The Protein Chip: Revolutionizing Protein Analysis and Discovery
Sep 04, 2024
Table of Contents
In the rapidly evolving field of biotechnology, the quest to understand the complexity of proteins and their functions has led to the development of innovative tools and technologies. One such breakthrough is the protein chip, a powerful tool that has transformed the landscape of protein analysis.
What Are Protein Chips?
Protein chips are an innovative technology that utilizes proteins as a key component of a diagnostic or analytical tool. These chips function similarly to traditional microarrays but leverage the specificity and binding capabilities of proteins to detect and quantify various biological molecules. By immobilizing proteins on a solid surface, researchers can create a high-throughput platform for studying protein interactions, enzyme activities, and other biochemical processes. This technology is valuable in fields such as biomarker discovery, drug development, and personalized medicine.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Biochips in Healthcare: 8 Groundbreaking Applications Shaping the Industry
- Gene Therapy’s Emergence: The “New” approach for Huntington’s disease
- FDA Approves Abbott’s Spinal Cord Stimulation Systems; Regen Lab Received CE Certification for Th...
- Navigating the Healthcare Horizon: Odyssey of Mergers, Funding, and Acquisitions in 2024
- Opportunities and Challenges for Cell and Gene Therapies
One of the significant advantages of protein chips is their ability to provide detailed information about protein function and interactions in a high-throughput manner. They can be used to analyze complex biological samples, identify potential disease markers, and screen for therapeutic targets. Additionally, protein chips have applications in clinical diagnostics, where they can be used to detect specific proteins associated with diseases or to monitor changes in protein levels over time. As the technology continues to evolve, protein chips are likely to become even more integral to research and clinical practice, offering new insights into the molecular mechanisms underlying health and disease.
How Does a Protein Chip Work?
The fundamental principle behind protein chips is the ability to capture and analyze proteins with high specificity and sensitivity. Here’s a step-by-step overview of how protein chips work:
Protein Immobilization: Proteins are attached to a solid surface in a systematic array. This can be achieved using various techniques, including covalent bonding or physical adsorption.
Sample Application: Biological samples, such as serum, plasma, or cell lysates, are applied to the protein chip. These samples contain a mixture of proteins, some of which will bind to the proteins on the chip.
Detection: After incubation, the unbound proteins are washed away. The bound proteins are then detected using various methods, such as fluorescence, chemiluminescence, or colorimetric assays. Specific binding events can be quantified to provide information about protein expression levels, interactions, and modifications.
Data Analysis: The data generated from the chip is analyzed using specialized software. This analysis helps in identifying patterns, making comparisons, and drawing conclusions about the proteins in the sample.
Applications and Challenges of Protein Chips
Protein chips represent a transformative technology in the field of proteomics, enabling high-throughput analysis of protein interactions and functions. These chips consist of a solid surface onto which various proteins are immobilized in an array format. Researchers use protein chips to study protein expression levels, identify protein-protein interactions, and investigate post-translational modifications. This technology facilitates comprehensive biomarker discovery, which is crucial for understanding disease mechanisms, developing targeted therapies, and personalizing medicine.
One of the key applications of protein chips is in biomarker discovery for diseases such as cancer and neurodegenerative disorders. By analyzing protein expression profiles from patient samples, researchers can identify potential biomarkers for early diagnosis, prognosis, and therapeutic targets. This application has profound implications for precision medicine, allowing for more tailored and effective treatments based on individual protein signatures.
Despite their powerful capabilities, protein chips face several challenges. One significant issue is the complexity of protein interactions and the variability in protein expression levels. Proteins can undergo various post-translational modifications, which can complicate the interpretation of data obtained from protein chips. Additionally, the dynamic nature of protein interactions and the influence of cellular context can lead to variability in results, making it challenging to achieve consistent and reproducible outcomes.
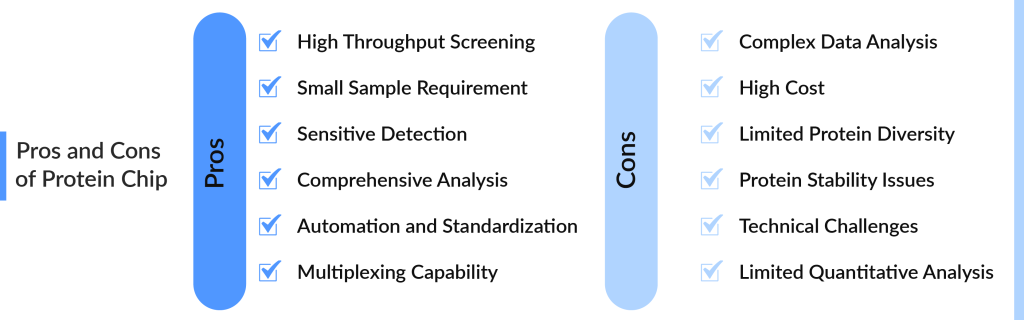
Another challenge is the high cost associated with protein chip technology. The development and maintenance of protein chips require advanced fabrication techniques and high-quality reagents, which can be expensive. Furthermore, the need for specialized equipment and expertise to analyze and interpret the data adds to the overall cost, limiting accessibility for some research groups and clinical labs.
To address these challenges, ongoing research focuses on improving the sensitivity, specificity, and reproducibility of protein chips. Advances in chip design, data analysis techniques, and standardization protocols are aimed at enhancing the reliability and utility of protein chips. Despite the hurdles, the continued development and refinement of this technology hold great promise for advancing our understanding of biology and improving healthcare outcomes.
Protein Chips Market Outlook
Protein chips are becoming an indispensable tool in drug discovery, biomarker identification, and disease diagnostics. As pharmaceutical companies and research institutions increasingly focus on understanding protein interactions and functions at a molecular level, the demand for protein chips is expected to rise. This technology enables the simultaneous analysis of thousands of proteins, making it a valuable asset in studying complex biological systems and disease mechanisms.
As per DelveInsight analysis, the global protein chips market is estimated to grow at a CAGR of ~7% during the forecast period from 2024 to 2030. One of the key factors contributing to the growth of the protein chips market is the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and cardiovascular disorders. These conditions require precise diagnostics and targeted therapies, both of which are facilitated by protein chip technologies. In particular, the oncology sector is witnessing a surge in the adoption of protein chips for identifying novel biomarkers and developing targeted treatments. Moreover, the growing emphasis on personalized medicine, which tailors treatment based on an individual’s protein expression profile, further propels market demand.
Technological advancements are also playing a crucial role in expanding the protein chips market. Innovations in microarray technology, data analysis software, and surface chemistry are enhancing the sensitivity, accuracy, and throughput of protein chips. These advancements not only improve the quality of research but also reduce costs, making protein chips more accessible to a broader range of laboratories and healthcare facilities. Additionally, the integration of artificial intelligence and machine learning in protein chip data analysis is opening new avenues for more sophisticated and predictive insights into protein function and disease pathways.
However, the protein chips market faces challenges such as high initial setup costs, technical complexities, and the need for skilled personnel to operate the equipment and analyze the data. Despite these challenges, the market is poised for robust growth due to the increasing demand for advanced diagnostic tools and the ongoing development of more user-friendly and cost-effective solutions. As research and development efforts continue, the protein chips market is expected to expand further, offering promising opportunities for stakeholders in the life sciences and healthcare sectors.
Key Companies Working in the Protein Chip Market
The protein chip market, a critical segment within the biotechnology industry, is seeing significant growth due to advancements in proteomics and the increasing demand for personalized medicine. Several key companies are leading the way in developing and commercializing protein chip technologies. One of the prominent players is Thermo Fisher Scientific, a global leader in serving science, which offers a range of protein microarray solutions. Their products are widely used in research for biomarker discovery, disease diagnostics, and drug development, leveraging their robust platforms for high-throughput analysis and accuracy.
Another major company in this market is Agilent Technologies, known for its comprehensive portfolio of protein microarray solutions. Agilent’s protein chips are recognized for their high sensitivity and precision, making them ideal for applications in clinical research and diagnostics. The company has also invested heavily in advancing its microarray technology, focusing on expanding its applications in personalized medicine, where the need for precise protein analysis is critical for tailoring treatments to individual patients.
Roche Diagnostics is also a key player in the protein chip market, particularly in the field of diagnostics. Roche’s protein chip platforms are designed to detect and quantify proteins with high specificity and sensitivity, which is crucial for early disease detection and monitoring. The company’s focus on innovation and its strong global presence makes it a leader in the integration of protein chips into clinical diagnostics, further driving the growth and adoption of this technology in healthcare settings.

Apart from these, several other companies are also actively working in the protein chip market such as RayBiotech, Inc., Sengenics Corporation LLC., CDI Labs., Creative Biolabs., Proteintech Group, Inc, QUOTIENT LIMITED, PerkinElmer Inc., Merck KGAA, Illumina Inc., Arrayit Corporation, Spectrum Solutions, ACROBiosystems, Sengenics Corporation LLC, and others.
Future Outlook of Protein Chip
The future outlook for protein chips is promising, driven by advancements in biotechnology, data analytics, and personalized medicine. Protein chips, which allow for the high-throughput analysis of protein interactions, are expected to play a critical role in the development of new diagnostic tools and therapeutic strategies. As technology continues to improve, protein chips are becoming more sensitive, cost-effective, and capable of analyzing complex biological systems. This evolution is likely to enhance their application in fields such as oncology, neurology, and infectious diseases, where understanding protein interactions can lead to more targeted and effective treatments.
Moreover, the integration of protein chips with artificial intelligence and machine learning is expected to revolutionize their use. By enabling the rapid analysis of large datasets, AI and ML can uncover patterns and correlations in protein interactions that were previously undetectable. This could accelerate drug discovery processes, improve the accuracy of diagnostic tests, and lead to the development of precision medicine tailored to individual patients’ molecular profiles. The ability to analyze proteins in real-time and at a single-cell level will also open up new avenues for research into disease mechanisms and therapeutic interventions.
In the long term, the widespread adoption of protein chip technology could transform healthcare by making personalized medicine the standard of care. As these chips become more accessible and integrated into clinical workflows, they could provide clinicians with detailed insights into a patient’s disease state, enabling more precise and timely interventions. Additionally, the global push towards digital health and telemedicine could further drive the demand for portable and easy-to-use protein chips, making sophisticated diagnostic tools available to a broader population. Overall, the future of protein chips is bright, with the potential to significantly impact research, diagnostics, and treatment across various medical fields.

Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Biochips in Healthcare: 8 Groundbreaking Applications Shaping the Industry
- FDA Approves Abbott’s Spinal Cord Stimulation Systems; Regen Lab Received CE Certification for Th...
- Exploring the Current Alzheimer’s Disease Drug Development Pipeline
- The Growing Burden Of Neurodegenerative Disorders
- Opportunities and Challenges for Cell and Gene Therapies



