 Key Technologies Pioneering Cybersecurity in the Healthcare Sector
- How is Telepsychiatry Fulfilling the Evolving Mental Healthcare Demand?
- Telehealth: Opportunities and Hurdles in Virtual Healthcare Market
- How Medical Drones Are Revolutionizing Healthcare: Transforming Patient Care, Delivery, and Emerg...
- The Evolution and Impact of Surgical Cameras in Modern Medicine
MMS often integrates with existing healthcare systems, such as Electronic Health Records (EHRs) and Electronic Medical Records (EMRs), to provide a seamless, interconnected approach to medication management. This enables healthcare providers to make data-driven decisions, track medication adherence, and maintain an accurate record of the patient’s medication history.
In addition to healthcare professionals, MMS also aims to empower patients, offering them tools to actively manage their own medication regimens. Features like medication reminders, side effect information, and patient education modules help foster a collaborative approach to healthcare, where patients are informed and involved in their treatment decisions.
Key Components of a Medication Management System
A medication management system consists of several interconnected components that ensure the safe and effective use of medications. The process begins with prescription and order entry, where physicians use electronic health records or computerized provider order entry (CPOE) systems to prescribe medications. These digital platforms include built-in safety features like allergy alerts, drug interaction warnings, and dosage recommendations, significantly reducing prescription errors. By digitizing this process, healthcare providers can ensure accuracy while streamlining communication between doctors, pharmacists, and nurses.
The medication dispensing stage ensures that prescribed medications are accurately distributed to patients. Automated dispensing systems (ADS), barcode verification, and robotic pharmacy solutions help reduce human errors in dispensing. Pharmacies use inventory management tools to track stock levels, prevent shortages, and minimize wastage. With digital prescriptions directly integrated into pharmacy databases, the risk of misinterpretation or illegible handwriting errors is significantly reduced, ensuring patients receive the correct medication in the right dosage.
Once the medication is dispensed, the administration process involves ensuring that the right patient receives the right medication at the right time. Barcoded medication administration (BCMA) technology allows nurses to scan patient wristbands and medication labels to verify the match before administering the drug. This step reduces the chances of wrong-patient errors and enhances adherence to treatment protocols. Additionally, smart infusion pumps help regulate intravenous medication delivery, preventing over- or under-dosage.
Finally, monitoring and patient engagement play a crucial role in ensuring treatment success. Healthcare providers continuously track medication adherence, side effects, and patient responses using real-time monitoring tools and clinical decision support systems (CDSS). Patients also benefit from mobile apps and digital reminders that help them stick to their medication schedules. With AI-powered analytics and predictive modeling, clinicians can adjust treatments proactively, ensuring optimal patient outcomes while minimizing adverse drug reactions.
Benefits of a Medication Management System
A MMS significantly enhances patient safety by minimizing medication errors, ensuring accurate prescriptions, and preventing adverse drug events. Automated features such as real-time alerts for drug interactions, allergy checks, and dosage recommendations help healthcare providers make informed decisions. Barcode scanning and eMAR further reduce human errors by verifying the correct patient, medication, dosage, and timing before administration. These safety measures help prevent potentially life-threatening mistakes and improve overall patient outcomes.
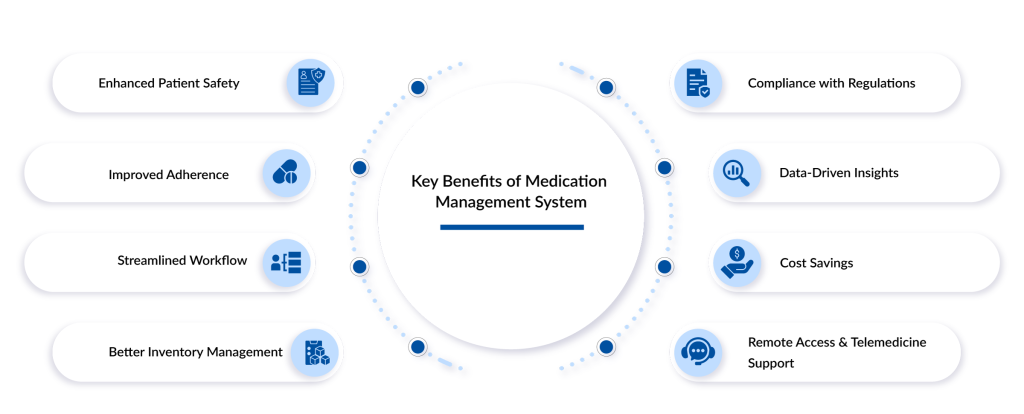
Another key benefit of an MMS is the improvement in medication adherence, especially for patients with chronic conditions. Non-adherence to prescribed medications is a common issue that leads to worsening health conditions and increased hospital readmissions. An MMS can integrate with mobile apps, automated reminders, and patient portals to keep patients on track with their medication schedules. By providing clear instructions and easy access to medication history, patients are more likely to follow their treatment plans, leading to better disease management and reduced healthcare costs.
Additionally, an MMS streamlines workflows for healthcare providers by automating time-consuming tasks such as prescription management, inventory tracking, and compliance documentation. Pharmacies and hospitals can efficiently manage medication stocks, reducing waste and preventing shortages. The system also ensures regulatory compliance by maintaining detailed records of medication usage, helping healthcare facilities meet industry standards. By improving operational efficiency, healthcare providers can focus more on patient care rather than administrative burdens.
Medication Management Systems: Market Dynamics and Prominent Companies
The medication management system market is witnessing significant growth, driven by the increasing adoption of digital healthcare solutions, the rising prevalence of chronic diseases, and the growing need to reduce medication errors. As per DelveInsight analysis, the medication management system is expected to grow at a CAGR of 11.20% during the forecast period from 2022 to 2032 to reach USD 8 billion by 2032.
With healthcare facilities prioritizing patient safety, regulatory compliance, and operational efficiency, advanced medication management systems have become essential. These systems help streamline medication prescription, dispensing, and administration while integrating with EHRs and pharmacy management systems to ensure seamless workflows. The rise in telemedicine, AI-driven prescription automation, and smart medication adherence tools are further fueling market expansion.
Governments and healthcare organizations worldwide are investing in e-prescribing, automated dispensing systems, and real-time medication tracking to enhance patient outcomes and reduce hospital readmissions. Strict regulatory frameworks, such as the U.S. FDA’s guidelines on medication safety and Europe’s Falsified Medicines Directive, are pushing healthcare providers to adopt robust medication management solutions. However, market growth is somewhat restrained by high implementation costs, data security concerns, and interoperability challenges between different healthcare IT systems.

Several key players dominate the medication management system market, each offering innovative solutions tailored to hospitals, pharmacies, and long-term care facilities. Key companies such as McKesson Corporation, GE HealthCare, BD, Omnicell, Inc., RedSail Technologies, LLC, BestRx, Capsa Healthcare, STOCKART, CareMeds Ltd., Swisslog Healthcare, Bluesight, Ubie Inc., ARxIUM, A-S Medication Solutions, DrFirst, Medical Information Technology, Inc., WellSky, Orion Health, Deenova S.r.l., Dedalus S.p.A., and others are currently active in the market.
With continued technological advancements, strategic partnerships, and regulatory shifts, the medication management system market is poised for sustained growth.
The Future of Medication Management Systems
The future of medication management systems is set to be driven by advanced technologies such as Artificial Intelligence, Machine Learning, and predictive analytics. AI-powered algorithms can analyze vast amounts of patient data to identify trends, predict potential medication errors, and recommend personalized treatment plans. Integration with wearable devices and Internet of Things technology will allow real-time monitoring of patients’ medication adherence, ensuring timely interventions for those at risk of missing doses or experiencing adverse reactions. Additionally, blockchain technology is emerging as a secure way to manage medication records, reducing the risk of fraud and enhancing transparency in the pharmaceutical supply chain.
Telehealth and remote patient monitoring are also expected to play a significant role in medication management, particularly for elderly and chronic disease patients. Mobile applications with AI-driven chatbots and virtual pharmacists will provide instant medication guidance, dosage reminders, and side effect monitoring. Moreover, robotic automation in hospital pharmacies and smart pill dispensers at home will further streamline the medication administration process, reducing human errors. As these innovations continue to evolve, the future of MMS will not only improve patient safety and efficiency but also make healthcare more accessible and personalized.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Medical Odyssey: Solving the Dynamic Puzzle of Global Tourism Market
- 7 Key Technologies Pioneering Cybersecurity in the Healthcare Sector
- How is Telepsychiatry Fulfilling the Evolving Mental Healthcare Demand?
- How Healthcare Apps are Adding New Perspectives to the Healthcare Industry?
- The Evolution and Impact of Electronic Health Records (EHRs) in Modern Healthcare