7 Hidradenitis Suppurativa Drugs Set to Hit the Market in the Next 5 Years
Sep 13, 2024
Table of Contents
Currently, leading hidradenitis suppurativa drugs on the market include UCB Biopharma’s BIMZELX (bimekizumab), Novartis’ COSENTYX (secukinumab), and AbbVie/Eisai’s HUMIRA (adalimumab). HUMIRA dominated the market until 2023, despite its US composition-of-matter patent expiring in December 2016. AbbVie maintained a stronger US patent defense than Europe, ensuring extended exclusivity. However, in June 2023, the European Commission approved COSENTYX, an IL-17A monoclonal antibody, for adults with moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa who did not respond to conventional systemic treatments. The FDA followed suit in October 2023, approving it for the same indication. In April 2024, UCB received marketing authorization from the European Commission for BIMZELX for similar treatment in adults with inadequate responses to systemic therapies.
The hidradenitis suppurativa drug market remains underserved, but it is expected to grow, supporting multiple blockbuster treatments, such as rheumatoid arthritis. If oral therapies demonstrate efficacy comparable to subcutaneous injections, they could become a preferred option in this overlooked market.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Prometic bags $50M; Vedanta receives $12M; Humira biosimilar deal
- Could Hidradenitis Suppurativa Be Another Psoriasis?
- How Novel Therapies Could Transform the Ulcerative Colitis Treatment Landscape
- HUMIRA Biosimilars in the US: The Talk of the Psoriatic Arthritis Treatment Market
- Novartis Cosentyx: First Biologic Hidradenitis Suppurativa Treatment After Almost Ten Years
Promising Hidradenitis Suppurativa Drugs to be Launch in the Next 5 Years
In the next five years, hidradenitis suppurativa treatment options are expected to advance significantly with the development of targeted biologics and novel immunomodulatory therapies. The research will likely focus on precision medicine approaches, improving personalized treatments, and exploring gene therapies to better address the underlying inflammatory mechanisms of hidradenitis suppurativa.
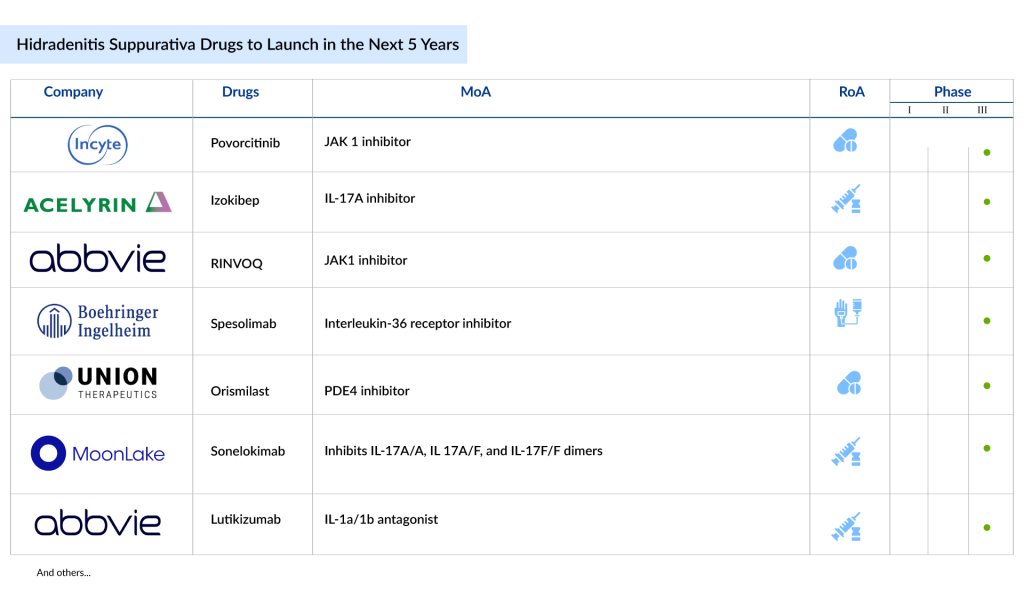
Some of the hidradenitis suppurativa drugs in the pipeline that can be launched in the coming 5 years include Povorcitinib (Incyte Corporation), Sonelokimab (MoonLake Immunotherapeutics), Izokibep (ACELYRIN), Spesolimab (Boehringer Ingelheim), Orismilast (UNION Therapeutics), RINVOQ (AbbVie), and Lutikizumab (AbbVie).
Let’s deep dive into the the assessment of these hidradenitis suppurativa drugs in detail.
Incyte Corporation’s Povorcitinib
Povorcitinib, developed by Incyte Corporation, is a targeted JAK1 inhibitor that effectively diminishes abscesses and inflammatory nodules in patients with moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa. This oral hidradenitis suppurativa medication is currently being evaluated in three Phase III clinical trials (STOP-HS studies) for its efficacy in treating moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa, with results expected in 2025. Povrocitinib may become the first oral medication to enter this rapidly expanding market. The outcomes of Povrocitinib outperform those of RINVOQ. The company also projects that povorcitinib could be launched for this condition by 2026-2027.
MoonLake Immunotherapeutics’ Sonelokimab
Sonelokimab (M1095) is an experimental humanized Nanobody weighing approximately 40 kDa, made up of three VHH domains connected by flexible glycine-serine linkers. It binds with high affinity to IL-17A and IL-17F through two of its domains, effectively blocking the formation of IL-17A/A, IL-17A/F, and IL-17F/F dimers.
The company has finished a Phase II trial for sonelokimab to treat moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa and is now assessing the drug in two Phase III hidradenitis suppurativa clinical trial studies. The 24-week topline results were shared at the AAD 2024 annual meeting. This Phase III program follows MoonLake’s announcement in February 2024 of a positive outcome from end-of-Phase II discussions with the US FDA and favorable feedback from the EMA, which endorsed MoonLake’s plan for advancing to Phase III.
The Phase III VELA program will involve 800 patients across VELA-1 and VELA-2. This is the first Phase III study in hidradenitis suppurativa to use HiSCR75 as the primary endpoint. The company anticipates topline results for the primary endpoint of the Phase III VELA trial at Week 16, along with data on other endpoints, to be available by mid-2025.
ACELYRIN’s Izokibep
Izokibep is a small protein therapeutic designed to effectively inhibit IL-17A with high potency due to its tight binding affinity. Its small molecular size, about one-tenth that of a monoclonal antibody, allows for significant tissue penetration, and its albumin-binding domain helps extend its half-life. Hidradenitis suppurativa clinical trial results suggest that these distinctive features of izokibep may offer substantial and unique benefits for patients, including the resolution of key disease symptoms.
In August 2024, ACELYRIN revealed that its Phase III trial of izokibep for hidradenitis suppurativa met the primary goal of HiSCR75 at 12 weeks. The latest data from trials show that izokibep achieves clinical responses comparable to those of next-generation IL-17 inhibitors. Moreover, targeting IL-17A with higher potency has been shown to provide similar or better clinical outcomes compared to broader IL-17 inhibitors, while avoiding associated safety issues. Izokibep is now being tested in advanced trials for moderate-to-severe hidradenitis suppurativa, moderate-to-severe psoriatic arthritis, and noninfectious uveitis. Additionally, the company has shifted its pipeline strategy to emphasize lonigutamab for thyroid eye disease, which is expected to extend its financial runway.
AbbVie’s RINVOQ
RINVOQ (upadacitinib), is a selective JAK1 inhibitor developed by AbbVie. JAKs are intracellular enzymes that relay signals from cytokine or growth factor receptors on the cell membrane, impacting hematopoiesis and immune cell functions. They achieve this by phosphorylating and activating Signal Transducers and Activators of Transcription (STATs) within the signaling pathway, thus influencing cellular activity and gene expression. Upadacitinib targets JAKs, thereby blocking the phosphorylation and activation of STATs and modulating the signaling pathway.
In August 2019, the FDA approved RINVOQ for treating psoriatic arthritis. By December 2021, it received FDA approval for managing moderate to severe rheumatoid arthritis. In March 2022, AbbVie announced that the FDA had approved RINVOQ for adults with moderately to severely active ulcerative colitis who did not respond adequately or were intolerant to one or more TNF blockers. Then, in May 2023, the FDA approved RINVOQ as a once-daily pill for moderately to severely active Crohn’s disease in adults.
In July 2023, AbbVie announced that the first patient had been treated in the Phase III Step-Up HS study. This trial is assessing RINVOQ for adults and adolescents with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa who have not responded to anti-TNF therapy or another approved non-anti-TNF treatment for hidradenitis suppurativa.
AbbVie’s Lutikizumab
Lutikizumab (ABT-981) is an investigational hidradenitis suppurativa drug with dual-variable domains that targets interleukin (IL) 1α and 1β. It is currently being researched for use in various immune-mediated conditions, such as hidradenitis suppurativa and ulcerative colitis. Research indicates that IL 1α and 1β levels are increased in hidradenitis suppurativa lesions. However, Lutikizumab is still under investigation and has not yet received approval from regulatory agencies, so its safety and effectiveness have not been confirmed.
In January 2024, AbbVie announced Phase II results indicating that adults with moderate to severe hidradenitis suppurativa who had not responded to anti-TNF therapy showed better response rates when treated with lutikizumab (ABT-981) at doses of 300 mg every other week or 300 mg weekly, achieving 59.5 percent (nominal p=0.027) and 48.7 percent (nominal p=0.197) respectively, compared to 35.0 percent for placebo in the primary endpoint of achieving HS Clinical Response (HiSCR 50) at week 16. As a result, AbbVie moved lutikizumab into Phase III of its clinical development program for hidradenitis suppurativa.
Boehringer Ingelheim’s Spesolimab
Spesolimab is a novel anti-IL-36 receptor antibody developed by Boehringer Ingelheim. It is currently being studied for various auto-inflammatory diseases linked to the IL-36 pathway, with generalized pustular psoriasis as the primary focus. Marketed under the name SPEVIGO, it is approved for treating GPP flares in adults across nearly 40 countries, including the USA, Japan, Mainland China, and the European Union, and is under evaluation by additional regulatory bodies. These approvals and reviews are based on encouraging results from the EFFISAYIL 1 Phase II trial. Spesolimab is currently being studied in Phase II for its potential to treat other skin conditions driven by IL-36, including Pyoderma Gangrenosum, Hidradenitis Suppurativa, and Netherton Syndrome.
What Lies Ahead in Hidradenitis Suppurativa Drug Treatment Space?
The future of hidradenitis suppurativa drug treatment is poised for significant advancements as research and development efforts intensify. Biologics have become essential in managing moderate-to-severe cases, potentially reshaping treatment strategies. Currently, the only biologics approved by the US FDA for treating hidradenitis suppurativa are HUMIRA (adalimumab) and COSENTYX (secukinumab). BIMZELX (bimekizumab) has been approved for this condition in Europe, and the US FDA accepted a supplemental Biologics License Application (sBLA) for BIMZELX in April 2024, which is now under review for the treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa.
HUMIRA, AbbVie’s leading product, exemplifies how a market monopoly can be maintained for a prolonged period. However, the introduction of biosimilars has significantly impacted HUMIRA’s sales in the 7MM. In Europe and Japan, HUMIRA biosimilars were introduced in 2018 and 2021, respectively. In January 2023, AMJEVITA became the first HUMIRA biosimilar launched in the US.
However, the limitations of existing therapies, including variable patient responses and significant side effects, have driven the need for more targeted and effective treatments. Promising developments are on the horizon, including JAK inhibitors, IL-17 inhibitors, and other biologics that target specific inflammatory pathways implicated in HS. These new therapies aim to offer more personalized and effective management of the condition, potentially reducing the severe pain and scarring associated with hidradenitis suppurativa.
Additionally, the focus is shifting toward understanding the genetic and immunological underpinnings of hidradenitis suppurativa to develop more precise therapies. This includes exploring the role of the microbiome, genetics, and environmental factors in disease progression. As clinical trials progress, we can expect the approval of novel therapies that not only target the symptoms but also address the underlying causes of hidradenitis suppurativa. With the integration of advanced biomarkers and personalized medicine approaches, the future treatment of hidradenitis suppurativa could significantly improve patient outcomes, offering hope for those suffering from this chronic and often debilitating condition.

FAQs
Currently, leading hidradenitis suppurativa drugs on the market include UCB Biopharma’s BIMZELX (bimekizumab), Novartis’ COSENTYX (secukinumab), and AbbVie/Eisai’s HUMIRA (adalimumab).
Some of the hidradenitis suppurativa drugs in the pipeline that can be launched in the coming 5 years include Povorcitinib (Incyte Corporation), Sonelokimab (MoonLake Immunotherapeutics), Izokibep (ACELYRIN), Spesolimab (Boehringer Ingelheim), Orismilast (UNION Therapeutics), RINVOQ (AbbVie), and Lutikizumab (AbbVie).
The hidradenitis suppurativa market is currently underserved. It is anticipated that, similar to rheumatoid arthritis, hidradenitis suppurativa has a sufficiently large market potential to support the co-existence of several blockbuster medications. According to DelveInsight’s analysis, the market size of hidradenitis suppurativa in the 7MM was USD 1.4 billion in 2023, and it is expected to increase by 2034.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Gilead faces lawsuit; Herceptin stalled; Lilly revs up, Abemaciclib gets nod; Key Humira patent g...
- Novartis Cosentyx: First Biologic Hidradenitis Suppurativa Treatment After Almost Ten Years
- Could Amgen’s Biosimilar Wezlana Pose a Challenge to Johnson & Johnson’s Stelara
- Analyzing the Growth of the Biosimilar Market Through Years
- Off-label Therapies Dominating the Behcet’s Syndrome Treatment Market