Major Drugs Decisions for Cardiovascular Diseases to Watch Through 2022
Feb 04, 2022
Table of Contents
The discovery of new classes of highly effective drug therapy for prevalent kinds of cardiovascular diseases has witnessed spectacular success in recent decades. The widespread use of these cardiovascular drugs, combined with smoking cessation and nonpharmacological therapy, is thought to be responsible for decreasing cardiovascular disease-related deaths.
Nonetheless, cardiovascular diseases continue to be the leading cause of morbidity and mortality in the western world, and they are becoming a global problem. There are various types of cardiovascular diseases, namely, Angina, Coronary Artery Disease, Atrial Fibrillation, Ischemic Heart disease, and many more. But cardiovascular diseases such as heart disease and stroke accounted for about one-third of all fatalities globally.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- AstraZeneca’s Farxiga; Incyte’s Jakavi; FDA Fast Track Status to HM43239 for R/R AML; Idorsia’s I...
- Siemens Healthineers’s COVID-19 Antigen Self-Test; Paragon’s R3ACT Stabilization System; Pulnovo ...
- DelveInsight’s Cardiovascular disorders based Gene Therapy Reports
- Medtronic Launches Infusion Set for Insulin Pumps; Penumbra’s Virtual Reality-Based Rehabil...
- Ipsen and Skyhawk Therapeutics Partnership; SynOx Therapeutics’ Phase III Trial; Roche’s Alecensa...
Furthermore, when the COVID-19 pandemic hit the world, cardiovascular disease immediately appeared as a key risk factor for severe cases, which frequently resulted in hospitalization and death. Despite this, new entrants into the cardiovascular drug pipeline have been few. In 2021, there were only 2 cardiovascular drugs that the FDA has approved. In 2022, the FDA and EMA are expected to approve some new cardiovascular drugs to treat various cardiovascular diseases.
The approval of these cardiovascular drugs will be a ray of hope to millions of people suffering from different cardiovascular diseases. Here are the cardiovascular drugs that people are watching closely.
Read more about Cardiovascular Disease: A major cause of health loss and global burden
Mavacamten
Drug Name: Mavacamten
Company: LianBio; MyoKardia
Disease: Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
Development Phase: Pre-registration
Originator: MyoKardia
MoA: Cardiac myosin inhibitors
About Mavacamten
Mavacamten developed by LianBio is a potential first-in-class, oral, allosteric modulator of cardiac myosin that is being studied for the treatment of cardiovascular diseases characterized by excessive cardiac contractility and inadequate diastolic filling of the heart. Mavacamten lowers cardiac muscle contractility by blocking excessive myosin-actin cross-bridge production, which causes hypercontractility, left ventricular hypertrophy, and decreased compliance. Mavacamten has consistently lowered indicators of heart wall stress, reduced excessive ventricular contractility, and enhanced diastolic compliance in clinical and preclinical trials.
Current Clinical Status
The FDA has extended its examination of Bristol Myers Squibb’s NDA for the planned cardiovascular drug mavacamten to give additional time to analyze its product information. The previous PDUFA date set by FDA was 28 January 2022. Now the extension until April 28, 2022, will provide the FDA more time to investigate the drug’s potential use in the symptomatic Obstructive Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy (oHCM) treatment in individuals. The FDA will particularly scrutinize modifications to the suggested Risk Evaluation Mitigation Strategy (REMS), which was included in the first application.
The NDA came on the heels of encouraging results from the Phase III EXPLORER-HCM study, which showed that patients improved in health status after 30 weeks when compared to those who received a placebo. Outcomes were examined using the 23-item Kansas City Cardiomyopathy Questionnaire Overall Summary Score (KCCQ OSS), with 36% demonstrating at least 5 points of improvement compared to 15% in the placebo group. The questions assessed symptoms, social and physical function, and quality of life.
The trial’s primary outcome was a composite functional analysis to determine mavacamten’s effect on symptoms and function. Secondary objectives were baseline changes in pVO2 at week 30, the postexercise LVOT gradient, the number of people reporting improvement in at least one NYHA class, and patient-reported outcomes. At week 30, researchers looked at baseline changes in circulating biomarkers, accelerometry, echocardiographic indices, and heart rhythm patterns.
About Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy
HCM is the most prevalent hereditary cardiovascular disease. It can be a persistent, debilitating, and progressive condition that causes shortness of breath, dizziness, and exhaustion in sufferers. However, it can also cause far more significant, life-altering problems, such as heart failure, arrhythmias, stroke, and sudden cardiac death. Mutations in sarcomere proteins in the heart muscle are the most prevalent cause of HCM.
As per DelveInsight’s Hypertrophic Cardiomyopathy Epidemiology Insights Report, the United States accounted for 109K diagnosed cases in 2020 which was the highest in the 7MM.
Aside from addressing HCM symptoms, there are no known effective cardiovascular drugs for HCM available in the market
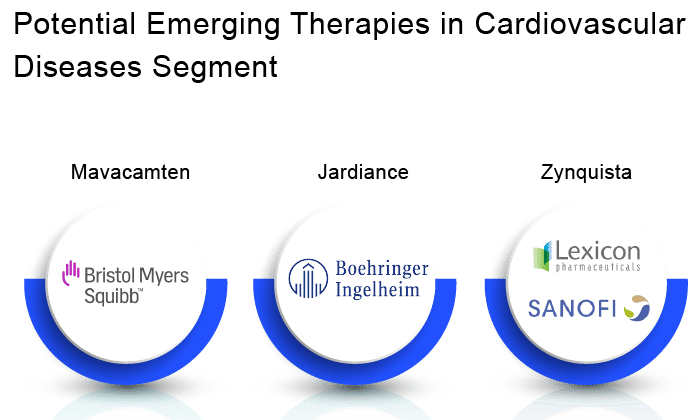
Jardiance
Drug Name: Jardiance
Company: Boehringer Ingelheim
Disease: Chronic HFpEF
Development Phase: Registered
Originator: Boehringer Ingelheim
MoA: Sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors
About Jardiance
Jardiance (Empagliflozin) is an oral, once-daily, highly selective sodium-glucose cotransporter 2 (SGLT2) inhibitor and the first type 2 diabetes drug in multiple countries to provide cardiovascular mortality risk reduction data on its label.
Current Clinical Status
The European Medicines Agency’s Committee for Medicinal Products for Human Use (CHMP) has issued a favorable opinion recommending Boehringer Ingelheim’s Jardiance (empagliflozin) for symptomatic Chronic Heart Failure treatment. The FDA has set a PDUFA date of May 2022.
The favorable judgment was based on findings from the landmark EMPEROR-Preserved Phase III study, which assessed the impact of empagliflozin 10 mg against placebo once-daily, both added to standard of treatment, in 5,988 persons with Heart Failure with LVEF more than 40%. Empagliflozin exhibited a remarkable 21% relative risk reduction (3.3% absolute risk reduction, 0.79 HR, 0.69-0.90 95% CI) for the composite main outcome of cardiovascular mortality or Hospitalization for Heart Failure in the study. There was no difference in benefit independent of ejection fraction or diabetes status.
The EMPEROR-Preserved study is part of the EMPOWER clinical program, the largest and most thorough of any SGLT2 inhibitor, which is investigating the impact of empagliflozin on persons with a wide range of cardio-renal-metabolic disorders.
Jardiance was first licensed in 2014 for the treatment of T2D, and then in 2016 for lowering the risk of cardiovascular mortality in T2D patients. Jardiance was authorized by the FDA in August for the treatment of Heart Failure with reduced Ejection Fraction (HFrEF), while Lilly and BI provided data indicating Jardiance’s efficacy in patients with HF with preserved Ejection Fraction (HfpEF) with or without diabetes.
Furthermore, several therapies, notably AstraZeneca’s Farxiga (dapagliflozin), Janssen’s Invokana (canagliflozin), Novartis’ Entresto (sacubitril+valsartan), and Bayer’s Verguvo (vericiguat), have also been licensed to treat HF or CKD in people with and without diabetes. If Jardiance receives FDA clearance for HFpEF, it will be the first medication to improve outcomes in all HF patients and will grab considerable market share in an increasingly congested SGLT-2I market.
About HFpEF
Heart Failure with preserved Ejection Fraction, commonly known as Diastolic Heart Failure, accounts for over half of the cases of Heart Failure in the US. It is more frequent in elderly men and women. It is caused by anomalies in active and passive ventricular relaxation, resulting in a decrease in stroke volume and cardiac output. Patients with Chronic Heart Failure symptoms and signs (e.g., weariness, weakness, dyspnea, orthopnea, paroxysmal nocturnal dyspnea, edema) should be suspected of having Heart Failure with Preserved Ejection Fraction.
Zynquista
Drug Name: Zynquista
Company: Lexicon Pharmaceuticals; Sanofi
Disease: Heart Failure
Development Phase: Pre-registration
Originator: Lexicon Pharmaceuticals
MoA: Sodium-glucose transporter 1 inhibitors; Sodium-glucose transporter 2 inhibitors
About Zynquista
Sotagliflozin, discovered utilizing Lexicon’s unique approach to gene science, is an oral dual inhibitor of two proteins (SGLT1 and SGLT2) involved in glucose control known as sodium-glucose co-transporter types 1 and 2. . SGLT1 is in charge of glucose absorption in the gastrointestinal tract, whereas SGLT2 is in charge of glucose reabsorption in the kidney.
Zynquista (Sotagliflozin) is approved in the European Union for use as an adjunct to insulin therapy to improve blood sugar control in individuals with Type 1 Diabetes with a BMI of 27 kg/m2 who were unable to achieve adequate glycemic control despite optimal insulin therapy, but it has not yet been commercially launched.
Current Clinical Status
In December 2021, Lexicon Pharmaceuticals, Inc. submitted a New Drug Application to the FDA, requesting approval for sotagliflozin to reduce the risk of death from cardiovascular diseases, hospitalisation for Heart Failure, and urgent visits for Heart Failure with Type 2 Diabetes in adult patients who have worsening heart failure or additional risk factors for HF, regardless of Left Ventricular Ejection Fraction. The FDA has a 60-day filing review time to decide if the NDA is complete and ready for submission.
The NDA submission of Zynquista was based on the results of the Phase 3 SOLOIST clinical study in patients with Type 2 Diabetes who had recently been hospitalized for worsening heart failure and Phase 3 SCORED clinical study in patients with Type 2 Diabetes, Chronic Kidney Disease, and cardiovascular diseases risk.
Both SOLOIST and SCORED met their major objectives, with overall tolerability comparable to placebo in both studies. Both studies’ findings were presented at the American Heart Association’s (AHA) Scientific Sessions 2020 Late-Breaking Science Session and published simultaneously in The New England Journal of Medicine (NEJM) as two separate articles titled “Sotagliflozin in Patients with Diabetes and Recent Worsening Heart Failure” and “Sotagliflozin in Patients with Diabetes and Chronic Kidney Disease.”
About Heart Failure
Heart Failure (HF) is a progressive, debilitating, and potentially fatal cardiovascular disease in which the heart is unable to provide adequate circulation to meet the body’s demands for oxygenated blood, or when doing so necessitates increased blood volume, resulting in fluid accumulation (congestion) in the lungs and peripheral tissues. Diabetes increases the risk of Heart Failure; yet, over half of all persons with Heart Failure do not have diabetes.
According to DelveInsight’s Heart Failure Epidemiology Insights Report, the total diagnosed prevalent cases were over 12 million in the 7MM, with the US accounting for 40.97% of total HF prevalent diagnosed cases in 2020.
What’s Ahead?
Cardiovascular diseases are the leading cause of death and morbidity worldwide, and significant progress has been made just in the last decade. Furthermore, the 21st-century cardiovascular diseases diagnosis and therapy will be shaped by new technology and improvements of existing approaches. At the molecular and subcellular levels, scientists are learning new things about cardiovascular diseases and how to treat them.

Several cardiology companies such as Sanofi, BMS, Novartis, Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Merck, Abbott, and others are working in cardiovascular drug development. Moreover, key Medtech players in the cardiovascular diseases market include Medtronic, St. Jude Medical, Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, Getinge, Terumo, W. L. Gore & Associates, Lepu Medical Technology, and several others are also developing cardiovascular medical devices to solve the problem of people suffering from various cardiovascular diseases.
Furthermore, the rise in the global burden of various cardiovascular diseases will allow other pharma and Medtech cardiology companies to develop innovative products and improve the cardiovascular diseases market landscape in the future.
Find out more about Cardiovascular Diseases and Top Players in Cardiology
FAQs
Cardiovascular disease (CVD) refers to any disorder that affects the heart or blood vessels. It is typically related to the formation of fatty deposits inside the arteries (atherosclerosis) and an increased risk of blood clots.
Several cardiology companies such as Sanofi, BMS, Novartis, Pfizer, Johnson & Johnson, AstraZeneca, Amgen, Merck, Abbott, and others are working in cardiovascular drug development.
Key Medtech players in the cardiovascular diseases market include Medtronic, St. Jude Medical, Boston Scientific, Edwards Lifesciences, Getinge, Terumo, W. L. Gore & Associates, Lepu Medical Technology, and several others are developing cardiovascular medical devices.
Downloads
Article in PDF
Recent Articles
- Tepezza receives approval; a new way to treat Alzheimer’s
- What are the Top Five Leading Causes of Deaths in the World?
- Daiichi Sankyo’s Intravenous Iron Replacement Therapy; ANeuroTech’s Adjunctive Anti-depression Dr...
- Aidoc’s Pneumothorax; Cook Medical’s Zenith Thoraco+ Endovascular System; GRAFIX Membrane S...
- Cardiovascular Disease: A major cause of health loss and a global burden