8 Emerging Obesity Trends Transforming Therapeutics Segment
Mar 12, 2025
Table of Contents
Obesity is the second leading cause of preventable death and is linked to numerous inflammatory conditions, which contribute to diseases like cardiovascular disease, diabetes, respiratory issues, mental health disorders, hypertension, obstructive sleep apnea, cancer, and high cholesterol. This poses a significant public health challenge that has been worsening over the past fifty years, with obesity rates climbing among both children and adults in developed and developing countries.
As reported by DelveInsight, around 188 million people across the seven major markets were living with obesity in 2023, with this figure projected to increase by 2034. Obesity rates in the United States have been steadily rising, particularly among the adult population. The highest prevalence of obesity in 2023 was observed in both adults (ages 19 and older) and children (ages 5-19). These numbers are expected to grow at a moderate CAGR for both groups.
Downloads
Click Here To Get the Article in PDF
Recent Articles
However, as the prevalence of obesity continues to rise, driven by factors such as sedentary lifestyles, poor dietary habits, and genetic predispositions, the market for obesity treatments is expanding and diversifying.
8 Key Obesity Trends Shaping the Landscape
The obesity treatment market has expanded rapidly in recent years, driven by rising awareness, technological advancements, and the introduction of new therapeutic modalities. Let’s explore the key obesity trends shaping the therapeutics segment.
Growth of Pharmacotherapy Options for Obesity
One of the most significant trends in obesity is the growing number of pharmacotherapy options. Historically, the market was dominated by a few obesity drugs, but recent years have seen a surge in new medications that target different aspects of obesity. For example, GLP-1 receptor agonists like Novo’s WEGOVY (semaglutide) have gained popularity due to their effectiveness in promoting weight loss by regulating appetite and glucose metabolism.
WEGOVY is prescribed in conjunction with a low-calorie diet and increased physical activity. It is administered as a weekly subcutaneous injection, providing convenience and consistency in obesity management. In June 2021, the FDA approved WEGOVY for long-term weight management in adults, marking a major milestone in obesity treatment. Since then, WEGOVY has become a key player in the profitable obesity market, which, according to DelveInsight, is projected to reach $12 billion in the US by 2034.
As obesity rates continue to rise globally, the expansion of pharmacotherapy options has become increasingly important. Newer drugs, such as those combining multiple mechanisms of action, offer enhanced effectiveness and may provide an alternative for individuals who struggle with traditional weight-loss methods like diet and exercise.
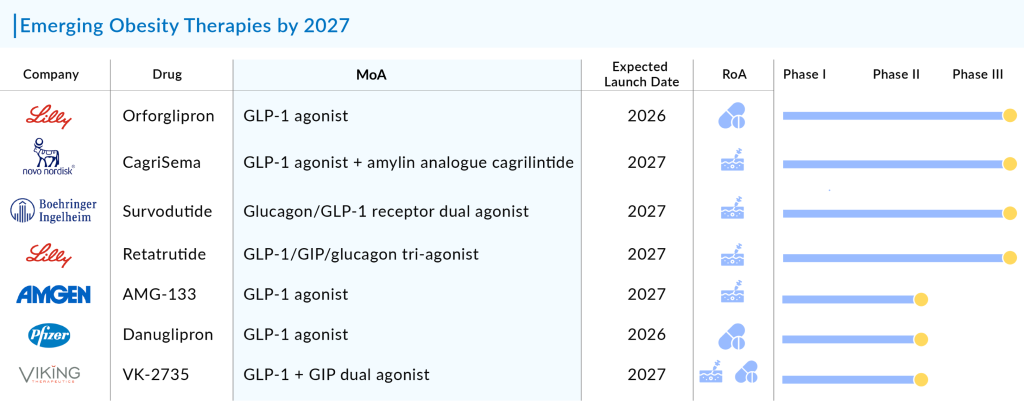
The most promising therapies that are set to hit the obesity drug market by 2027 are Novo Nordisk’s Semaglutide oral, Eli Lilly and Company’s Tirzepatide, Saniona’s Tesomet, Raziel Therapeutics’ RZL-012, Empros Pharma’s EMP16, D&D Pharmatech’s DD01, Zealand Pharma’s ZP 8396, ERX Pharmaceuticals’ ERX-1000, Zealand Pharma’s Survodutide, Sciwind Biosciences’ Ecnoglutide, Carmot Therapeutics’ CT-868, D&D Pharmatech’s DD01, and others.The expected launch of these new obesity medications, especially the latest GLP-1 agonists, is set to greatly impact both the field of obesity treatment and the market for GLP-1 agonists.
Personalized and Precision Medicine for Obesity
Another obesity trend that is revolutionizing the sector is personalized and precision medicine. Personalized and precision medicine for obesity represents a transformative approach to managing and treating this complex condition. Unlike traditional one-size-fits-all treatments, personalized medicine tailors interventions based on an individual’s genetic, environmental, and lifestyle factors. This method involves assessing a person’s unique genetic makeup to identify specific risk factors and potential responses to various treatments. For instance, genetic testing can reveal predispositions to obesity-related conditions and guide the selection of targeted therapies, dietary recommendations, and exercise regimens that are more effective for the individual.
Precision medicine also emphasizes the integration of advanced technologies, such as wearable devices and digital health tools, to monitor real-time data and adjust treatment plans dynamically. This continuous feedback loop allows for more accurate tracking of progress and personalized adjustments to strategies, enhancing overall effectiveness. By focusing on individual variability, personalized and precision medicine aims not only to improve treatment outcomes but also to reduce the risk of obesity-related complications, offering a more nuanced and effective approach to combating this global health issue.
Digital Health and Telemedicine for Obesity
Digital health and telemedicine are among the major obesity trends that are changing the course of managing obesity. Digital health and telemedicine are transforming the management of obesity by offering innovative and accessible solutions. With the rise of wearable devices and mobile apps for obesity, individuals can now track their physical activity, dietary intake, and weight in real-time. These tools provide valuable data for healthcare providers to monitor progress and adjust treatment plans accordingly. Telemedicine enhances this by facilitating remote consultations with specialists, enabling patients to receive personalized advice and support without the need for frequent in-person visits. This approach not only makes healthcare more convenient but also allows for continuous and comprehensive management of obesity.
Moreover, digital health platforms for obesity often integrate educational resources and behavioral health support, helping individuals develop healthier habits and overcome psychological barriers related to weight management. Online support groups and virtual counseling can provide motivation and accountability, which are crucial for long-term success. By leveraging these technologies, patients can benefit from a more tailored and engaging approach to obesity treatment, ultimately improving outcomes and promoting a healthier lifestyle.
Several companies such as Noom, MyFitnessPal, Weight Watchers, Lose It!, Slimming World, Curv, Rise, HealthifyMe, BariatricPal, Carb Manager, Lumen, BetterMe, Yazio, Cronometer, Healthi, and others are currently developing mobile apps for obesity. As these apps advance, their capacity to incorporate different support systems will strengthen their role in managing obesity, turning them into essential tools for both individuals and healthcare providers.

Bariatric Surgery and Non-Invasive Procedures for Obesity Management
Bariatric surgery and non-invasive procedures are two prominent approaches to managing obesity, each with distinct benefits and considerations. Bariatric surgery, such as gastric bypass or sleeve gastrectomy, involves surgical intervention to reduce stomach size or alter the digestive tract, leading to significant weight loss and improvement in obesity-related conditions. This option is often recommended for individuals with severe obesity who have not achieved sustainable weight loss through other means. While bariatric surgery can offer substantial long-term benefits, it requires careful consideration of potential risks, long-term lifestyle changes, and ongoing medical follow-up.
Non-invasive procedures, on the other hand, provide alternative solutions without the need for surgery. These include options like endoscopic weight loss procedures, such as the intragastric balloon, which temporarily reduces stomach capacity, and various behavioral therapies aimed at lifestyle modifications. These approaches generally have lower risk profiles compared to surgical interventions and can be effective for individuals with moderate obesity or those looking for less permanent solutions. Non-invasive methods often focus on gradual, sustainable weight loss and can be tailored to individual needs, though they may require ongoing adherence to lifestyle changes for long-term success.
Focus on Behavioral and Lifestyle Interventions to Manage Obesity
Behavioral and lifestyle interventions are pivotal in managing obesity, as they address the root causes and promote sustainable, long-term health changes. These interventions emphasize altering daily habits and behaviors that contribute to weight gain. Strategies such as cognitive-behavioral therapy can help individuals recognize and modify unhealthy eating patterns and emotional triggers for overeating. Additionally, incorporating regular physical activity into one’s routine and making gradual, achievable changes to diet are fundamental aspects of these interventions. For instance, setting realistic goals for weight loss and adopting a balanced diet that includes whole foods can significantly improve weight management.
Moreover, lifestyle interventions often involve support systems and ongoing monitoring to ensure adherence and progress. Community-based programs, online support groups, and regular check-ins with healthcare professionals can provide motivation and accountability. Education on portion control, understanding nutritional labels, and developing healthy cooking skills also play a critical role in fostering a healthier lifestyle. By focusing on these behavioral and lifestyle changes, individuals can create a more effective and personalized approach to managing obesity, ultimately leading to better overall health and well-being.
Rising Demand for Combination Obesity Therapies
The rising demand for combination obesity therapies reflects a growing recognition that obesity is a complex, multifaceted condition requiring a multifaceted approach. Traditional weight loss strategies, such as diet and exercise, often fall short for many individuals, prompting healthcare providers and researchers to explore more integrated solutions. Combination therapies, which blend different modalities such as medications, behavioral interventions, and lifestyle changes, are increasingly seen as a more comprehensive approach to managing obesity. This trend is driven by the need for more personalized treatments that address various aspects of obesity, from metabolic dysfunction to psychological factors.
Over 100 obesity medications are currently in development, with a strong focus on GLP-1 receptor agonists. These drugs are intended to manage type 2 diabetes and obesity by lowering blood glucose levels and regulating metabolism. Various companies are working to enhance existing treatments and develop new obesity therapies.
This includes investigating combinations of GLP-1 with other entero-pancreatic hormones, such as glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide (GIP), glucagon, and amylin. These combinations are being tested in clinical trials to potentially increase the effectiveness of GLP-1 receptor agonists in promoting weight loss and providing cardiovascular benefits.
Several pharmaceutical companies, including Biolexis Therapeutics, Arrowhead Pharmaceuticals, and Viking Therapeutics, have presented their pre-clinical research at the American Diabetes Association (ADA) 2024 conference. These presentations are crucial for addressing the intricate challenges in modern obesity management, underscoring a collective commitment to improving treatment strategies and enhancing patient outcomes.
As awareness of obesity’s impact on overall health continues to increase, there is a corresponding rise in demand for innovative treatment options. Combination therapies offer the potential for enhanced efficacy by targeting multiple pathways involved in weight regulation. For instance, combining appetite-suppressing medications with agents that improve metabolic health can provide a more holistic approach to weight management. Furthermore, advancements in biotechnology and personalized medicine are fueling the development of tailored combination therapies, promising better outcomes for individuals struggling with obesity. The emphasis on combination therapies represents a significant shift towards more nuanced and effective treatment paradigms in the battle against obesity.
Regulatory and Reimbursement Landscape in Obesity
The regulatory and reimbursement landscape for obesity treatment has evolved significantly in recent years, reflecting a growing recognition of obesity as a complex, chronic disease rather than just a lifestyle issue. Regulatory agencies such as the FDA have approved a range of pharmacological treatments and medical devices aimed at managing obesity, highlighting the importance of evidence-based interventions.
For instance, In November 2023, the FDA approved Eli Lilly’s ZEPBOUND (tirzepatide) injection, for the treatment of obesity that activates both GIP and GLP-1 hormone receptors. However, these treatments often face rigorous scrutiny and lengthy approval processes, which can delay patient access to new therapies. Additionally, the approval of newer treatments frequently requires robust clinical data demonstrating not only efficacy but also long-term safety.
On the reimbursement front, the landscape is similarly complex. Coverage for obesity treatments varies widely among insurers and healthcare systems. While some public and private payers have begun to offer coverage for obesity-related medications and surgical procedures, many still have restrictive policies or limited benefits, reflecting ongoing debates about cost-effectiveness and long-term outcomes. Efforts to advocate for broader coverage are ongoing, with an emphasis on demonstrating the overall economic value of obesity management in reducing comorbid conditions and improving quality of life. The interplay between regulatory approvals and reimbursement policies will continue to shape the accessibility and adoption of obesity treatments in the coming years.
Emphasis on Preventive Measures for Obesity
Emphasizing preventive measures for obesity is crucial in addressing the growing epidemic and its associated health risks. Prevention starts with fostering healthy lifestyle habits from a young age, including balanced nutrition and regular physical activity. Schools and communities can play a pivotal role by integrating comprehensive health education programs that promote an understanding of healthy eating and the benefits of exercise. Encouraging family involvement in meal planning and physical activities can create supportive environments that make adopting healthier choices easier and more enjoyable.
Additionally, preventive strategies should extend to public policies and urban planning to create environments that support healthy living. This includes ensuring access to affordable, nutritious food and creating safe, accessible spaces for physical activity. Healthcare providers also have a role in prevention by offering regular screenings, personalized advice, and support for maintaining a healthy weight. By prioritizing these preventive measures, society can mitigate the impact of obesity, reduce the prevalence of related chronic conditions, and enhance overall public health.
Conclusion: Navigating the Future
The obesity treatment market is at a pivotal moment, characterized by unprecedented advancements and evolving obesity trends. As new pharmacotherapies, personalized treatment approaches, and digital health tools gain prominence, the landscape of obesity management is becoming increasingly dynamic and multifaceted. These developments offer hope for more effective and individualized treatments, potentially improving outcomes for millions of people struggling with obesity.
However, the path forward is not without challenges. The integration of new treatments into clinical practice requires careful consideration of cost-effectiveness, long-term outcomes, and patient accessibility. Additionally, addressing the broader social and environmental determinants of obesity remains crucial. A multifaceted approach that includes prevention, early intervention, and a focus on holistic well-being will be essential in tackling the obesity epidemic.
Looking ahead, the obesity treatment market will likely see continued innovation and refinement, driven by ongoing research and a deeper understanding of the disease. Collaboration between researchers, healthcare providers, policymakers, and patients will be key to advancing treatment options and improving public health outcomes. As the field evolves, the commitment to addressing both the immediate and root causes of obesity will be critical in shaping a healthier future for individuals and communities worldwide.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Redefining Liver Disease in the Metabolic Era: From NASH to MASH and the Rise of Obesity‐targeted...
- FDA Grants Priority Review to Merck’s Application for KEYTRUDA Plus Padcev; Roche and Carmot Ther...
- Body Contouring Devices: Understanding the Key Factors Determining the Market Growth and Evolving...
- Booming Healthcare sector in MENA: Lucrative opportunity for Global pharma players
- Digestive Health Products: Exploring the Market Dynamics and Key Factors Driving the Demand